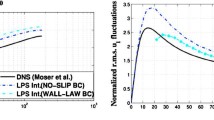
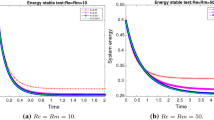
Abstract
We propose, analyze, and test a penalty projection-based robust efficient and accurate algorithm for the Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) of the time-dependent Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow problems in convection-dominated regimes. The algorithm uses the Elsässer variables formulation and discrete Hodge decomposition to decouple the stochastic MHD system into four sub-problems (at each time-step for each realization) which are much easier to solve than solving the coupled saddle point problems. Each of the sub-problems is designed in a sophisticated way so that at each time-step the system matrix remains the same for all the realizations but with different right-hand-side vectors which allows saving a huge amount of computer memory and computational time. Moreover, the scheme is equipped with Ensemble Eddy Viscosity (EEV) and grad-div stabilization terms. The unconditional stability with respect to the time-step size of the algorithm is proven rigorously. We prove the proposed scheme converges to an equivalent non-projection-based coupled MHD scheme for large grad-div stabilization parameter values. We examine how Stochastic Collocation Methods (SCMs) can be combined with the proposed penalty projection UQ algorithm. Finally, a series of numerical experiments are given which verify the predicted convergence rates, show the algorithm’s performance on benchmark channel flow over a rectangular step, a regularized lid-driven cavity problem with high random Reynolds number and high random magnetic Reynolds number, and the impact of the EEV stabilization in the MHD UQ algorithm.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data will be provided upon request.
References
Aggul, M.: A grad-div stabilized penalty projection algorithm for fluid-fluid interaction. Appl. Math. Comput. 414, 126670 (2022)
Aggul, M., Eroglu, F.G., Kaya, S.: Artificial compression method for MHD system in Elsässer variables. Appl. Numer. Math. 185, 72–87 (2023)
Akbas, M., Kaya, S., Mohebujjaman, M., Rebholz, L.: Numerical analysis and testing of a fully discrete, decoupled penalty-projection algorithm for MHD in Elsässer variable. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 13(1), 90–113 (2016)
Babuska, I., Nobile, F., Tempone, R.: A stochastic collocation method for elliptic partial differential equations with random input data. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(3), 1005–1034 (2007)
Balajewicz, M.J., Dowell, E.H., Bernd, R.N.: Low-dimensional modelling of high-reynolds-number shear flows incorporating constraints from the Navier-Stokes equation. J. Fluid Mech. 729, 285 (2013)
Berselli, L.C., Iliescu, T., Layton, W.J.: Mathematics of Large Eddy Simulation of Turbulent Flows. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Biskamp, D.: Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Case, M., Labovsky, A., Rebholz, L.G., Wilson, N.: A high physical accuracy method for incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. Ser. B 1(2), 219–238 (2010)
Chen, S., Zhu, Y.: Subpattern-based principle component analysis. Pattern Recogn. 37(5), 1081–1083 (2004)
Chkifa, A., Cohen, A., Migliorati, G., Nobile, F., Tempone, R.: Discrete least squares polynomial approximation with random evaluations- application to parametric and stochastic elliptic PDEs. ESAIM Math. Model. Num. Anal. 49, 815–837 (2015)
Chorin, A.J.: Numerical solution of the Navier-Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 22(104), 745–762 (1968)
Çıbık, A., Eroglu, F.G., Kaya, S.: Analysis of second order time filtered backward Euler method for MHD equations. J. Sci. Comput. 82(2), 1–25 (2020)
Davidson, P.A.: An Introduction to Magnetohydrodynamics. Cambridge Texts in Applied Mathematics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Davis, T.A.: Algorithm 832: UMFPACK v4.3–an unsymmetric-pattern multifrontal method. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. (TOMS) 30(2), 196–199 (2004)
Erkmen, D., Kaya, S., Çıbık, A.: A second order decoupled penalty projection method based on deferred correction for MHD in Elsässer variable. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 371, 112694 (2020)
Erkmen, D., Labovsky, A.: Note on the usage of grad-div stabilization for the penalty-projection algorithm in magnetohydrodynamics. Appl. Math. Comput. 349, 48–52 (2019)
Fick, L., Maday, Y., Patera, A.T., Taddei, T.: A stabilized POD model for turbulent flows over a range of Reynolds numbers: optimal parameter sampling and constrained projection. J. Comput. Phys. 371, 214–243 (2018)
Fujita, T., Stensrud, D.J., Dowell, D.C.: Surface data assimilation using an ensemble Kalman filter approach with initial condition and model physics uncertainties. Mon. Weather Rev. 135(5), 1846–1868 (2007)
Girault, V., Raviart, V.: Finite Element Methods for Navier-Stokes Equations: Theory and Algorithms. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1986)
Gunzburger, M., Iliescu, T., Mohebujjaman, M., Schneier, M.: An evolve-filter-relax stabilized reduced order stochastic collocation method for the time-dependent Navier-Stokes equations. SIAM/ASA J. Uncertain. Quantif. 7(4), 1162–1184 (2019)
