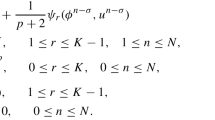Abstract
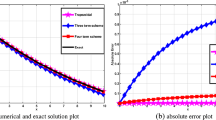
In this paper, we construct two new linear, decoupled, unconditionally energy stable finite element schemes for electrohydrodynamic model of charge transport with variable density dielectric fluid. The fully-decoupled schemes are achieved by the property of two nonlocal auxiliary variables and applying the operator Strang-splitting method. At each time step, all variables can be computed independently by solving a sequence of linear finite element schemes and algebraic equations. The solvability and unconditionally energy stability of the two schemes are rigorously demonstrated. Numerical experiments verify the effectiveness and stability of the proposed schemes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Cai, W., Li, B., Li, Y.: Error analysis of a fully discrete finite element method for variable density incompressible flows in two dimensions. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 55, S103–S147 (2021)
Chen, C., Yang, X.: Fully-discrete finite element numerical scheme with decoupling structure and energy stability for the Cahn–Hilliard phase-field model of two-phase incompressible flow system with variable density and viscosity. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 55(5), 2323–2347 (2021)
Chen, C., Yang, X.: Highly efficient and unconditionally energy stable semi-discrete time-marching numerical scheme for the two-phase incompressible flow phase-field system with variable-density and viscosity. Sci. China Math. 65, 1–26 (2022)
Chen, H., Mao, J., Shen, J.: Error estimate of Gauge-Uzawa methods for incompressible flows with variable density. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 364, 112321 (2020)
Chicón, R., Castellanos, A., Martin, E.: Numerical modelling of Coulomb-driven convection in insulating liquids. J. Fluid Mech. 344, 43–66 (1997)
Cimpeanu, R., Papageorgiou, D.T., Petropoulos, P.G.: On the control and suppression of the Rayleigh–Taylor instability using electric fields. Phys. Fluids 26(2), 022105 (2014)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Methods for Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Algorithms, vol. 5. Springer (2012)
Guermond, J.L., Salgado, A.: A fractional step method based on a pressure Poisson equation for incompressible flows with variable density. C. R. Math. 346(15–16), 913–918 (2008)
Hecht, F.: New development in FreeFem++. J. Numer. Math. 20(3–4), 251–266 (2012)
Kupershtokh, A., Medvedev, D.: Lattice Boltzmann equation method in electrohydrodynamic problems. J. Electrostat. 64(7–9), 581–585 (2006)
Li, T.F., Wu, J., Luo, K., Yi, H.L.: Lattice Boltzmann simulation of electro-hydro-dynamic (EHD) natural convection heat transfer in horizontal cylindrical annuli. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 98, 106–115 (2018)
Li, Y., Mei, L., Ge, J., Shi, F.: A new fractional time-stepping method for variable density incompressible flows. J. Comput. Phys. 242, 124–137 (2013)
López-Herrera, J., Popinet, S., Herrada, M.A.: A charge-conservative approach for simulating electrohydrodynamic two-phase flows using volume-of-fluid. J. Comput. Phys. 230(5), 1939–1955 (2011)
Luo, K., Li, T., Wu, J., Yi, H., Tan, H.: Mesoscopic simulation of electrohydrodynamic effects on laminar natural convection of a dielectric liquid in a cubic cavity. Phys. Fluids 30(10), 103601 (2018)
Luo, K., Pérez, A.T., Wu, J., Yi, H., Tan, H.: Efficient lattice Boltzmann method for electrohydrodynamic solid–liquid phase change. Phys. Rev. E 100(1), 013306 (2019)
Pan, M., Fu, C., Zhu, W., Jiao, F., He, D.: Linear, second-order, unconditionally energy stable scheme for an electrohydrodynamic model with variable density and conductivity. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 125, 107329 (2023)
Pan, M., He, D., Pan, K.: Unconditionally energy stable schemes for an electrohydrodynamic model of charge transport in dielectric liquids. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 361, 112817 (2020)
Pan, M., He, D., Pan, K.: Energy stable finite element method for an electrohydrodynamic model with variable density. J. Comput. Phys. 424, 109870 (2021)
