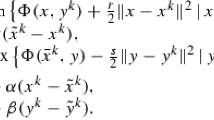Abstract
The convex–concave minimax problem, also known as the saddle-point problem, has been extensively studied from various aspects including the algorithm design, convergence condition and complexity. In this paper, we propose a generalized asymmetric forward–backward–adjoint algorithm (G-AFBA) to solve such a problem by utilizing both the proximal techniques and the extrapolation of primal-dual updates. Besides applying proximal primal-dual updates, G-AFBA enjoys a more relaxed convergence condition, namely, more flexible and possibly larger proximal stepsizes, which could result in significant improvements in numerical performance. We study the global convergence of G-AFBA as well as its sublinear convergence rate on both ergodic iterates and non-ergodic optimality error. The linear convergence rate of G-AFBA is also established under a calmness condition. By different ways of parameter and problem setting, we show that G-AFBA has close relationships with several well-established or new algorithms. We further propose an adaptive and a stochastic (inexact) versions of G-AFBA. Our numerical experiments on solving the robust principal component analysis problem and the 3D CT reconstruction problem indicate the efficiency of both the deterministic and stochastic versions of G-AFBA.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Notes
Recently, its weak convergence was established in [2] when \(\alpha >1/2\) and \(\tau \sigma L<4/(1+2\alpha ).\)
Note that (3.3) is equivalent to \( \theta (u)-\theta (\tilde{u}^{k})+\big \langle u-\tilde{u}^{k}, {\mathcal {J}}(\tilde{u}^{k})\big \rangle \ge (u-\tilde{u}^{k})^{\top }Q(u^{k}-\tilde{u}^{k})\).
References
Arrow, K., Hurwicz, L., Uzawa, H.: Studies in Linear and Non-linear Programming, Stanford Mathematical Studies in the Social Sciences, vol. II. Stanford University Press, Stanford (1958)
Banert, S., Upadhyaya,M., Giselsson, P.: The Chambolle–Pock method converges weakly with \(\theta >1/2\) and \(\tau \sigma \Vert L\Vert ^2<4/(1+2\theta )\) (2023). arXiv:2309.03998v1
Bai, J., Chang, X., Li, J., Xu, F.: Convergence revisit on generalized symmetric ADMM. Optimization 70, 149–168 (2021)
Bai, J., Hager, W., Zhang, H.: An inexact accelerated stochastic ADMM for separable convex optimization. Comput. Optim. Appl. 81, 479–518 (2022)
Bai, J., Jia, L., Peng, Z.: A new insight on augmented Lagrangian method with applications in machine learning. J. Sci. Comput. 99, 53 (2024)
Bai, J., Bian, F., Chang, X., Du, L.: Accelerated stochastic Peaceman–Rachford method for empirical risk minimization. J. Oper. Res. Soc. China 11, 783–807 (2023)
Bian, F., Liang, J., Zhang, X.: A stochastic alternating direction method of multipliers for non-smooth and non-convex optimization. Inverse Prob. 37, 075009 (2021)
Candes, E., Li, X., Ma, Y., Wright, J.: Robust principal component analysis? J. ACM 58, 1–37 (2011)
Chambolle, A., Pock, T.: A first-order primal-dual algorithm for convex problems with applications to imaging. J. Math. Imaging Vision 40, 120–145 (2011)
Chambolle, A., Pock, T.: On the ergodic convergence rates of a first-order primal-dual algorithm. Math. Program. 159, 253–287 (2016)
Chambolle, A., Ehrhardt, M., Richtarik, P., Schonlieb, C.: Stochastic primal-dual hybrid gradient algorithm with arbitrary sampling and imaging applications. SIAM J. Optim. 28, 2783–2808 (2018)
Chang, X., Yang, J., Zhang, H.: Golden ratio primal-dual algorithm with line search. SIAM J. Optim. 32, 1584–1613 (2022)
Chandrasekaran, V., Sanghavi, S., Parrilo, P., Willsky, A.: Rank-sparsity incoherence for matrix decomposition. SIAM J. Optim. 21, 572–596 (2011)
Condat, L.: A primal-dual splitting method for convex optimization involving Lipschitzian, proximable and linear composite terms. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 158, 460–479 (2013)
Condat, L., Kitahara, D., Contreras, A., Hirabayashi, A.: Proximal splitting algorithms for convex optimization: a tour of recent advances, with new twists. SIAM Rev. 65, 375–435 (2023)
Deng, W., Yin, W.: On the global and linear convergence of the generalized alternating direction method of multipliers. J. Sci. Comput. 66, 889–916 (2016)
Eckstein, J., Bertsekas, D.: On the Douglas–Rachford splitting method and the proximal point algorithm for maximal monotone operators. Math. Program. 55, 293–318 (1992)
Gabay, D., Mercier, B.: A dual algorithm for the solution of nonlinear variational problems via finite-element approximations. Comput. Math. Appl. 2, 17–40 (1976)
Gao, H.: Fast parallel algorithms for the X-ray transform and its adjoint. Med. Phys. 39, 7110–7120 (2012)
Goldstein, T., Li, M., Yuan, X.: Adaptive primal-dual splitting methods for statistical learning and image processing. NeurIPS, pp. 2089–2097 (2015)
Hayden, S., Stanley, O.: A low patch-rank interpretation of texture. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 6, 226–262 (2013)
He, B., Yuan, X.: On the \(o(1/n)\) convergence rate of the Douglas–Rachford alternating direction method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50, 700–709 (2012)
