Abstract
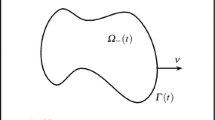
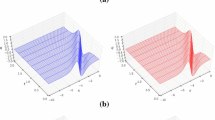
In this paper, for the highly nonlinear hydrodynamically coupled elastic bending energy model of vesicle membranes, based on the discontinuous Galerkin (DG) method for spatial discretization, a linear, decoupled, and second-order time-accurate numerical scheme is constructed. The scheme combines several efficient approaches, including the scalar auxiliary variable (SAV) method for the linearization of the nonlinear energy potential, the implicit-explicit (IMEX) discretization method for dealing with the nonlinear coupling terms, and the projection method for the Navier–Stokes equations. We also rigorously establish the energy stability and optimal error estimates, and also carry out several numerical examples to demonstrate the accuracy, stability, and efficiency of the proposed fully discrete DG scheme, numerically.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbas, M., Kaya, S., Rebholz, L.: On the stability at all times of linearly extrapolated BDF2 timestepping for multiphysics incompressible flow problems. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 33(4), 999–1017 (2017)
Arnold, D.N., Brezzi, F., Cockburn, B., Marini, L.D.: Unified analysis of discontinuous Galerkin methods for elliptic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 39(5), 1749–1779 (2002)
Baker, G.A.: Finite element methods for elliptic equations using nonconforming elements. Math. Comp. 31, 45–59 (1977)
Barthès-Biesel, D.: Motion and deformation of elastic capsules and vesicles in flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 48(1), 25–52 (2016)
Campelo, F., Cruz, A., Pérez-Gil, J., Vázquez, L., Hernández-Machado, A.: Phase-field model for the morphology of monolayer lipid domains. Eur. Phys. J. 35(6), 1–8 (2012)
Campelo, F., Hernández-Machado, A.: Shape instabilities in vesicles: a phase-field model. Eur. Phys. J. 143(1), 101–108 (2007)
Canham, P.B.: The minimum energy of bending as a possible explanation of the biconcave shape of the human red blood cell. J. Theor. Biol. 26(1), 61–81 (1970)
Chaabane, N., Girault, V., Puelz, C., Rivière, B.: Convergence of IPDG for coupled time-dependent Navier–Stokes and Darcy equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 324, 25–48 (2017)
Chadwick, R.S.: Axisymmetric indentation of a thin incompressible elastic layer. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 62(5), 1520–1530 (2002)
Chen, R., Ji, G., Yang, X., Zhang, H.: Decoupled energy stable schemes for phase-field vesicle membrane model. J. Comput. Phys. 302, 509–523 (2015)
Chen, W., Liu, Q., Shen, J.: Error estimates and blow-up analysis of a finite-element approximation for the parabolic-elliptic Keller–Segel system. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mod. 19, 275–298 (2022)
Chen, W., Zhang, Y., Li, W., Wang, Y., Yan, Y.: Optimal convergence analysis of a second order scheme for a thin film model without slope selection. J. Sci. Comput. 80(3), 1716–1730 (2019)
Cheng, Q., Shen, J.: Multiple scalar auxiliary variable (MSAV) approach and its application to the phase-field vesicle membrane model. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 40(6), A3982–A4006 (2018)
Cockburn, B., Kanschat, G., Schötzau, D., Schwab, C.: Local discontinuous Galerkin methods for the Stokes system. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40(1), 319–343 (2002)
Cockburn, B., Karniadakis, G.E., Shu, C.: The Development of Discontinuous Galerkin Methods. Springer (2000)
Di Pietro, D.A., Ern, A.: Discrete functional analysis tools for discontinuous Galerkin methods with application to the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Math. Comp. 79(271), 1303–1330 (2010)
Du, Q., Li, M., Liu, C.: Analysis of a phase field Navier–Stokes vesicle-fluid interaction model. Disc. Contin. Dyn. Syst. B. 8(3), 539–556 (2007)
Du, Q., Liu, C., Wang, X.: A phase field approach in the numerical study of the elastic bending energy for vesicle membranes. J. Comput. Phys. 198(2), 450–468 (2004)
