Abstract
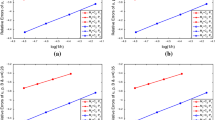
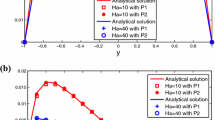
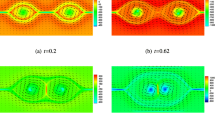
This paper studies several decoupled penalty methods to overcome the saddle point system of the steady state 2D/3D incompressible magnetohydronamics (MHD). These approaches combine the Oseen iteration and two-level technique with strong uniqueness condition \(0<\frac{\sqrt{2}C_{0}^{2}\max \{1,\sqrt{2}S_{c}\}\Vert {\mathbf{F }}\Vert _{-1}}{(\min \{R_{e}^{-1},S_{c}C_{1}R_{m}^{-1}\})^2}\le 1-\left( \frac{\Vert \mathbf{F }\Vert |_{-1}}{\Vert |\mathbf{F }\Vert _{0}}\right) ^{\frac{1}{2}}<1\) satisfied. For the convenience of implementation, we employ two different simple Lagrange finite element pairs \(P_{1}b-P_{1}-P_{1}b\) and \(P_{1}-P_{0}-P_{1}\) for velocity field, pressure and magnetic field, respectively. Rigorous analysis of the optimal error estimate and stability are provided. We present comprehensive numerical experiments, which indicate the effectiveness of the proposed methods for both two dimensional and three-dimensional problems.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerbeau, J., Bris, C., Lelièvre, T.: Mathematical Methods for the Magnetohydrodynamics of Liquid Metals. Numerical Mathematics and Scientific Computation. Oxford University Press, New York (2006)
Gunzburger, M., Meir, A., Peterson, J.: On the existence, uniquess and finite element approximation of solutions of the equations of sationary, incompressible magnetohydrodynamic. Math. Comput. 56, 523–563 (1991)
Moreau, R.: Magneto-Hydrodynamics. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Berlin (1990)
Sermange, M., Temam, R.: Some mathematical questions related to the MHD equations. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 36, 635–664 (1983)
Hu, K., Ma, Y., Xu, J.: Stable finite element methods preserving \(\nabla \cdot {B}=0\) exactly for MHD models. Numer. Math. 135, 371–396 (2017)
Zhao, J., Mao, S., Zheng, W.: Anisotropic adaptive finite element method for magnetohydrodynamic flow at high Hartmann numbers. Appl. Math. Mech. 37, 1479–1500 (2016)
Li, L., Zheng, W.: A robust solver for the finite element approximation of stationary incompressible MHD equations in 3D. J. Comput. Phys. 351, 254–270 (2017)
Gerbeau, J.: A stabilized finite element method for the incompressible magnetohydrodynamic equations. Numer. Math. 87, 83–111 (2000)
Ravindran, S.: Linear feedback control and approximation for a system governed by unsteady MHD equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 524–541 (2008)
Salah, N., Soulaimani, A., Habashi, W.: A finite element method for magnetohydrodynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190, 5867–5892 (2001)
Meir, A., Schmidt, P.: Analysis and numerical approximation of a stationary MHD flow problem with nonideal boundary. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 36, 1304–1332 (1999)
Qiu, W., Shi, K.: A mixed DG method and an HDG method for incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. arXiv:1702.01473 [math.NA]
Gao, H., Qiu, W.: A linearized energy preserving finite element method for the dynamical incompressible magnetohydrodynamics equations. arXiv:1801.01252 [math.NA]
Badia, S., Codina, R., Planas, R.: Analysis of an unconditionally convergent stabilized finite element formulation for incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 22, 621–636 (2015)
Greif, C., Li, D., Schötz, D., Wei, X.: A mixed finite element method with exactly divergence-free velocities for incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Comput. Method Appl. Mech. Eng. 199, 45–48 (2010)
Su, H., Feng, X., Huang, P.: Iterative methods in penalty finite element discretization for the steady MHD equations. Comput. Method Appl. Mech. Eng. 304, 521–545 (2016)
Su, H., Feng, X., Zhao, J.: Two-level penalty Newton iterative method for the 2D/3D stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics equations. J. Sci. Comput. 70(3), 1144–1179 (2017)
Su, H., Mao, S., Feng, X.: Optimal error estimates of penalty based iterative methods for steady incompressible magnetohydrodynamics equations with different viscosities. J. Sci. Comput. 79(2), 1078–1110 (2019)
Shen, J.: On error estimates of some higher order projection and penalty-projection methods for Navier–Stokes equations. Numer. Math. 62, 49–73 (1992)
