Abstract
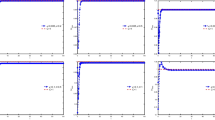
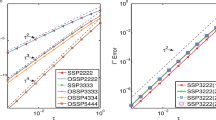
This paper presents two highly efficient numerical schemes for the time-fractional Allen–Cahn equation that preserve the maximum bound principle and energy dissipation in discrete settings. To this end, we utilize a generalized auxiliary variable approach proposed in a recent paper (Ju et al. in SIAM J Numer Anal 60:1905–1931, 2022) to reformulate the governing equation into an equivalent system that follows a modified energy functional and the maximum bound principle at each continuous level. By combining the L1-type formula of the Riemann–Liouville fractional derivative with the Crank–Nicolson method, we construct two novel linearly implicit schemes by introducing the first- and second-order stabilized terms, respectively. These schemes are proved to be energy stable and maximum bound principle preserving on nonuniform time meshes with the help of the discrete orthogonal convolution technique. In addition, we obtain the unique solvability of the proposed schemes without any time-space step ratio. Finally, we report extensive numerical results to verify the correctness of the theoretical analysis and the performance of the proposed schemes in long-time simulations.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Akinyemi, L., Iyiola, O., Akpan, U.: Iterative methods for solving fourth-and sixth-order time-fractional Cahn–Hillard equation. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 43, 4050–4074 (2020)
Allen, S., Cahn, J.: Ground state structures in ordered binary alloys with second neighbor interactions. Acta Metall. 20, 423–433 (1972)
Alsaedi, A., Ahmad, B., Kirane, M.: Maximum principle for certain generalized time and space fractional diffusion equations. Quart. Appl. Math. 73, 163–175 (2015)
Anderson, D., McFadden, G., Wheeler, A.: Diffuse-interface methods in fluid mechanics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30, 139–165 (1998)
Cahn, J., Hilliard, J.: Free energy of a nonuniform system. I. Interfacial free energy. J. Chem. Phys 28, 258–267 (1958)
Clarke, S., Vvedensky, D.: Origin of reflection high-energy electron-diraction intensity oscillations during molecular-beam epitaxy: a computational modeling approach. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 2235–2238 (1987)
Du, Q., Liu, C., Wang, X.: A phase field approach in the numerical study of the elastic bending energy for vesicle membranes. J. Comput. Phys. 198, 450–468 (2004)
Du, Q., Ju, L., Li, X., Qiao, Z.: Maximum principle preserving exponential time differencing schemes for the nonlocal Allen–Cahn equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 57, 875–898 (2019)
Du, Q., Yang, J., Zhou, Z.: Time-fractional Allen–Cahn equations: analysis and numerical methods. J. Sci. Comput. 85, 42 (2020)
Du, Q., Ju, L., Li, X., Qiao, Z.: Maximum bound principles for a class of semilinear parabolic equations and exponential time-differencing schemes. SIAM Rev. 57, 317–359 (2021)
Fan, E., Li, C.: Diffusion in Allen–Cahn equation: normal vs anomalous. Physica D 457, 133973 (2024)
Fritz, M., Lima, E., Nikolic, V., Oden, J., Wohlmuth, B.: Local and nonlocal phase-field models of tumor growth and invasion due to ECM degradation. Math. Models Meth. Appl. Sci. 29, 2433–2468 (2019)
Fritz, M., Rajendran, M., Wohlmuth, B.: Time-fractional Cahn–Hilliard equation: well-posedness, degeneracy, and numerical solutions. Comput. Appl. Appl. 188, 66–87 (2022)
Furihata, D.: A stable and conservative finite difference scheme for the Cahn–Hilliard equation. Numer. Math. 87, 675–699 (2001)
Gao, Z., Zhang, H., Qian, X., Song, S.: High-order unconditionally maximum-principle-preserving parametric integrating factor Runge–Kutta schemes for the nonlocal Allen–Cahn equation. Appl. Numer. Math. 194, 97–114 (2023)
Hawkins-Daarud, A., Zee, K., Oden, J.: Numerical simulation of a thermodynamically consistent four-species tumor growth model. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 8, 3–24 (2012)
Hou, D., Xu, C.: Highly efficient and energy dissipative schemes for the time fractional Allen–Cahn equation. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 43, A3305–A3327 (2021)
