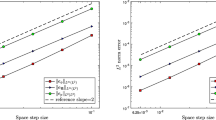
Abstract
In this paper, an efficient low-dissipation high-order TENO scheme is proposed for ideal MHD flows. For high computational efficiency, a troubled-cell indicator based on the ENO-like stencil selection strategy in TENO schemes is introduced to isolate the discontinuities from smooth regions. While the high-order linear scheme is adopted for the smooth regions, a low-dissipation TENO scheme is applied for capturing discontinuities detected by the troubled-cell indicator. The case-independent parameters are given based on spectral analysis. Both the governing equations of the ideal MHD and the Hamilton–Jacobi type constrained transport equation for divergence-free condition can be solved by the newly proposed scheme. Since most computational regions are resolved by the linear scheme without expensive characteristic decomposition, flux splitting and nonlinear weight calculation, the proposed scheme is highly efficient. A set of benchmark cases has been simulated to demonstrate the performance of the proposed scheme. Numerical results reveal that remarkable speedup is achieved by the present scheme while the oscillation-free property and the high-order accuracy are preserved.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availibility
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Alfvén, H.: Existence of electromagnetic-hydrodynamic waves. Nature 150(3805), 405–406 (1942)
Christlieb, A.J., Rossmanith, J.A., Tang, Q.: Finite difference weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes with constrained transport for ideal magnetohydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 268, 302–325 (2014)
Fu, L., Tang, Q.: High-order low-dissipation targeted ENO schemes for ideal magnetohydrodynamics. J. Sci. Comput. 80(1), 692–716 (2019)
Brackbill, J.U., Barnes, D.C.: The effect of nonzero \(\nabla \cdot B\) on the numerical solution of the magnetohydrodynamic equations. J. Comput. Phys. 35(3), 426–430 (1980)
Balsara, D.S., Kim, J.: A comparison between divergence-cleaning and staggered-mesh formulations for numerical magnetohydrodynamics. Astrophys. J. 602(2), 1079 (2004)
Zachary, A.L., Malagoli, A., Colella, P.: A higher-order Godunov method for multidimensional ideal magnetohydrodynamics. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 15(2), 263–284 (1994)
Powell, K.G., Roe, P.L., Linde, T.J., Gombosi, T.I., De Zeeuw, D.L.: A solution-adaptive upwind scheme for ideal magnetohydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 154(2), 284–309 (1999)
Dedner, A., Kemm, F., Kröner, D., Munz, C.-D., Schnitzer, T., Wesenberg, M.: Hyperbolic divergence cleaning for the MHD equations. J. Comput. Phys. 175(2), 645–673 (2002)
Cockburn, B., Li, F., Shu, C.-W.: Locally divergence-free discontinuous Galerkin methods for the Maxwell equations. J. Comput. Phys. 194(2), 588–610 (2004)
Evans, C.R., Hawley, J.F.: Simulation of magnetohydrodynamic flows-A constrained transport method. Astrophys. J. 332, 659–677 (1988)
Tóth, G.: The \(\nabla \cdot B= 0\) constraint in shock-capturing magnetohydrodynamics codes. J. Comput. Phys. 161(2), 605–652 (2000)
von Neumann, J., Richtmyer, R.: A method for the numerical calculation of hydrodynamic shocks. J. Appl. Phys. 21, 232 (1950)
Jameson, A.: Analysis and design of numerical schemes for gas dynamics, 1: artificial diffusion, upwind biasing, limiters and their effect on accuracy and multigrid convergence. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 4, 171–218 (1994)
Premasuthan, S., Liang, C., Jameson, A.: Computation of flows with shocks using the Spectral Difference method with artificial viscosity, I: Basic formulation and application. J. Comput. Phys. 98, 111–121 (2014)
Harten, A.: A high resolution scheme for the computation of weak solutions of hyperbolic conservation Laws. J. Comput. Phys. 49, 357–393 (1983)
Kim, K.H., Kim, C.: Accurate, efficient and monotonic numerical methods for multi-dimensional compressible flows Part II: Multi-dimensional limiting process. J. Comput. Phys. 208, 570–615 (2005)
Harten, A., Engquist, B., Osher, S., Chakravarthy, S.R.: Uniformly high order accurate essentially non-oscillatory schemes, III. J. Comput. Phys. 71, 231–303 (1987)
