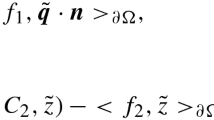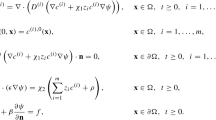Abstract
In this paper, a linearized local conservative mixed finite element method is proposed and analyzed for Poisson–Nernst–Planck (PNP) equations, where the mass fluxes and the potential flux are introduced as new vector-valued variables to equations of ionic concentrations (Nernst–Planck equations) and equation of the electrostatic potential (Poisson equation), respectively. These flux variables are crucial to PNP equations on determining the Debye layer and computing the electric current in an accurate fashion. The Raviart–Thomas mixed finite element is employed for the spatial discretization, while the backward Euler scheme with linearization is adopted for the temporal discretization and decoupling nonlinear terms, thus three linear equations are separately solved at each time step. The proposed method is more efficient in practice, and locally preserves the mass conservation. By deriving the boundedness of numerical solutions in certain strong norms, an unconditionally optimal error analysis is obtained for all six unknowns: the concentrations p and n, the mass fluxes \({{\varvec{J}}}_p=\nabla p + p {\varvec{\sigma }}\) and \({{\varvec{J}}}_n=\nabla n - n {\varvec{\sigma }}\), the potential \(\psi \) and the potential flux \({\varvec{\sigma }}= \nabla \psi \) in \(L^{\infty }(L^2)\) norm. Numerical experiments are carried out to demonstrate the efficiency and to validate the convergence theorem of the proposed method.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 June 2018
The original version of this article contained a mistake. There are error in line breaks in Eqs. 4.3 and 4.4 and the word “quad” was included inadvertently in Eq. 4.4.
References
Bochev, P., Lehoucq, R.: On the finite element solution of the pure Neumann problem. SIAM Rev. 47, 50–66 (2005)
Biler, P., Dolbeault, J.: Long time behavior of solutions of Nernst–Planck and Debye–Hückel drift–diffusion systems. Ann. Henri Poincaré 1, 461–472 (2000)
Biler, P., Hebisch, W., Nadzieja, T.: The Debye system: existence and large time behavior of solutions. Nonlinear Anal. 23, 1189–1209 (1994)
Brenner, S., Scott, L.: The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods. Springer, New York (2002)
Brera, M., Jerome, J., Mori, Y., Sacco, R.: A conservative and monotone mixed-hybridized finite element approximation of transport problems in heterogeneous domains. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199, 2709–2770 (2010)
Brezzi, F., Marini, L., Micheletti, S., Pietra, P., Sacco, R., Wang, S.: Discretization of semiconductor device problems (I). Handb. Numer. Anal. XIII, 317–441 (2005)
Brunk, M., Kværnø, A.: Positivity preserving discretization of time dependent semiconductor drift–diffusion equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 62, 1289–1301 (2012)
Cherrier, P., Milani, A.: Linear and Quasi-linear Evolution Equations in Hilbert Spaces. Grad. Stud. Math., vol. 135. AMS, Providence (2012)
Demlow, A.: Suboptimal and optimal convergence in mixed finite element methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 39, 1938–1953 (2002)
Dawson, C., Sun, S., Wheeler, M.: Compatible algorithm for coupled flow and transport. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 193, 2562–2580 (2004)
Debye, P., Huckel, E.: Zur theorie der elektrolyte. Phys. Zeitschr. 24, 185–206 (1923)
Duran, R.: Error analysis in \(L^p,1\le p \le \infty \), for mixed finite element methods for linear and quasi-linear elliptic problems. RAIRO Model. Math. Anal. Numer. 22, 371–387 (1988)
Flavell, A., Machen, M., Eisenberg, R., Kabre, J., Liu, C., Li, X.: A conservative finite difference scheme for Poisson–Nernst–Planck equations. J. Comput. Electron. 15, 1–15 (2013)
Frank, F., Knabner, P.: Convergence analysis of a BDF2/mixed finite element discretization of a Darcy–Nernst–Planck–Poisson system. ESAIM M2AN 51, 1883–1902 (2017)
Frank, F., Ray, N., Knabner, P.: Numerical investigation of homogenized Stokes–Nernst–Planck–Poisson systems. Comput. Visual. Sci. 14, 385–400 (2011)
Gajewski, H., Gröger, K.: On the basic equations for carrier transport in semiconductors. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 113, 12–35 (1986)
Gao, H., He, D.: Linearized conservative finite element methods for the Nernst–Planck–Poisson equations. J. Sci. Comput. 72, 1269–1289 (2017)
Gao, H., Qiu, W.: Error analysis of mixed finite element methods for nonlinear parabolic equations. J. Sci. Comput. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-018-0643-8
He, D., Pan, K.: An energy preserving finite difference scheme for the Poisson–Nernst–Planck system. Appl. Math. Comput. 287–288, 214–223 (2016)
He, M., Sun, P.: Error analysis of mixed finite element method for Poisson–Nernst–Planck system. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 33, 1924–1948 (2017)
He, M., Sun, P.: Mixed finite element analysis for the Poisson-Nernst-Planck/Stokes coupling. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 341, 61–79 (2018)
