Abstract
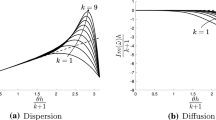
For the simulation of flow fields with a broad range of length scales, designing numerical schemes with good spectral properties is one of the most important issues. To improve the spectral properties of the semi-discrete finite different schemes, the authors have previously proposed the idea of optimizing the dispersion and dissipation properties separately and a class of finite difference scheme with minimized dispersion and controllable dissipation properties is thus developed (Sun et al. J Comput Phys 230:4616–4635, 2011, 270:238–254, 2014). In the present paper, we further investigated this idea and extend it to the fully discrete scheme. In other words, the dispersion and dissipation errors induced by the temporal discretization are taken into consideration in the present paper. Moreover, a scale sensor is designed in the control of dissipation error to ensure the numerical scheme can automatically adjust its dissipation according to the local characteristic of the flow field. To achieve the shock-capturing capability, this optimized scheme is blended with the WENO-Z scheme to form a hybrid scheme. A number of benchmark test cases including the transportation of a linear wave, the propagation of a sound wave packet, the Shu–Osher problem, the double Mach reflection problem and the Rayleigh–Taylor instability problem are employed to verify the good spectral properties and robust shock-capturing capability of the proposed scheme.

























Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Lele, S.: Compact finite difference schemes with spectral-like resolution. J. Comput. Phys. 103, 16–42 (1992)
Tam, C., Webb, J.: Dispersion-relation-preserving finite difference schemes for computational acoustics. J. Comput. Phys. 107, 262–281 (1993)
Harten, A., Engquist, B., Osher, S., et al.: Uniformly high order essentially non-oscillatory schemes III. J. Comput. Phys. 71, 231–303 (1987)
Jiang, G.S., Shu, C.W.: Efficient implementation of weighted ENO schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 126, 202–228 (1996)
Martín, M., Taylor, E., Wu, M., et al.: A bandwidth-optimized WENO scheme for effective direct numerical simulation of compressible turbulence. J. Comput. Phys. 220, 270–289 (2006)
Adams, N., Shariff, K.: A high-resolution hybrid compact-eno scheme for shock/turbulence interaction problems. J. Comput. Phys. 127, 27–51 (1996)
Pirozzoli, S.: Conservative hybrid compact-weno schemes for shock-turbulence interaction. J. Comput. Phys. 178, 81–117 (2002)
Ren, Y.X., Liu, M., Zhang, H.X.: A characteristic-wise compact weno scheme for solving hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 192, 365–386 (2003)
Shi, Y.F., Gao, Y.: A fifth order alternative compact-weno finite difference scheme for compressible Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. 397, 108873 (2019)
Kim, D., Kwon, J.: A high-order accurate hybrid scheme using a central flux scheme and a weno scheme for compressible flow field analysis. J. Comput. Phys. 210, 554–583 (2005)
Costa, B., Don, W.: Multi-domain hybrid spectral-weno methods for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 224, 970–991 (2007)
Hu, X.Y., Wang, Q., Adams, N.: An adaptive central-upwind weighted essentially non-oscillatory scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 8952–8965 (2010)
Zhao, G.Y., Sun, M.B., Mei, Y., et al.: An efficient adaptive central-upwind weno-cu6 numerical scheme with a new sensor. J. Sci. Comput. 81, 649–670 (2019)
Vevek, U., Zhang, B., New, T.: An efficient hybrid method for solving Euler equations. J. Sci. Comput. 81, 732–762 (2019)
Yu, C.H., Wang, D., He, Z., et al.: An optimized dispersion-relation-preserving combined compact difference scheme to solve advection equations. J. Comput. Phys. 300, 92–115 (2015)
Henrick, A., Aslam, T., Powers, J.: Mapped weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes: achieving optimal order near critical points. J. Comput. Phys. 207, 542–567 (2005)
Taylor, E., Wu, M., Martín, M.: Optimization of nonlinear error for weighted essentially non-oscillatory methods in direct numerical simulations of compressible turbulence. J. Comput. Phys. 223, 384–397 (2007)
Borges, R., Carmona, M., Costa, B., et al.: An improved weighted essentially non-oscillatory scheme for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 3191–3211 (2008)
Castro, M., Costa, B., Don, W.: High order weighted essentially non-oscillatory weno-z schemes for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 1766–1792 (2011)
Wang, B.S., Li, P., Gao, Z., et al.: An improved fifth order alternative weno-z finite difference scheme for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 374, 469–477 (2018)
Xu, W.Z., Wu, W.G.: An improved third-order weno-z scheme. J. Sci. Comput. 75, 1808–1841 (2018)
Wang, Y.H., Wang, B.S., Don, W.: Generalized sensitivity parameter free fifth order weno finite difference scheme with z-type weights. J. Sci. Comput. 81, 1329–1358 (2019)
Arshed, G., Hoffmann, K.: Minimizing errors from linear and nonlinear weights of weno schemes for broadband applications with shock waves. J. Sci. Comput. 246, 58–77 (2013)
Weirs, V., Candler, G.: Optimization of weighted eno schemes for dns of compressible turbulence. AIAA Paper 97–1940 (1997)
Sun, Z.S., Ren, Y.X., Larricq, C., et al.: A class of finite difference scheme with low dispersion and controllable dissipation for dns of compressible turbulence. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 4616–4635 (2011)
Sun, Z.S., Luo, L., Ren, Y.X., et al.: A sixth order hybrid finite difference scheme based on the minimized dispersion and controllable dissipation technique. J. Comput. Phys. 270, 238–254 (2014)
Hu, X.G., Zhang, H.X.: Developing high-order weighted compact nonlinear schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 165, 22–44 (2000)
Hu, F.Q., Hussaini, M., Manthey, J.: Low-dissipation and low-dispersion Runge–Kutta schemes for computational acoustics. J. Comput. Phys. 124, 177–191 (1996)
Bogey, C., Bailly, C.: A family of low dispersive and low dissipative explicit schemes for flow and noise computations. J. Comput. Phys. 194, 194–214 (2004)
Bernardini, M., Pirozzoli, S.: A general strategy for the optimization of Runge–Kutta schemes for wave propagation phenomena. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 4182–4199 (2009)
Ramboer, J., Broeckhoven, T., Smirnov, S., et al.: Optimization of time integration schemes coupled to spatial discretization for use in CAA applications. J. Comput. Phys. 213, 777–802 (2006)
Rajpoot, M., Sengupta, T., Dutt, P.: Optimal time advancing dispersion relation preserving schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 3625–3651 (2010)
Sengupta, T., Rajpoot, M., Bhumkar, Y.: Space-time discretizing optimal drp schemes for flow and wave propagation problems. Computers & fluids 47, 144–154 (2011)
Hu, X.Y., Adams, N.: Dispersion-dissipation condition for finite difference schemes arXiv:1204.5088v1
Li, Y.H., Chen, C.W., Ren, Y.X.: A class of high-order finite difference schemes with minimized dispersion and adaptive dissipation for solving compressible flow. J. Comput. Phys. (under review)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the project 91952110 of NSFC, the project 2019-JCJQ-JJ-103 and the project 201801U8001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Hu, Y., Ren, Y. et al. An Optimal Finite Difference Scheme with Minimized Dispersion and Adaptive Dissipation Considering the Spectral Properties of the Fully Discrete Scheme. J Sci Comput 89, 32 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01637-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01637-2