Hou, D., Xu, C.: A second order energy dissipative scheme for time fractional \(L^2\) gradient flows using SAV approach. J. Sci. Comput. 90, 25 (2022)
Hou, T., Tang, T., Yang, J.: Numerical analysis of fully discretized Crank–Nicolson scheme for fractional-in-space Allen–Cahn equations. J. Sci. Comput. 72, 1214–1231 (2017)
Hou, D., Zhu, H., Xu, C.: Highly efficient schemes for time-fractional Allen–Cahn equation using extended SAV approach. Numer. Algorithms 88, 1077–1108 (2021)
Huang, C., Stynes, M.: Optimal \(H^1\) spatial convergence of a fully discrete finite element method for the time-fractional Allen–Cahn equation. Adv. Comput. Math. 46, 63 (2020)
Ji, B., Liao, H., Zhang, L.: Simple maximum-principle preserving time-stepping methods for time-fractional Allen–Cahn equation. Adv. Comput. Math. 46, 37 (2020)
Ji, B., Liao, H., Gong, Y., Zhang, L.: Adaptive linear second-order energy-stable schemes for time-fractional Allen–Cahn equation with volume constrain. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 90, 105366 (2020)
Jia, J., Zhang, H., Xu, H., Jiang, X.: An efficient second order stabilized scheme for the two dimensional time fractional Allen–Cahn equation. Appl. Numer. Math. 165, 216–231 (2021)
Jin, B., Li, B., Zhou, Z.: Subdiffusion with time-dependent coefficients: improved regularity and second-order time stepping. Numer. Math. 145, 883–913 (2020)
Ju, L., Li, X., Qiao, Z.: Generalized SAV-exponential integrator schemes for Allen–Cahn type gradient flows. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 60, 1905–1931 (2022)
Li, D.: Energy-dissipation for time-fractional phase-field equations. Commun. Pure Appl. Anal. 21, 3371–3387 (2022)
Li, C., Cai, M.: Theory and Numerical Approximations of Fractional Integrals and Derivatives. SIAM, Philadelphia (2020)
Li, D., Wu, C., Zhang, Z.: Linearized Galerkin FEMs for nonlinear time fractional parabolic problems with non-smooth solutions in time direction. J. Sci. Comput. 80, 403–419 (2019)
Liao, H., McLean, W., Zhang, J.: A discrete Grönwall inequality with application to numerical schemes for subdiffusion problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 57, 218–237 (2019)
Liao, H., Tao, T., Zhou, T.: A second-order and nonuniform time-stepping maximum-principle preserving scheme for time-fractional Allen–Cahn equations. J. Comput. Phys. 414, 109473 (2020)
Liao, H., Tang, T., Zhou, T.: An energy-stable and maximum bound preserving scheme with variable time steps time fractional Allen–Cahn equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 43, A3503–A3526 (2021)
Liao, H., Zhu, X., Wang, J.: The variable-step L1 scheme preserving a compatible energy law for time-fractional Allen–Cahn equation. Numer. Math. Theory Methods Appl. 15, 1128–1146 (2022)
Liao, H., Liu, N., Lyu, P.: Discrete gradient structure of a second-order variable-step method for nonlinear integro-differential models. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 61, 2157–2181 (2023)
Liao, H., Zhu, X., Sun, H.: Asymptotically compatible energy and dissipation law of the nonuniform L2-1\(_\sigma \) scheme for time fractional Allen–Cahn model. J. Sci. Comput. 99, 46 (2024)
Liu, Z., Huang, X.. Li.. J..: Accurate and efficient algorithms with unconditional energy stability for the time fractional Cahn–Hilliard and Allen–Cahn equations. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 37, 2613–2633 (2021)
Liu, H., Cheng, A., Wang, H., Zhao, J.: Time-fractional Allen–Cahn and Cahn–Hilliard phase-field models and their numerical investigation. Comput. Math. Appl. 76, 1876–1892 (2018)
Ma, L., Chen, R., Yang, X., Zhang, H.: Numerical approximations for Allen–Cahn type phase field model of two-phase incompressible fluids with moving contact lines. Commun. Comput. Phys. 27, 867–889 (2017)
Olver, P.: Applications of Lie Groups to Differential Equations, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (1993)
Qin, H., Li, D., Zhang, Z.: A novel scheme to capture the initial dramatic evolutions of nonlinear subdiffusion equations. J. Sci. Comput. 89, 65 (2021)
Quan, C., Wang, B.: Energy stable L2 schemes for time-fractional phase-field equations. J. Comput. Phys. 458, 111085 (2022)
