Abstract
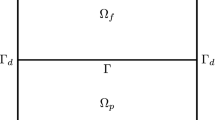
In this paper, we consider two different types of numerical schemes for the nonstationary stochastic Stokes–Darcy equations with multiplicative noise. Firstly, we consider the Chorin-type time-splitting scheme for the Stokes equation in the free fluid region. The Darcy equation and an elliptic equation for the intermediate velocity of free fluid coupled with the interface conditions are solved, and then the velocity and pressure in free fluid region are updated by an elliptic system. Secondly, we further consider the artificial compressibility method (ACM) which separates the fully coupled Stokes–Darcy model into two smaller subphysics problems. The ACM reduces the storage and the computational time at each time step, and allows parallel computing for the decoupled problems. The pressure in free fluid region only needs to be updated at each time step without solving an elliptic system. We utilize the RT\(_1\)-P\(_1\) pair finite element space and the interior penalty discontinuous Galerkin (IPDG) scheme based on the BDM\(_1\)-P\(_0\) finite element space in the spatial discretizations. Under usual assumptions for the multiplicative noise, we prove that both of the Chorin-type scheme and the ACM are unconditionally stable. We present the error estimates for the time semi-discretization of the Chorin-type scheme. Numerical examples are provided to verify the stability estimates for both of schemes. Moreover, we test the convergence rate for the velocity in time for both of schemes, and the convergence rate for the pressure approximation in time average is also tested.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Arbogast, T., Brunson, D.S.: A computational method for approximating a Darcy-Stokes system governing a vuggy porous media. Comput. Geosci. 11, 207–218 (2007)
Ambartsumyan, I., Khattatov, E., Wang, C., Yotov, I.: Stochastic multiscale flux basis for Stokes-Darcy flows. J. Comput. Phys. 401, 109011 (2020)
Breit, D., Dogson, A.: Convergence rates for the numerical approximation of the 2D stochastic Navier-Stokes equations. Numer. Math. 147, 553–578 (2021)
Beavers, G.S., Joseph, D.D.: Boundary conditions at a naturally permeable wall. J. Fluid Mech. 30, 197–207 (1967)
Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods. Springer (1991)
Camano, J., Gatica, G.N., Oyarzua, R., Ruiz-Baier, R., Venegas, P.: New fully-mixed finite element methods for the Stokes-Darcy coupling. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 295, 362–395 (2015)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., Hu, X., Hua, F., Wang, X., Zhao, W.: Finite element approximation for Stokes-Darcy flow with Beavers-Joseph interface conditions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 4239–4256 (2010)
Carelli, E., Hausenblas, E., Prohl, A.: Time-splitting methods to solve the stochastic incompressible Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50, 2917–2939 (2012)
Carelli, E., Prohl, A.: Rates of convergence for discretizations of the stochastic incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50, 2467–2496 (2012)
Chen, R.M., Layton, W., McLaughlin, M.: Analysis of variable-step/non-autonomous artificial compression methods. J. Math. Fluid Mech. 21, 30 (2019)
Chen, H., Wang, X.-P.: A one-domain approach for modeling and simulation of free fluid over a porous media. J. Comp. Phys. 259, 650–671 (2014)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1978)
Chorin, A.J.: Numerical solution of the Navier-Stokes equations. Math. Comp. 22, 745–762 (1968)
Chorin, A.J.: A numerical method for solving incompressible viscous flow problems. J. Comp. Phys. 2, 12–26 (1967)
Da Prato, G., Zabczyk, J.: Stochastic Equations in Infinite Dimensions. Cambridge University Press (1991)
DeCaria, V., Illiescu, T., Layton, W., McLaughlin, M., Schneier, M.: An artificial compression reduced order model. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 58, 565–589 (2020)
DeCaria, V., Layton, W., McLaughlin, M.: A conservative, second order, unconditionally stable artificial compression method. Comput. Method. Appl. M. 325, 733–747 (2017)
Dixon, J., McKee, S.: Weakly singular Gronwall inequalities. ZAMM Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 66, 535–544 (1986)
Feng, X., Prohl, A., Vo, L.: Optimally convergent mixed finite element methods for the stochastic Stokes equations. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 41, 2280–2310 (2021)
Feng, X., Qiu, H.: Analysis of fully discrete mixed finite element methods for time-dependent stochastic Stokes equations with multiplicative noise. J. Sci. Comp. 88, 1573–7691 (2021)