Gunzburger, M.D., Webster, C.G., Zhang, G.: Stochastic finite element methods for partial differential equations with random input data. Acta Numer. 23, 521–650 (2014)
Hecht, F.: New development in Freefem++. J. Numer. Math. 20, 251–266 (2012)
Heister, T., Mohebujjaman, M., Rebholz, L.: Decoupled, unconditionally stable, higher order discretizations for MHD flow simulation. J. Sci. Comput. 71, 21–43 (2017)
Heywood, J.G., Rannacher, R.: Finite-element approximation of the nonstationary Navier-Stokes problem part iv: error analysis for second-order time discretization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 27, 353–384 (1990)
Hossain, A., Molla, M.M., Kamrujjaman, M., Mohebujjaman, M., Saha, S.C.: MHD mixed convection of non-Newtonian Bingham nanofluid in a wavy enclosure with temperature-dependent thermophysical properties: A sensitivity analysis by response surface methodology. Energies 16(11), 4408 (2023)
Jiang, N.: A higher order ensemble simulation algorithm for fluid flows. J. Sci. Comput. 64, 264–288 (2015)
Jiang, N.: A second order ensemble method based on a blended BDF timestepping scheme for time dependent Navier-Stokes equations. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 33(1), 34–61 (2017)
Jiang, N., Kaya, S., Layton, W.: Analysis of model variance for ensemble based turbulence modeling. Comput. Methods Appl. Math. 15, 173–188 (2015)
Jiang, N., Layton, W.: An algorithm for fast calculation of flow ensembles. Int. J. Uncertain. Quantif. 4, 273–301 (2014)
Jiang, N., Layton, W.: Numerical analysis of two ensemble eddy viscosity numerical regularizations of fluid motion. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 31, 630–651 (2015)
Jiang, N., Layton, W., McLaughlin, M., Rong, Y., Zhao, H.: On the foundations of eddy viscosity models of turbulence. Fluids 5(4), 167 (2020)
Jiang, N., Li, Y., Yang, H.: An artificial compressibility Crank-Nicolson leap-frog method for the Stokes-Darcy model and application in ensemble simulations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 59(1), 401–428 (2021)
Jiang, N., Yang, H.: Unconditionally stable, second order, decoupled ensemble schemes for computing evolutionary Boussinesq equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 192, 241–260 (2023)
Johnson, B., Gibson, N.L., Cotilla-Sanchez, E.: A coupled Karhunen-Loève and anisotropic sparse grid interpolation method for the probabilistic load flow problem. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 193, 107044 (2021)
Kuberry, P., Larios, A., Rebholz, L.G., Wilson, N.E.: Numerical approximation of the Voigt regularization for incompressible Navier-Stokes and magnetohydrodynamic flows. Comput. Math. Appl. 64(8), 2647–2662 (2012)
Landau, L.D., Lifshitz, E.M.: Electrodynamics of Continuous Media. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1960)
Layton, W.: Introduction to the Numerical Analysis of Incompressible Viscous Flows. Computational Science and Engineering. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (2008)
Lee, H.K., Olshanskii, M.A., Rebholz, L.G.: On error analysis for the 3d Navier-Stokes equations in velocity-vorticity-helicity form. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 49(2), 711–732 (2011)
Lee, K., Carlberg, K., Elman, H.C.: Stochastic least-squares Petrov-Galerkin method for parameterized linear systems. SIAM/ASA J. Uncertain. Quantif. 6(1), 374–396 (2018)
Lee, M.W., Dowell, E.H., Balajewicz, M.J.: A study of the regularized lid-driven cavity’s progression to chaos. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 71, 50–72 (2019)
Lewis, J.M.: Roots of ensemble forecasting. Mon. Weather Rev. 133, 1865–1885 (2005)
Li, Y., Ma, Y., An, R.: Decoupled, semi-implicit scheme for a coupled system arising in magnetohydrodynamics problem. Appl. Numer. Math. 127, 142–163 (2018)
Li, Y., Trenchea, C.: Partitioned second order method for magnetohydrodynamics in Elsässer variables. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. B 23(7), 2803 (2018)
Linke, A.: Collision in a cross-shaped domain-A steady 2d Navier-Stokes example demonstrating the importance of mass conservation in CFD. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198(41–44), 3278–3286 (2009)
Linke, A., Neilan, M., Rebholz, L.G., Wilson, N.E.: A connection between coupled and penalty projection timestepping schemes with FE spatial discretization for the Navier-Stokes equations. J. Numer. Math. 25(4), 229–248 (2017)
Palmer, T.N., Leutbecher, M.: Ensemble forecasting. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 3515–3539 (2008)
Maître, O.P.L., Knio, O.M.: Spectral Methods for Uncertainty Quantification. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Martin, W.J., Xue, M.: Sensitivity analysis of convection of the 24 May 2002 IHOP case using very large ensembles. Mon. Weather Rev. 134(1), 192–207 (2006)
Mohebujjaman, M.: High order efficient algorithm for computation of MHD flow ensembles. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 14(5), 1111–1137 (2022)
Mohebujjaman, M., Buenrostro, C., Kamrujjaman, M., Khan, T.: Decoupled algorithms for non-linearly coupled reaction-diffusion competition model with harvesting and stocking. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 436, 115421 (2024)