Shen, J.: On error estimates of the penalty method for unsteady Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 32, 386–403 (1995)
He, Y.: Optimal error estimate of the penalty finite element method for the time-dependent Navier–Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 74, 1201–1216 (2005)
He, Y., Li, J., Yang, X.: Two-level penalized finite element methods for the stationary Navier–Stoke equations. Int. J. Inf. Syst. Sci. 2, 131–143 (2006)
An, R., Li, Y.: Error analysis of first-order projection method for time-dependent magnetohydrodynamics equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 112, 167–181 (2017)
Lu, X., Huang, P.: A modular grad-div stabilization for the 2D/3D nonstationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamic equations. J. Sci. Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-019-01114-x
Wu, J., Liu, D., Feng, X., Huang, P.: An efficient two-step algorithm for the stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamic equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 302, 21–33 (2017)
Wang, L., Li, J., Huang, P.: An efficient two-level algorithm for the 2D/3D stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics based on the finite element method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 98, 183–190 (2018)
Zhu, T., Su, H., Feng, X.: Some Uzawa-type finite element iterative methods for the steady incompressible magnetohydrodynamic equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 302, 34–47 (2017)
Zhang, Q., Su, H., Feng, X.: A partitioned finite element scheme based on Gauge–Uzawa method for time-dependent MHD equations. Numer. Algorithms 78(1), 277–295 (2018)
Ping, Y., Su, H., Feng, X.: Parallel two-step finite element algorithm for the stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamic equations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 29(8), 2709–2727 (2019)
Xu, J.: A novel two two-grid method for semilinear elliptic equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 15, 231–237 (1994)
Xu, J.: Two-grid discretization techniques for linear and nonlinear PDEs. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 33, 1759–1777 (1996)
Dong, X., He, Y., Zhang, Y.: Convergence analysis of three finite element iterative methods for the 2D/3D stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 276, 287–311 (2014)
He, Y.: Two-level method based on fnite element and Crank–Nicolson extrapolation for the time-dependent Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41, 1263–1285 (2003)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Method for Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Algorithms. Springer, Berlin (1987)
He, Y., Li, J.: Convergence of three iterative methods based on the finite element discretization for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 1351–1359 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work is in part supported by the NSF of China (Grant Nos. 11701493) and the GRF of Hong Kong (Grant Nos. 9041980, 9042081)” shoud be replaced by “This work is in part supported by the NSF of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Nos. XJEDU2020I001, 2016D01C073, 2019D01C047), the NSF of China (Nos. 11701493, 61962056)”, Tianshan Youth Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (No.2017Q079), 2019 Autonomous Region University Research Program (No.XJEDU2019Y002), the Xinjiang Provincial University Research Foundation of China (No.XJEDU2018I002) and the Matching Projects for Study Abroad of People’s Goverment of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (No. 2219-51160000313).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work is in part supported by the NSF of China (Grant Nos. 11701493) and the GRF of Hong Kong (Grant Nos. 9041980, 9042081).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Feng, X. & Zhao, J. On Two-Level Oseen Penalty Iteration Methods for the 2D/3D Stationary Incompressible Magnetohydronamics. J Sci Comput 83, 11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-020-01186-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-020-01186-0
Keywords
- Magnetohydrodynamics equations
- Penalty finite element method
- Two-level method
- Inf-sup condition
- Error estimate