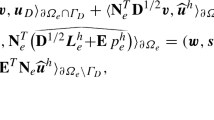Abstract
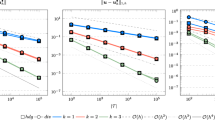
The Stokes system with constant viscosity can be cast into different formulations by exploiting the incompressibility constraint. For instance, the rate of strain tensor in the weak formulation can be replaced by the velocity-gradient yielding a decoupling of the velocity components in the different coordinate directions. Consequently, the discretization of this partly decoupled formulation leads to fewer nonzero entries in the stiffness matrix. This is of particular interest in large scale simulations where a reduced memory bandwidth requirement can help to significantly accelerate the computations. In the case of a piecewise constant viscosity, as it typically arises in multi-phase flows, or when the boundary conditions involve traction, the situation is more complex, and one has to treat the cross derivatives in the original Stokes system with care. A naive application of the standard vectorial Laplacian results in a physically incorrect solution, while formulations based on the rate of strain tensor increase the computational effort globally. Here, we propose a new approach that is consistent with the stress-divergence formulation and preserves the decoupling advantages of the velocity-gradient-divergence formulation in isoviscous subdomains. The modification is equivalent to locally changing the discretization stencils at interfaces or boundaries. Hence, the more expensive discretization is of lower complexity, making the additional computational cost in large scale simulations negligible. We establish consistency and convergence properties and show that in a massively parallel setup, the multigrid solution of the resulting discrete systems is faster than for the classical stress-divergence formulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amestoy, P.R., Guermouche, A., L’Excellent, J.Y., Pralet, S.: Hybrid scheduling for the parallel solution of linear systems. Parallel Comput. 32(2), 136–156 (2006)
Baker, A.H., Klawonn, A., Kolev, T., Lanser, M., Rheinbach, O., Yang, U.M.: Scalability of classical algebraic multigrid for elasticity to half a million parallel tasks. In: Bungartz, H.J., Neumann, P., Nagel, W.E. (eds.) Software for Exascale Computing - SPPEXA 2013-2015, pp. 113–140. Springer, Cham (2016). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-40528-5_6
Bastian, P., Blatt, M., Dedner, A., Engwer, C., Klöfkorn, R., Kornhuber, R., Ohlberger, M., Sander, O.: A generic grid interface for parallel and adaptive scientific computing. Part II: implementation and tests in DUNE. Computing 82(2–3), 121–138 (2008)
Bauer, S., Bunge, H.P., Drzisga, D., Gmeiner, B., Huber, M., John, L., Mohr, M.R., Rüde, U., Stengel, H., Waluga, C., Weismüller, J., Wellein, G., Wittmann, M., Wohlmuth, B.: Hybrid Parallel Multigrid Methods for Geodynamical Simulations. Springer, Cham (2016). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-40528-5_10
Bergen, B., Gradl, T., Rüde, U., Hülsemann, F.: A massively parallel multigrid method for finite elements. Comput. Sci. Eng. 8(6), 56–62 (2006)
Bergen, B., Hülsemann, F.: Hierarchical hybrid grids: data structures and core algorithms for multigrid. Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 11, 279–291 (2004)
Bey, J.: Tetrahedral grid refinement. Computing 55(4), 355–378 (1995)
Boffi, D., Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed Finite Element Methods and Applications. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Boffi, D., Cavallini, N., Gardini, F., Gastaldi, L.: Local mass conservation of Stokes finite elements. J. Sci. Comput. 52(2), 383–400 (2012)
Brezzi, F., Pitkäranta, J.: On the stabilization of finite element approximations of the Stokes equations. In: Hackbusch, W. (ed.) Efficient Solutions of Elliptic Systems. Springer, Berlin (1984)
Centre, J.S.: JUQUEEN: IBM Blue Gene/Q supercomputer system at the jülich supercomputing centre. J. Large-scale Res Facil. (2015). doi:10.17815/jlsrf-1-18
Cousins, B.R., Le Borne, S., Linke, A., Rebholz, L.G., Wang, Z.: Efficient linear solvers for incompressible flow simulations using Scott-Vogelius finite elements. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 29(4), 1217–1237 (2013)