Mohebujjaman, M., Rebholz, L.G.: An efficient algorithm for computation of MHD flow ensembles. Comput. Methods Appl. Math. 17, 121–137 (2017)
Mohebujjaman, M., Rebholz, L.G., Iliescu, T.: Physically constrained data-driven correction for reduced-order modeling of fluid flows. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 89(3), 103–122 (2019)
Mohebujjaman, M., Shiraiwa, S., Labombard, B., Wright, J.C., Uppalapati, K.K.: Scalability analysis of direct and iterative solvers used to model charging of superconducting pancake solenoids. Eng. Res. Express 5(1), 015045 (2023)
Mohebujjaman, M., Wang, H., Rebholz, L.G., Mahbub, M.A.A.: An efficient algorithm for parameterized magnetohydrodynamic flow ensembles simulation. Comput. Math. Appl. 112, 167–180 (2022)
Neda, M., Takhirov, A., Waters, J.: Ensemble calculations for time relaxation fluid flow models. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 32(3), 757–777 (2016)
Nobile, F., Tempone, R., Webster, C.G.: An anisotropic sparse grid stochastic collocation method for partial differential equations with random input data. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 46(5), 2411–2442 (2008)
O’Leary, D.P.: The block conjugate gradient algorithm and related methods. Linear Algebra Appl. 29, 293–322 (1980)
Giraldo Osorio, J.D., Garcia Galiano, S.G.: Building hazard maps of extreme daily rainy events from PDF ensemble, via REA method, on Senegal river basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 15, 3605–3615 (2011)
Proctor, J.L., Brunton, S.L., Kutz, J.N.: Dynamic mode decomposition with control. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 15(1), 142–161 (2016)
Robinson, J.C., Rodrigo, J.L., Sadowski, W.: The Three-Dimensional Navier-Stokes Equations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2016)
Simoncini, V., Gallopoulos, E.: A hybrid block GMRES method for nonsymmetric systems with multiple right-hand sides. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 66(1–2), 457–469 (1996)
Stoyanov, M.: Hierarchy-direction selective approach for locally adaptive sparse grids. Technical Report ORNL/TM-2013/384, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, One Bethel Valley Road, Oak Ridge (2013)
Stoyanov, M.: User manual: Tasmanian sparse grids. Technical Report ORNL/TM-2015/596, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, One Bethel Valley Road, Oak Ridge (2015)
Stoyanov, M., Lebrun-Grandie, D., Burkardt, J., Munster, D.: Tasmanian (9 2013)
Stoyanov, M.K., Webster, C.G.: A dynamically adaptive sparse grids method for quasi-optimal interpolation of multidimensional functions. Comput. Math. Appl. 71(11), 2449–2465 (2016)
Temam, R.: Sur l’approximation de la solution des équations de Navier-Stokes par la méthode des pas fractionnaires (II). Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 33, 377–385 (1969)
Trenchea, C.: Unconditional stability of a partitioned IMEX method for magnetohydrodynamic flows. Appl. Math. Lett. 27, 97–100 (2014)
Wang, C., Wang, J., Wise, S.M., Xia, Z., Xu, L.: Convergence analysis of a temporally second-order accurate finite element scheme for the Cahn-Hilliard-Magnetohydrodynamics system of equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 436, 115409 (2024)
Wilson, N., Labovsky, A., Trenchea, C.: High accuracy method for magnetohydrodynamics system in Elsässer variables. Comput. Methods Appl. Math. 15(1), 97–110 (2015)
Rebholz, L.G., Xie, X., Mohebujjaman, M., Iliescu, T.: Data-driven filtered reduced order modeling of fluid flows. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 40(3), B834–B857 (2018)
Yang, J., He, Y., Zhang, G.: On an efficient second order backward difference Newton scheme for MHD system. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 458(1), 676–714 (2018)
Zhang, G.-D., Yang, J., Bi, C.: Second order unconditionally convergent and energy stable linearized scheme for MHD equations. Adv. Comput. Math. 44(2), 505–540 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Leo G. Rebholz for sharing his thoughts, and two anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions which greatly improved the manuscript. Alabama Supercomputer Authority (ASA) is acknowledged for generous allotment of computing time.
Funding
This work was supported by NSF grant DMS-2425308.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This work is supported by NSF grant DMS-2425308. Texas A &M International University provided the logistic support.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Muhammad Mohebujjaman was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) grant DMS-2425308, and Texas A &M International University. Julian Miranda was supported by the NSF grant DMS-2213274.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mohebujjaman, M., Miranda, J., Mahbub, M.A.A. et al. An Efficient and Accurate Penalty-projection Eddy Viscosity Algorithm for Stochastic Magnetohydrodynamic Flow Problems. J Sci Comput 101, 2 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-024-02633-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-024-02633-y
Keywords
- Magnetohydrodynamics
- Uncertainty quantification
- Fast ensemble calculation
- Ensemble eddy viscosity
- Stochastic collocation methods
- Penalty-projection method