Feng, X., Vo, L.: Analysis of Chorin-type projection methods for the stochastic Stokes equations with general multiplicative noises, Stoch. PDE: Anal. Comp. pp. 1–38, (2022)
Guermond, J., Minev, P.: High-order time stepping for the Navier-Stokes equations with minimal computational complexity. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 310, 92–103 (2017)
Guermond, J., Minev, P.: High-order adaptive time stepping for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 41, A770–A788 (2019)
He, X., Jiang, N., Qiu, C.: An artificial compressibility ensemble algorithm for a stochastic Stokes-Darcy model with random hydraulic conductivity and interface conditions. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 121, 712–739 (2020)
Jiang, N., Li, Y., Yang, H.: An artificial compressibility Crank-Nicolson leap-frog method for the Stokes-Darcy model and application in ensemble simulations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 59, 401–428 (2021)
Kanschat, G., Rivière, B.: A strongly conservative finite element method for the coupling of Stokes and Darcy flow. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 5933–5943 (2010)
Karper, T., Mardal, K.-A., Winther, R.: Unified finite element discretizations of coupled Darcy-Stokes flow. Numer. Meth. Part. D. E. 25, 311–326 (2009)
Kruse, R.: Strong and Weak Approximation of Semilinear Stochastic Evolution Equations. Springer (2014)
Kumar, P., Luo, P., Gaspar, F.J., Oosterlee, C.W.: A multigrid multilevel Monte Carlo method for transport in the Darcy-Stokes system. J. Comput. Phys. 371, 382–408 (2018)
Kuznetsov, B., Vladimirova, N., Yanenko, N.: Numerical Calculation of the Symmetrical Flow of Viscous Incompressible Liquid around a Plate (in Russian), Studies in Mathematics and its Applications, Moscow: Nauka, (1966)
Layton, W., McLaughlin, M.: Doubly-adaptive artificial compression methods for incompressible flow. J. Numer. Math. 28, 175–192 (2020)
Li, Y., Hou, Y., Rong, Y.: A second-order artificial compression method for the evolutionary Stokes-Darcy system. Numer. Algorithms 84, 1019–1048 (2020)
Lord, G.J., Powell, C.E., Shardlow, T.: An Introduction to Computational Stochastic PDEs: Galerkin Approximation and Finite Elements. Cambridge University Press (2014)
Márquez, A., Meddahi, S., Sayas, F.-J.: Strong coupling of finite element methods for the Stokes-Darcy problem. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 35, 969–988 (2015)
Roman, L.J., Sarkis, M.: Stochastic galerkin method for elliptic SPDEs: a white noise approach. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 6, 941–955 (2006)
Saffman, P.G.: On the boundary condition at the interface of a porous media. Stud. Appl. Math. 1, 93–101 (1971)
Tartakovsky, A.M., Tartakovsky, D.M., Meakin, P.: Stochastic Langevin model for flow and transport in porous media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 044502 (2008)
Temam, R.: Une méthode d’approximation des solutions des équations de Navier-Stokes. Bull. Soc. Math. France 98, 115–152 (1968)
Temam, R.: Sur l’approximation de la solution des équations de Navier-Stokes par la méthode des pas fractionnaires (I). Arch. Rational. Mech. Anal. 33, 135–153 (1969)
Temam, R.: Sur l’approximation de la solution des équations de Navier-Stokes par la méthode des pas fractionnaires (II), Arch. Rational. Mech. Anal., 33, pp. 377–385 (1969)
Xiang, Y., Huang, C., Chen, H.: Optimal convergence analysis of a fully discrete scheme for the stochastic Stokes-Darcy equations. J. Sci. Comput. 94, 13 (2023)
Yang, Z., Li, X., He, X., Ming, J.: A stochastic collocation method based on sparse grids for a stochastic Stokes-Darcy model. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. S 15, 893–912 (2022)
Zhang, D.: Stochastic Methods for Flow in Porous Media: Coping with Uncertainties, Academic, (2002)
Funding
The work of Huangxin Chen was supported by the National Key Research and Development Project of China (Grant No. 2023YFA1011702) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12122115). The work of Can Huang was supported by the NSF of China (Grant No. 12271457). The work of Shuyu Sun was supported by King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) through the Grants BAS/1/1351-01 and URF/1/5028-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Huang, C., Sun, S. et al. Stabilized Variational Formulations of Chorin-Type and Artificial Compressibility Methods for the Stochastic Stokes–Darcy Equations. J Sci Comput 101, 22 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-024-02663-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-024-02663-6