Heywood, J., Rannacher, R.: Finite element approximation of the nonstationary Navier–Stokes problem IV: error analysis for second-order time discretization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 27, 353–384 (1990)
Hou, Y., Li, B., Sun, W.: Error analysis of splitting Galerkin methods for heat and sweat transport in textile materials. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51, 88–111 (2013)
Johnson, C., Thomee, V.: Error estimates for some mixed finite element methods for parabolic type problems. RAIRO Anal. Numer. 15, 41–78 (1981)
Li, B., Lu, B., Wang, Z., McCammon, J.A.: Solutions to a reduced Poisson–Nernst–Planck system and determination of reaction rates. Physica A 389, 1329–1345 (2010)
Liu, H., Wang, Z.: A free energy satisfying finite difference method for Poisson–Nernst–Planck equations. J. Comput. Phys. 268, 363–376 (2014)
Liu, Y., Shu, C.: Analysis of the local discontinuous Galerkin method for the drift–diffusion model of semiconductor devices. Sci. China Math. 59, 115–140 (2016)
Logg, A., Mardal, K., Wells, G. (eds.): Automated Solution of Differential Equations by the Finite Element Method. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Lu, B., Holst, M., McCammon, J., Zhou, Y.: Poisson–Nernst–Planck equations for simulating biomolecular diffusion–reaction processes I: finite element solutions. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 6979–6994 (2010)
Mauri, A., Bortolossi, A., Novielli, G., Sacco, R.: 3D finite element modeling and simulation of industrial semiconductor devices including impact ionization. J. Math. Ind. 5, 18 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13362-015-0015-z
Metti, M., Xu, J., Liu, C.: Energetically stable discretizations for charge transport and electrokinetic models. J. Comput. Phys. 306, 1–18 (2016)
Mirzadeh, M., Gibou, F.: A conservative discretization of the Poisson–Nernst–Planck equations on adaptive Cartesian grids. J. Comput. Phys. 274, 633–653 (2014)
Mock, M.: An initial value problem from semiconductor device theory. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 5, 597–612 (1974)
Naga, A., Zhang, Z.: The polynomial-preserving recovery for higher order finite element methods in 2D and 3D. Disc. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 5, 769–798 (2005)
Prohl, A., Schmuck, M.: Convergent discretizations for the Nernst–Planck–Poisson system. Numer. Math. 111, 591–630 (2009)
Prohl, A., Schmuck, M.: Convergent finite element for discretizations of the Navier–Stokes–Nernst–Planck–Poisson system. M2AN Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 44, 531–571 (2010)
Scharfetter, D., Gummel, H.: Large signal analysis of a silicon read diode oscillator. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 16, 64–77 (1969)
Schmuck, M.: Analysis of the Navier–Stokes–Nernst–Planck–Poisson system. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 19, 993–1015 (2009)
Sun, W., Sun, Z.: Finite difference methods for a nonlinear and strongly coupled heat and moisture transport system in textile materials. Numer. Math. 120, 153–187 (2012)
Sun, Y., Sun, P., Zheng, B., Lin, G.: Error analysis of finite element method for Poisson–Nernst–Planck equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 301, 28–43 (2016)
Thomee, V.: Galerkin Finite Element Methods for Parabolic Problems. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Wei, G., Zheng, Q., Chen, Z., Xia, K.: Variational multiscale models for charge transport. SIAM Rev. 54, 699–754 (2012)
Xu, S., Chen, M., Majd, S., Yue, X., Liu, C.: Modeling and simulating asymmetrical conductance changes in Gramicidin pores. Mol. Based Math. Biol. 2, 34–55 (2014)
Raviart, R., Thomas, J.: A mixed finite element method for 2nd order elliptic problems. In: Galligani, I., Magenes, E. (eds.) Mathematical Aspects of Finite Element Methods. Lecture Notes in Math, vol. 606. Springer, New York (1977)
Zheng, Q., Chen, D., Wei, G.: Second-order Poisson Nernst–Planck solver for ion channel transport. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 5239–5262 (2011)
Zienkiewicz, O., Zhu, J.: The superconvergence patch recovery and a posteriori error estimates, part I: the recovery technique. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 33, 1331–1364 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The work of the first author was supported in part by the National Science Foundation of China No. 11501227 and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, HUST, P.R. China, under Grant Nos. 2014QNRC025, 2015QN13, and 2017KFYXJJ089. The work of the second author was partially supported by NSF Grant DMS-1418806.
The original version of this article was revised: The errors in Eqs. 4.3 and 4.4 have been corrected.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, H., Sun, P. A Linearized Local Conservative Mixed Finite Element Method for Poisson–Nernst–Planck Equations. J Sci Comput 77, 793–817 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-018-0727-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-018-0727-5
Keywords
- Poisson–Nernst–Planck equations
- Mixed finite element method
- Raviart–Thomas element
- Unconditional convergence
- Optimal error estimate
- Conservative schemes