Pan, M., Wang, Q., He, D., Pan, K.: Positive-definiteness preserving and energy stable time-marching scheme for a diffusive Oldroyd-B electrohydrodynamic model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 95(8), 105630 (2021)
Pérez, A., Vázquez, P., Wu, J., Traoré, P.: Electrohydrodynamic linear stability analysis of dielectric liquids subjected to unipolar injection in a rectangular enclosure with rigid sidewalls. J. Fluid Mech. 758, 586–602 (2014)
Pyo, J.H., Shen, J.: Gauge-Uzawa methods for incompressible flows with variable density. J. Comput. Phys. 221(1), 181–197 (2007)
Si, Z., He, D.: Unconditional stability and error estimates of FEMs for the electro-osmotic flow in micro-channels. p. 10.48550. arXiv arXiv:2210.10550 (2022)
Stuetzer, O.M.: Magnetohydrodynamics and electrohydrodynamics. Phys. Fluids 5(5), 534–544 (1962)
Temam, R.: Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Numerical Analysis, vol. 2, 3rd edn. North-Holland, Amsterdam, New York, Oxford (1984)
Traoré, P., Pérez, A.: Two-dimensional numerical analysis of electroconvection in a dielectric liquid subjected to strong unipolar injection. Phys. Fluids 24(3), 037102 (2012)
Traoré, P., Pérez, A., Koulova, D., Romat, H.: Numerical modelling of finite-amplitude electro-thermo-convection in a dielectric liquid layer subjected to both unipolar injection and temperature gradient. J. Fluid Mech. 658, 279–293 (2010)
Traoré, P., Wu, J.: On the limitation of imposed velocity field strategy for Coulomb-driven electroconvection flow simulations. J. Fluid Mech. 727, 1–12 (2013)
Vázquez, P., Castellanos, A.: Stability analysis of the 3D electroconvective charged flow between parallel plates using the particle-in-cell method. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Dielectric Liquids, pp. 1–4. IEEE (2011)
Vázquez, P., Castellanos, A.: Numerical simulation of EHD flows using discontinuous Galerkin finite element methods. Comput. Fluids 84, 270–278 (2013)
Vazquez, P., Soria, C., Castellanos, A.: Numerical simulation of two-dimensional EHD plumes mixing finite element and particle methods. In: The 17th Annual Meeting of the IEEE Lasers and Electro-Optics Society, 2004. LEOS 2004., pp. 122–125. IEEE (2004)
Wang, L., Wei, Z., Li, T., Chai, Z., Shi, B.: A lattice Boltzmann modelling of electrohydrodynamic conduction phenomenon in dielectric liquids. Appl. Math. Model. 95, 361–378 (2021)
Wang, Z., Chen, C., Li, Y., Yang, X.: Decoupled finite element scheme of the variable-density and viscosity phase-field model of a two-phase incompressible fluid flow system using the volume-conserved Allen–Cahn dynamics. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 420, 114773 (2023)
Wu, J., Traoré, P.: A finite-volume method for electro-thermoconvective phenomena in a plane layer of dielectric liquid. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 68(5), 471–500 (2015)
Yang, X.: Efficient linear, fully-decoupled and energy stable numerical scheme for a variable density and viscosity, volume-conserved, hydrodynamically coupled phase-field elastic bending energy model of lipid vesicles. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 400, 115479 (2022)
Yao, H., Xu, C., Azaiez, M.: Stable and decoupled schemes for an electrohydrodynamics model. Math. Comput. Simul. 206, 689–708 (2023)
Funding
The authors have disclosed the funding on the footnote of the title page.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This paper is supported by National Key R &D Program of China (No. 2022YFA1004500), Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (No. 2021J01034) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 20720220038).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Chen, H. Decoupled and Unconditionally Energy Stable Finite Element Schemes for Electrohydrodynamic Model with Variable Density. J Sci Comput 96, 78 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02304-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02304-4
Keywords
- Electrohydrodynamic model with variable density
- Fully-decoupled
- Finite element method
- Unconditional energy stability