Liu, X.D., Osher, S., Chan, T.: Weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 115, 200–212 (1994)
Jiang, G.S., Shu, C.-W.: Efficient implementation of weighted ENO schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 126(1), 202–228 (1996)
Henrick, A.K., Aslam, T., Powers, J.M.: Mapped weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes: achieving optimal order near critical points. J. Comput. Phys. 207, 542–567 (2005)
Borges, R., Carmona, M., Costa, B., Don, W.S.: An improved weighted essentially non-oscillatory scheme for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 3191–3211 (2008)
Acker, F., Borges, R.R., Costa, B.: An improved WENO-Z scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 313, 726–753 (2016)
Levy, D., Puppo, G., Russo, G.: Central WENO schemes for hyperbolic systems of conservation laws. ESAIM: Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Analysis-Modélisation Mathématique et Analyse Numérique 33(3), 547–571 (1999)
Levy, D., Puppo, G., Russo, G.: Compact central WENO schemes for multidimensional conservation laws. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 22(2), 656–672 (2000)
Pirozzoli, S.: Conservative hybrid compact-WENO schemes for shock-turbulence interaction. J. Comput. Phys. 178(1), 81–117 (2002)
Ren, Y.-X., Liu, M., Zhang, H.: A characteristic-wise compact WENO scheme for solving hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 192, 365–386 (2003)
Balsara, D.S., Garain, S., Shu, C.-W.: An efficient class of WENO schemes with adaptive order. J. Comput. Phys. 326, 780–804 (2016)
Zhu, J., Qiu, J.: A new fifth order finite difference WENO scheme for solving hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 318, 110–121 (2016)
Sun, Z., Inaba, S., Xiao, F.: Boundary variation diminishing (BVD) reconstruction: a new approach to improve Godunov schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 322, 309–325 (2016)
Semplice, M., Visconti, G.: Efficient implementation of adaptive order reconstructions. J. Sci. Comput. 83(1), 1–27 (2020)
Tsoutsanis, P., Dumbser, M.: Arbitrary high order central non-oscillatory schemes on mixed-element unstructured meshes. Comput. Fluids 225, 104961 (2021)
Dumbser, M., Zanotti, O.: Very high order \(P_NP_M\) schemes on unstructured meshes for the resistive relativistic MHD equations. J. Comput. Phys. 228(18), 6991–7006 (2009)
Suresh, A., Huynth, H., Suresh, A., Huynth, H.: Accurate monotonicity-preserving schemes with Runge–Kutta time stepping. In: 13th Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, p 2037
Badia, S., Bonilla, J.: Monotonicity-preserving finite element schemes based on differentiable nonlinear stabilization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 313, 133–158 (2017)
Johnsen, E., Larsson, J., Bhagatwala, A.V., Cabot, W.H., Moin, P., Olson, B.J., Rawat, P.S., Shankar, S.K., Sjögreen, B., Yee, H., Zhong, X., Lele, S.K.: Assessment of high-resolution methods for numerical simulations of compressible turbulence with shock waves. J. Comput. Phys. 229(4), 1213–1237 (2010)
Fu, L., Karp, M., Bose, S.T., Moin, P., Urzay, J.: Shock-induced heating and transition to turbulence in a hypersonic boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 909, A8 (2021)
Fu, L., Hu, X.Y., Adams, N.A.: A family of high-order targeted ENO schemes for compressible-fluid simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 305, 333–359 (2016)
Fu, L., Hu, X.Y., Adams, N.A.: Targeted ENO schemes with tailored resolution property for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 349, 97–121 (2017)
Fu, L., Hu, X.Y., Adams, N.A.: A new class of adaptive high-order targeted ENO schemes for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 374, 724–751 (2018)
Fu, L.: A low-dissipation finite-volume method based on a new TENO shock-capturing scheme. Comput. Phys. Commun. 235, 25–39 (2019)
Fu, L.: A very-high-order TENO scheme for all-speed gas dynamics and turbulence. Comput. Phys. Commun. 244, 117–131 (2019)
Li, Y., Fu, L., Adams, N.A.: A low-dissipation shock-capturing framework with flexible nonlinear dissipation control. J. Comput. Phys. 428, 109960 (2021)