Dongarra, J., Beckman, P., Moore, T., Aerts, P., Aloisio, G., Andre, J.C., Barkai, D., Berthou, J.Y., Boku, T., Braunschweig, B., Cappello, F., Chapman, B., Chi, X., Choudhary, A., Dosanjh, S., Dunning, T., Fiore, S., Geist, A., Gropp, B., Harrison, R., Hereld, M., Heroux, M., Hoisie, A., Hotta, K., Jin, Z., Ishikawa, Y., Johnson, F., Kale, S., Kenway, R., Keyes, D., Kramer, B., Labarta, J., Lichnewsky, A., Lippert, T., Lucas, B., Maccabe, B., Matsuoka, S., Messina, P., Michielse, P., Mohr, B., Mueller, M.S., Nagel, W.E., Nakashima, H., Papka, M.E., Reed, D., Sato, M., Seidel, E., Shalf, J., Skinner, D., Snir, M., Sterling, T., Stevens, R., Streitz, F., Sugar, B., Sumimoto, S., Tang, W., Taylor, J., Thakur, R., Trefethen, A., Valero, M., Van Der Steen, A., Vetter, J., Williams, P., Wisniewski, R., Yelick, K.: The international exascale software project roadmap. Int. J. High Perform. Comput. Appl. 25(1), 3–60 (2011)
Falgout, R., Meier-Yang, U.: hypre: a library of high performance preconditioners. Comput. Sci.-ICCS 2002, 632–641 (2002)
Gerya, T.: Introduction to Numerical Geodynamic Modelling. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2009)
Gmeiner, B., Huber, M., John, L., Rüde, U., Wohlmuth, B.: A quantitative performance study for Stokes solvers at the extreme scale. J. Comput Sci. 17, part 3, 509 – 521 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.jocs.2016.06.006. Recent Advances in Parallel Techniques for Scientific Computing
Gmeiner, B., Rüde, U., Stengel, H., Waluga, C., Wohlmuth, B.: Performance and scalability of hierarchical hybrid multigrid solvers for stokes systems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 37(2), C143–C168 (2015)
Gmeiner, B., Rüde, U., Stengel, H., Waluga, C., Wohlmuth, B.: Towards textbook efficiency for parallel multigrid. Numer. Math. Theory Methods Appl. 8(1), 22–46 (2015). doi:10.4208/nmtma.2015.w10si
Gmeiner, B., Waluga, C., Wohlmuth, B.: Local mass-corrections for continuous pressure approximations of incompressible flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 52(6), 2931–2956 (2014)
Grand, S.P., van der Hilst, R.D., Widiyantoro, S.: Global seismic tomography: a snapshot of convection in the earth. GSA Today 7, 1–7 (1997)
Gross, S., Reusken, A.: Numerical Methods for Two-phase Incompressible Flows, vol. 40. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Hager, B., Clayton, R.: Mantle convection. In: Peltier, W.R. (ed.) Constraints on the Structure of Mantle Convection Using Seismic Observations, Flow Models, and the Geoid, pp. 657–764. Gordon and Breach, New York (1989)
Hansbo, P., Larson, M.G., Zahedi, S.: A cut finite element method for a Stokes interface problem. Appl. Numer. Math. 85, 90–114 (2014)
Hartley, R., Roberts, G., White, N., Richardson, C.: Transient convective uplift of an ancient buried landscape. Nat. Geosci. 4, 562–565 (2011)
Haskell, N.A.: The motion of a fluid under a surface load. Physics 6, 265–269 (1935)
Heywood, J.G., Rannacher, R., Turek, S.: Artificial boundaries and flux and pressure conditions for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 22(5), 325–352 (1996)
Hughes, T.J.R., Franca, L.P.: A new finite element formulation for computational fluid dynamics: VII. the Stokes problem with various well-posed boundary conditions: symmetric formulations that converge for all velocity/pressure spaces. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 65(1), 85–96 (1987)
Ito, K., Li, Z.: Interface conditions for Stokes equations with a discontinuous viscosity and surface sources. Appl. Math. Lett. 19(3), 229–234 (2006)
Limache, A., Idelsohn, S., Rossi, R., Oñate, E.: The violation of objectivity in Laplace formulations of the Navier-Stokes equations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 54(6–8), 639–664 (2007)
Logg, A., Mardal, K.A., Wells, G.N.: DOLFIN: a C++/Python finite element library. In: Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering, vol. 84, chap. 10. Springer (2012)
May, D., Brown, J., Pourhiet, L.L.: A scalable, matrix-free multigrid preconditioner for finite element discretizations of heterogeneous Stokes flow. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 290, 496–523 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.cma.2015.03.014