Quan, C., Tang, T., Yang, J.: How to define dissipation-preserving energy for time-fractional phase-field equations. CSIAM Trans. Appl. Math. 1, 478–490 (2020)
Quan, C., Tang, T., Wang, B., Yang, J.: A decreasing upper bound of energy for time-fractional phase-field equations. Commun. Comput. Phys. 33, 962–991 (2023)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: Numerical approximations of Allen–Cahn and Cahn–Hilliard equations. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 28, 1669–1691 (2010)
Shen, J., Xu, J., Yang, J.: The scalar auxiliary variable (SAV) approach for gradient flows. J. Comput. Phys. 353, 407–416 (2018)
Stynes, M., O’Riordan, E., Gracia, J.: Error analysis of a finite difference method on graded meshes for a time-fractional diffusion equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 5, 1057–1079 (2017)
Sun, Z., Gao, G.: Fractional Differential Equations: Finite Difference Methods. Secience Press, Beijing (2020)
Tang, T., Qiao, Z.: Efficient numerical methods for phase-field equations (in Chinese). Sci. Sin. Math. 50, 1–20 (2020)
Tang, T., Yang, J.: Implicit-explicit scheme for the Allen–Cahn equation preserves the maximum principle. J. Comput. Math. 34, 451–461 (2016)
Tang, T., Yu, H., Zhou, T.: On energy dissipation theory and numerical stability for time-fractional phase field equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 41, A3757–A3778 (2019)
van der Waals, J.: The thermodynamic theory of capillarity under the hypothesis of a continuous variation of density. J. Stat. Phys. 20, 200–244 (1979)
Xing, Z., Wen, L.: Numerical analysis of the nonuniform fast L1 formula for nonlinear time-space fractional parabolic equations. J. Sci. Comput. 95, 58 (2023)
Xu, X., Di, Y., Yu, H.: Sharp-interface limits of a phase-field model with a generalized Navier slip boundary condition for moving contact lines. J. Fluid Mech. 849, 805–833 (2018)
Yang, X.: Linear, first and second-order, unconditionally energy-stable numerical schemes for the phase field model of homopolymer blends. J. Comput. Phys. 327, 294–316 (2016)
Yang, Z., Zeng, F.: A linearly stabilized convolution quadrature method for the time-fractional Allen–Cahn equation. Appl. Math. Lett. 144, 108698 (2023)
Yao, C., Fan, H., Zhao, Y., Shi, Y., Wang, F.: Fast algorithm for nonlocal Allen–Cahn equation with scalar auxiliary variable approach. Appl. Math. Lett. 126, 107805 (2022)
Yu, Y., Zhang, J., Qin, R.: The exponential SAV approach for the time-fractional Allen–Cahn and Cahn–Hilliard phase-field models. J. Sci. Comput. 33, 94 (2023)
Zhang, H., Yan, J., Qian, X., Gu, X., Song, S.: On the preserving of the maximum principle and energy stability of high-order implicit-explicit Runge–Kutta schemes for the space-fractional Allen–Cahn equation. Numer. Algorithms 88, 1309–1336 (2021)
Zhang, G., Huang, C., Alikhanov, A., Yin, B.: A high-order discrete energy decay and maximum-principle preserving scheme for time fractional Allen–Cahn equation. J. Sci. Comput. 96, 39 (2023)
Zhao, J., Chen, L., Wang, H.: On power law scaling dynamics for time-fractional phase field models during coarsening. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 70, 257–270 (2019)
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12301508), Key Laboratory of Control of Power Transmission and Conversion (SJTU), Ministry of Education (Grant No. 2021AA02), and Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science foundation (No. 20224BCD41001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no Conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any study with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12301508) and Key Laboratory of Control of Power Transmission and Conversion (SJTU), Ministry of Education (Grant No. 2021AA02).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H., Hu, D., Huang, H. et al. Linearly Implicit Schemes Preserve the Maximum Bound Principle and Energy Dissipation for the Time-fractional Allen–Cahn Equation. J Sci Comput 101, 25 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-024-02667-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-024-02667-2