Haimovich, O., Frankel, S.H.: Numerical simulations of compressible multicomponent and multiphase flow using a high-order targeted ENO (TENO) finite-volume method. Comput. Fluids 146, 105–116 (2017)
Dong, H., Fu, L., Zhang, F., Liu, Y., Liu, J.: Detonation simulations with a fifth-order TENO scheme. Commun. Comput. Phys. 25(5), 1357–1393 (2019)
Di Renzo, M., Fu, L., Urzay, J.: HTR solver: an open-source exascale-oriented task-based multi-GPU high-order code for hypersonic aerothermodynamics. Comput. Phys. Commun. 107262 (2020)
Lusher, D.J., Sandham, N.D.: Shock-wave/boundary-layer interactions in transitional rectangular duct flows. Flow Turbul Combust 1–22 (2020)
Hamzehloo, A., Lusher, D.J., Laizet, S., Sandham, N.D.: On the performance of WENO/TENO schemes to resolve turbulence in DNS/LES of high-speed compressible flows. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 93(1), 176–196 (2021)
Peng, J., Liu, S., Li, S., Zhang, K., Shen, Y.: An efficient targeted ENO scheme with local adaptive dissipation for compressible flow simulation. J. Comput. Phys. 425, 109902 (2021)
Cockburn, B., Shu, C.-W.: TVB Runge–Kutta local projection discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for conservation laws. II. General framework. Math. Comput. 52(186), 411–435 (1989)
Harten, A.: ENO schemes with subcell resolution. J. Comput. Phys. 83(1), 148–184 (1989)
Li, G., Qiu, J.: Hybrid weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes with different indicators. J. Comput. Phys. 229(21), 8105–8129 (2010)
Krivodonova, L., Xin, J., Remacle, J.-F., Chevaugeon, N., Flaherty, J.E.: Shock detection and limiting with discontinuous Galerkin methods for hyperbolic conservation laws. Appl. Numer. Math. 48(3–4), 323–338 (2004)
Helzel, C., Rossmanith, J.A., Taetz, B.: An unstaggered constrained transport method for the 3D ideal magnetohydrodynamic equations. J. Comput. Phys. 230(10), 3803–3829 (2011)
Jiang, G.-S., Peng, D.: Weighted ENO schemes for Hamilton-Jacobi equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 21(6), 2126–2143 (2000)
Fu, L., Hu, X.Y., Adams, N.A.: A targeted ENO scheme as implicit model for turbulent and genuine subgrid scales. Commun. Comput. Phys. 26(2), 311–345 (2019)
Fu, L., Hu, X.Y., Adams, N.A.: Improved five- and six-point targeted essentially nonoscillatory schemes with adaptive dissipation. AIAA J. 57(3), 1143–1158 (2019)
Ducros, F., Ferrand, V., Nicoud, F., Weber, C., Darracq, D., Gacherieu, C., Poinsot, T.: Large-eddy simulation of the shock/turbulence interaction. J. Comput. Phys. 152(2), 517–549 (1999)
Gottlieb, S., Shu, C.-W., Tadmor, E.: Strong stability-preserving high-order time discretization methods. SIAM Rev. 43(1), 89–112 (2001)
Torrilhon, M.: Uniqueness conditions for Riemann problems of ideal magnetohydrodynamics. J. Plasma Phys. 69(03), 253–276 (2003)
Ryu, D., Jones, T.: Numerical magetohydrodynamics in astrophysics: algorithm and tests for one-dimensional flow. Astrophys. J. 442, 228–258 (1995)
Susanto, A.: High-order finite-volume schemes for magnetohydrodynamics (2014). http://hdl.handle.net/10012/8597
Orszag, S.A., Tang, C.-M.: Small-scale structure of two-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 90(01), 129–143 (1979)
Kawai, S.: Divergence-free-preserving high-order schemes for magnetohydrodynamics: an artificial magnetic resistivity method. J. Comput. Phys. 251, 292–318 (2013)
Yang, Y., Wan, M., Shi, Y., Yang, K., Chen, S.: A hybrid scheme for compressible magnetohydrodynamic turbulence. J. Comput. Phys. 306, 73–91 (2016)
Balsara, D.S., Spicer, D.S.: A staggered mesh algorithm using high order Godunov fluxes to ensure solenoidal magnetic fields in magnetohydrodynamic simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 149(2), 270–292 (1999)
Acknowledgements
Lin Fu acknowledges the generous startup fund from The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (No. R9280) and the fund from Shenzhen Municipal Central Government Guides Local Science and Technology Development Special Funds Funded Projects (No. 2021Szvup138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, L. An Efficient Low-Dissipation High-Order TENO Scheme for MHD Flows. J Sci Comput 90, 55 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01722-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01722-6