Du, Q., Liu, C., Wang, X.: Simulating the deformation of vesicle membranes under elastic bending energy in three dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 212(2), 757–777 (2006)
Feng, X., Karakashian, O.A.: Two-level nonoverlapping additive Schwarz methods for a discontinuous Galerkin approximation of the biharmonic problem. J. Sci. Comput. 39, 1343–1365 (2001)
Feng, X., Li, Y.: Analysis of symmetric interior penalty discontinuous Galerkin methods for the Allen-Cahn equation and the mean curvature flow. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 35(4), 1622–1651 (2015)
Girault, V., Rivière, B.: DG approximation of coupled Navier–Stokes and Darcy equations by Beaver–Joseph–Saffman interface condition. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47(3), 2052–2089 (2009)
Girault, V., Rivière, B., Wheeler, M.F.: A splitting method using discontinuous Galerkin for the transient incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. ESAIM: M2AN. 39(6), 1115–1147 (2005)
Girault, V., Rivière, B., Wheeler, M.F.: A discontinuous Galerkin method with non-overlapping domain decomposition for the Stokes and Navier–Stokes problems. Math. Comp. 74(249), 53–84 (2005)
Guermond, J.L., Minev, P., Shen, J.: An overview of projection methods for incompressible flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 195(44), 6011–6145 (2006)
Guermond, J.L., Shen, J.: Velocity-correction projection methods for incompressible flows. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41(1), 112–134 (2003)
Guermond, J.L., Shen, J.: On the error estimates for the rotational pressure-correction projection methods. Math. Comp. 73(248), 1719–1737 (2004)
Guillén-González, F., Tierra, G.: Unconditionally energy stable numerical schemes for phase-field vesicle membrane model. J. Comput. Phys. 354, 67–85 (2018)
Gu, R., Wang, X., Gunzburger, M.: A two phase field model for tracking vesicle-vesicle adhesion. J. Math. Biol. 73(5), 1293–1319 (2016)
Helfrich, W.: Elastic properties of lipid bilayers: Theory and possible experiments. Z. Naturforsch. C 28(11), 693–703 (1973)
Hocine, S., Brûlet, A., Jia, L., Yang, J., Di Cicco, A., Bouteiller, L., et al.: Structural changes in liquid crystal polymer vesicles induced by temperature variation and magnetic fields. Soft Matter 7(6), 2613–2623 (2011)
Hu, Z., Wise, S.M., Wang, C., Lowengrub, J.S.: Stable and efficient finite-difference nonlinear-multigrid schemes for the phase field crystal equation. J. Comput. Phys. 228(15), 5323–5339 (2009)
Kay, D., Styles, V., Süli, E.: Discontinuous Galerkin finite element approximation of the Cahn–Hilliard equation with convection. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47(4), 2660–2685 (2009)
Kim, J.: A generalized continuous surface tension force formulation for phase-field models for multi-component immiscible fluid flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198(37), 3105–3112 (2009)
Lipowsky, R.: The morphology of lipid membranes. Curr. Opin. Struc. Biol. 5(4), 531–540 (1995)
Li, X., Shen, J.: Stability and error estimates of the SAV Fourier-spectral method for the phase field crystal equation. Adv. Comput. Math. 46(3) (2020)
Liu, C., Masri, R., Rivière, B.: Convergence of a decoupled splitting scheme for the Cahn–Hilliard–Navier–Stokes system, arXiv:2210.05625 (2022)
Liu, C., Rivière, B.: A priori error analysis of a discontinuous Galerkin method for Cahn–Hilliard–Navier–Stokes equations. CSIAM Trans. Appl. Math. 1(1), 104–141 (2020)
Lowengrub, J.S., Rätz, A., Voigt, A.: Phase-field modeling of the dynamics of multicomponent vesicles: Spinodal decomposition, coarsening, budding, and fission. Phys. Rev. E. 031926 (2009)
Miehe, C., Hofacker, M., Welschinger, F.: A phase field model for rate-independent crack propagation: Robust algorithmic implementation based on operator splits. Comput. Method. Appl. Math. 199(45), 2765–2778 (2010)
Nayanajith, P.G.H., Saha, S.C., Gu, Y.T.: Deformation properties of single red blood cell in a stenosed microchannel. In: APCOM ISCM, 11-14th December, 2013, Singapore
