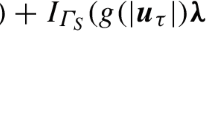Abstract
This paper is devoted to the development and analysis of a pressure projection stabilized mixed finite element method, with continuous piecewise linear approximations of velocities and pressures, for solving a hemivariational inequality of the stationary Stokes equations with a nonlinear non-monotone slip boundary condition. We present an existence result for an abstract mixed hemivariational inequality and apply it for a unique solvability analysis of the numerical method for the Stokes hemivariational inequality. An optimal order error estimate is derived for the numerical solution under appropriate solution regularity assumptions. Numerical results are presented to illustrate the theoretical prediction of the convergence order.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Atkinson, K., Han, W.: Theoretical Numerical Analysis: A Functional Analysis Framework, 3rd edn. Springer, New York (2009)
Barboteu, M., Bartosz, K., Han, W., Janiczko, T.: Numerical analysis of a hyperbolic hemivariational inequality arising in dynamic contact. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 53, 527–550 (2015)
Barboteu, M., Bartosz, K., Kalita, P.: An analytical and numerical approach to a bilateral contact problem with nonmonotone friction. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 23, 263–276 (2013)
Barth, T., Bochev, P.B., Gunzburger, M., Shadid, J.: A taxonomy of consistently stabilized finite element methods for the Stokes problem. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 25, 1585–1607 (2004)
Becker, R., Braack, M.: A finite elements pressure gradient stabilization for the Stokes equations based on local projections. Calcolo 38, 173–199 (2000)
Blasco, J., Codina, R.: Stabilization finite elements method for the transient Navier-Stokes equations based on a pressure gradient projection. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 182, 277–300 (2000)
Bochev, P.B., Dohrmann, C.R., Gunzburger, M.D.: Stabilization of low-order mixed finite elements for the Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44, 82–101 (2006)
Bochev, P.B., Gunzburger, M.D.: An absolutely stable pressure-Poisson stabilized finite element method for the Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 42, 1189–1207 (2004)
Brenner, S.C., Scott, R.L.: The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods. Texts in Applied Mathematics, Vol. 15, Springer-Verlag (2008)
Carl, S., Le, V.K., Motreanu, D.: Nonsmooth Variational Problems and Their Inequalities: Comparison Principles and Applications. Springer, New York (2007)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. North Holland, Amsterdam (1978)
Clarke, F.H.: Optimization and Nonsmooth Analysis. Wiley, Interscience, New York (1983)
Fang, C., Czuprynski, K., Han, W., Cheng, X.L., Dai, X.: Finite element method for a stationary Stokes hemivariational inequality with slip boundary condition. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 40, 2696–2716 (2020)
Feng, F., Han, W., Huang, J.: Virtual element method for an elliptic hemivariational inequality with applications to contact mechanics. J. Sci. Comput. 81, 2388–2412 (2019)
Granas, A., Dugundji, J.: Fixed Point Theory. Springer-Verlag, New York Inc (2003)
Han, W.: Numerical analysis of stationary variational-hemivariational inequalities with applications in contact mechanics. Math. Mech. Solids 23, 279–293 (2018)
Han, W., Czuprynski, K., Jing, F.: Mixed finite element method for a hemivariational inequality of stationary Navier-Stokes equations. J. Sci. Comput. 89, (2021), article number 8
Han, W., Migórski, S., Sofonea, M.: A class of variational-hemivariational inequalities with applications to frictional contact problems. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 46, 3891–3912 (2014)
Han, W., Sofonea, M.: Numerical analysis of hemivariational inequalities in contact mechanics. Acta Numer. 28, 175–286 (2019)
Han, W., Sofonea, M., Barboteu, M.: Numerical analysis of elliptic hemivariational inequalities. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 55, 640–663 (2017)
Han, W., Sofonea, M., Danan, D.: Numerical analysis of stationary variational-hemivariational inequalities. Numer. Math. 139, 563–592 (2018)
Han, W., Wang, C.: Numerical analysis of a parabolic hemivariational inequality for semipermeable media. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 389, (2021), article number 113326
Haslinger, J., Miettinen, M., Panagiotopoulos, P.D.: Finite Element Method for Hemivariational Inequalities: Theory, Methods and Applications. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht (1999)
He, Y., Wang, A., Mei, L.: Stabilized finite element method for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. J. Eng. Math. 51, 367–380 (2005)
Jing, F., Han, W., Zhang, Y., Yan, W.: Analysis of an a posteriori error estimator for a variational inequality governed by the Stokes equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 372, (2020), article number 112721
Li, J., Jing, F., Chen, Z., Liu, X.: A priori and a posteriori estimates of stabilized mixed finite volume methods for the incompressible flow arising in arteriosclerosis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 363, 35–52 (2020)
Li, Y., Li, K.: Pressure projection stabilized finite element method for Navier-Stokes equations with nonlinear slip boundary conditions. Computing 87, 113–133 (2010)
Li, Y., Li, K.: Pressure projection stabilized finite element method for Stokes problem with nonlinear slip boundary conditions. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 235, 3673–3682 (2011)
Ling, M., Wang, F., Han, W.: The nonconforming virtual element method for a stationary Stokes hemivariational inequality with slip boundary condition. J. Sci. Comput. 85, (2020), article number 56
Migórski, S., Ochal, A., Sofonea, M.: Nonlinear Inclusions and Hemivariational Inequalities: Models and Analysis of Contact Problems. Springer-Verlag, New York (2013)
Naniewicz, Z., Panagiotopoulos, P.D.: Mathematical Theory of Hemivariational Inequalities and Applications. Marcel Dekker, New York (1995)
Nečas, J., Hlaváček, I.: Mathematical Theory of Elastic and Elastico-Plastic Bodies: An Introduction. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam, Oxford, New York (1981)
Panagiotopoulos, P.D.: Hemivariational Inequalities, Applications in Mechanics and Engineering. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1993)
Scott, R.L., Zhang, S.: Finite element interpolation of nonsmooth functions satisfying boundary conditions. Math. Comput. 54, 483–493 (1990)
Silvester, D.J.: Optimal low order finite element methods for incompressible flow. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 111, 357–368 (1994)
Sofonea, M., Migórski, S.: Variational-Hemivariational Inequalities with Applications. Chapman & Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton-London (2018)
Temam, R.: Navier-Stokes Equations: Theory and Numerical Analysis. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1979)
Wang, F., Qi, H.: A discontinuous Galerkin method for an elliptic hemivariational inequality for semipermeable media. Appl. Math. Lett. 109, (2020), article number 106572
Wang, F., Wu, B., Han, W.: The virtual element method for general elliptic hemivariational inequalities. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 389, (2021), article number 113330
Xu, W., Huang, Z., Han, W., Chen, W., Wang, C.: Numerical analysis of history-dependent hemivariational inequalities and applications to viscoelastic contact problems with normal penetration. Comput. Math. Appl. 77, 2596–2607 (2019)
Funding
The work of second author was supported by Simons Foundation Collaboration, USA, Grants No. 850737, and by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie Grant Agreement No. 823731 CONMECH. The work of third author was supported by NNSF of China Grant No. 12001478, and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Grant Nos. 2021GXNSFFA196004 and 2020GXNSFBA297137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, M., Han, W. & Zeng, S. A Pressure Projection Stabilized Mixed Finite Element Method for a Stokes Hemivariational Inequality. J Sci Comput 92, 13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-01871-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-01871-2