Mitrovica, J.X.: Haskell [1935] revisited. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 555–569 (1996)
Müller, E.H., Scheichl, R.: Massively parallel solvers for elliptic partial differential equations in numerical weather and climate prediction. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 140(685), 2608–2624 (2014)
Müller, R.D., Sdrolias, M., Gaina, C., Roest, W.R.: Age, spreading rates, and spreading asymmetry of the world’s ocean crust. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 9, 1525–2027 (2008)
Neff, P., Pauly, D., Witsch, K.J.: Poincaré meets Korn via Maxwell: extending Korn’s first inequality to incompatible tensor fields. J. Differ. Equ. 258(4), 1267–1302 (2015)
Neilan, M.: Discrete and conforming smooth de Rham complexes in three dimensions. Math. Comput. 84, 2059–2081 (2015)
Notay, Y., Napov, A.: A massively parallel solver for discrete Poisson-like problems. J. Comput. Phys 281(C), 237–250 (2015)
Olshanskii, M.A., Reusken, A.: Analysis of a Stokes interface problem. Numer. Math. 103(1), 129–149 (2006)
Parnell-Turner, R., White, N., Henstock, T., Murton, B., Maclennan, J., Jones, S.M.: A continuous 55 million year record of transient mantle plume activity beneath Iceland. Nat. Geosci. 7, 914–919 (2014)
Pironneau, O.: Finite Element Methods for Fluids. Wiley, Chichester (1989)
Pompe, W.: Counterexamples to Korn’s inequality with non-constant rotation coefficients. Math. Mech. Solids 16, 172–176 (2011)
Quarteroni, A., Valli, A.: Domain Decomposition Methods for Partial Differential Equations. Numerical Mathematics and Scientific Computation. Clarendon Press, Wotton-under-Edge (1999)
Rannacher, R.: On the numerical solution of the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. ZAMM - J. Appl. Math. Mech. / Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 73(9), 203–216 (1993)
Röhrig-Zöllner, M., Thies, J., Kreutzer, M., Alvermann, A., Pieper, A., Basermann, A., Hager, G., Wellein, G., Fehske, H.: Increasing the performance of the Jacobi-Davidson method by blocking. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 37(6), C697–C722 (2015)
Rudi, J., Malossi, A., Isaac, T., Stadler, G., Gurnis, M., Staar, P., Ineichen, Y., Bekas, C., Curioni, A., Ghattas, O.: An extreme-scale implicit solver for complex PDEs: Highly heterogeneous flow in Earth’s mantle. In: Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, pp. 5:1–5:12 (2015)
Schöberl, J., Zulehner, W.: On Schwarz-type smoothers for saddle point problems. Numer. Math. 95(2), 377–399 (2003)
Scott, L., Zhang, S.: Finite element interpolation of nonsmooth functions satisfying boundary conditions. Math. Comput. 54(190), 483–493 (1990)
Scott, L.R., Vogelius, M.: Norm estimates for a maximal right inverse of the divergence operator in spaces of piecewise polynomials. Modélisation mathématique et analyse numérique 19(1), 111–143 (1985)
Stixrude, L., Lithgow-Bertelloni, C.: Thermodynamics of mantle minerals - I. Physical properties. Geophys. J. Int. 162, 610–632 (2005)
Weismüller, J., Gmeiner, B., Ghelichkhan, S., Huber, M., John, L., Wohlmuth, B., Rüde, U., Bunge, H.P.: Fast asthenosphere motion in high-resolution global mantle flow models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42(18), 7429–7435 (2015)
Zhang, S.: A new family of stable mixed finite elements for the 3d Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 74(250), 543–554 (2005)
Zulehner, W.: Analysis of iterative methods for saddle point problems: a unified approach. Math. Comput. 71(238), 479–505 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported (in part) by the German Research Foundation (DFG) through the Priority Programme 1648 “Software for Exascale Computing” (SPPEXA) and through WO671/11-1. The authors gratefully acknowledge the Gauss Centre for Supercomputing (GCS) for providing computing time through the John von Neumann Institute for Computing (NIC) on the GCS share of the supercomputer JUQUEEN at Jülich Supercomputing Centre (JSC).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huber, M., Rüde, U., Waluga, C. et al. Surface Couplings for Subdomain-Wise Isoviscous Gradient Based Stokes Finite Element Discretizations. J Sci Comput 74, 895–919 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-017-0470-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-017-0470-3