Rivière, B.: Discontinuous Galerkin Methods for Solving Elliptic and Parabolic Equations: Theory and Implementation. SIAM, Philadelphia (2008)
Shen, J.: On error estimates of the projection methods for the Navier–Stokes equations: second-order schemes. Math. Comp. 65, 1039–1065 (1996)
Shen, J., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: Second-order convex splitting schemes for gradient flows with Ehrlich–Schwoebel type energy: application to thin film epitaxy. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(1), 105–125 (2012)
Sidhu, V.K., Vorhölter, F., Niehaus, K., Watt, S.A.: Analysis of outer membrane vesicle associated proteins isolated from the plant pathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. BMC Microbiol. 8(1), 87 (2008)
Wang, X., Du, Q.: Modelling and simulations of multi-component lipid membranes and open membranes via diffuse interface approaches. J. Math. Biol. 56(3), 347–371 (2008)
Wang, X., Ju, L., Du, Q.: Efficient and stable exponential time differencing Runge–Kutta methods for phase field elastic bending energy models. J. Comput. Phys. 316, 21–38 (2016)
Wang, C., Wang, J., Xia, Z., Xu, L.: Optimal error estimates of a Crank-Nicolson finite element projection method for magnetohydrodynamic equations. ESAIM: M2AN. 56(3), 767 (2022)
Wang, X., Zou, G., Wang, B.: The stabilized penalty-projection finite element method for the Navier–Stokes–Cahn–Hilliard–Oono system. Appl. Numer. Math. 165, 376–413 (2021)
Wells, G.N., Kuhl, E., Garikipati, K.: A discontinuous Galerkin method for the Cahn-Hilliard equation. J. Comput. Phys. 218(2), 860–877 (2006)
Yang, X., Ju, L.: Efficient linear schemes with unconditional energy stability for the phase field elastic bending energy model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 315, 691–712 (2017)
Yang, X.: Numerical approximations of the Navier–Stokes equation coupled with volume-conserved multi-phase-field vesicles system: Fully-decoupled, linear, unconditionally energy stable and second-order time-accurate numerical scheme. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 375, 113600 (2021)
Yang, X.: A novel fully-decoupled, second-order time-accurate, unconditionally energy stable scheme for a flow-coupled volume-conserved phase-field elastic bending energy model. J. Comput. Phys. 432, 110015 (2021)
Yang, X.: On a novel fully-decoupled, second-order accurate energy stable numerical scheme for a binary fluid-surfactant phase-field model. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 43, B479–B507 (2021)
Yang, X.: On a novel full decoupling, Linear, Second-order accurate, and unconditionally energy stable numerical scheme for the anisotropic phase-field dendritic crystal growth model. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 122, 4129–4153 (2021)
Yang, X.: Efficient linear, fully-decoupled and energy stable numerical scheme for a variable density and viscosity, volume-conserved, hydrodynamically coupled phase-field elastic bending energy model of lipid vesicles. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 400, 115479 (2022)
Zou, G., Wang, B., Yang, X.: A fully-decoupled discontinuous Galerkin approximation of the Cahn-Hilliard-Brinkman-Ohta-Kawasaki tumor growth model. ESAIM: M2AN. 56, 2141–2180 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the reviewers for the constructive comments and valuable suggestions which have improved the paper. The work of G. Zou was partially supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M662476), and the Key Scientific Research Projects of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province, China (23A110006). The work of X. Yang was partially supported by National Science Foundation of USA with Grant Number DMS-2012490.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, Ga., Li, Z. & Yang, X. Fully Discrete Discontinuous Galerkin Numerical Scheme with Second-Order Temporal Accuracy for the Hydrodynamically Coupled Lipid Vesicle Model. J Sci Comput 95, 5 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02129-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02129-1