He, B., You, Y., Yuan, X.: On the convergence of primal-dual hybrid gradient algorithm. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 7, 2526–2537 (2014)
He, B., Ma, F., Xu, S., Yuan, X.: A generalized primal-dual algorithm with improved convergence condition for saddle point problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 15, 1157–1183 (2022)
He, B., Xu, S., Yuan, X.: On convergence of the Arrow–Hurwicz method for saddle point problems. J. Math. Imaging Vision 64, 662–671 (2022)
He, X., Huang, N., Fang, Y.: Non-ergodic convergence rate of an inertial accelerated primal-dual algorithm for saddle point problems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 140, 108289 (2024)
Huang, F., Chen, S.: Mini-batch stochastic ADMMs for nonconvex nonsmooth optimization (2019). arXiv: 1802.03284
Jiang, F., Cai, X., Wu, Z., Han, D.: Approximate first-order primal-dual algorithms for saddle point problems. Math. Comput. 90, 1227–1262 (2021)
Jiang, F., Wu, Z., Cai, X., Zhang, H.: A first-order inexact primal-dual algorithm for a class of convex-concave saddle point problems. Numer. Algor. 88, 1109–1136 (2021)
Jiang, F., Cai, X., Han, D.: Inexact asymmetric forward–backward–adjoint splitting algorithms for saddle point problems. Numer. Algor. 94, 479–509 (2023)
Jiang, F., Zhang, Z., He, H.: Solving saddle point problems: a landscape of primal-dual algorithm with larger stepsizes. J. Glob. Optim. 85, 821–846 (2023)
Korpelevič, G.: An extragradient method for finding saddle points and for other problems. Èkon. Mat. Metody 12, 747–756 (1976)
Latafat, P., Patrinos, P.: Asymmetric forward–backward–adjoint splitting for solving monotone inclusions involving three operators. Comput. Optim. Appl. 68, 57–93 (2017)
Li, Z., Yan, M.: New convergence analysis of a primal-dual algorithm with large stepsizes. Adv. Comput. Math. 47, 1–20 (2021)
Lions, P., Mercier, B.: Splitting algorithms for the sum of two nonlinear operators. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 16, 964–979 (1979)
O’Connor, D., Vandenberghe, L.: On the equivalence of the primal-dual hybrid gradient method and Douglas–Rachford splitting. Math. Program. 179, 85–108 (2020)
Polyak, B.: Some methods of speeding up the convergence of iteration methods. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phy. 4, 1–17 (1964)
Rockafellar, R.: Convex Analysis. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2015)
Robinson, S.: Some Continuity Properties of Polyhedral Multifunctions. Mathematical Programming at Oberwolfach, pp. 206–214. Springer, Berlin (1981)
Sun, H., Tai, X., Yuan, J.: Efficient and convergent preconditioned ADMM for the Potts models. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 43, B455–B478 (2021)
Tao, M., Yuan, X.: Recovering low-rank and sparse components of matrices from incomplete and noisy observations. SIAM J. Optim. 21, 57–81 (2011)
Vũ, B.: A splitting algorithm for dual monotone inclusions involving cocoercive operators. Adv. Comput. Math. 38, 667–681 (2013)
Wang, N., Li, J.: A class of preconditioners based on symmetric-triangular decomposition and matrix splitting for generalized saddle point problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 43, 2998–3025 (2023)
Xian, W., Huang, F., Zhang, Y., Huang, H.: A faster decentralized algorithm for nonconvex minimax problems. NeurIPS (2021). https://openreview.net/forum?id=rjIjkiyAJao
Xu, S.: A dual-primal balanced augmented Lagrangian method for linearly constrained convex programming. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 69, 1015–1035 (2023)
Xu, S.: A search direction inspired primal-dual method for saddle point problems. Optimization Online (2020). https://optimization-online.org/2019/11/7491/
Xu, Z., Zhang, H., Xu, Y., Lan, G.: A unified single-loop alternating gradient projection algorithm for nonconvex-concave and convex-nonconcave minimax problems. Math. Program. 201, 635–706 (2023)
Yang, J., Zhang, Y.: Alternating direction algorithms for \(\ell _1\)-problems in compressive sensing. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 33, 250–278 (2011)
Yang, L., Pong, T., Chen, X.: Alternating direction method of multipliers for a class of nonconvex and nonsmooth problems with applications to background/foreground extraction. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 10, 74–110 (2017)
Zhang, X., Burger, M., Osher, S.: A unified primal-dual algorithm framework based on Bregman iteration. J. Sci. Comput. 46, 20–46 (2011)
Zhu, M., Chan, T.: An Efficient Primal-Dual Hybrid Gradient Algorithm for Total Variation Image Restoration, CAM Report 08-34. UCLA, Los Angeles, CA (2008)
Zhu, Y., Liu, D., Dinh, Q.: New primal-dual algorithms for a class of nonsmooth and nonlinear convex–concave minimax problems. SIAM J. Optim. 32, 2580–2611 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous referees for providing very constructive comments, which have significantly improved the quality of the paper.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (12471298, 12171479), the Shaanxi Fundamental Science Research Project for Mathematics and Physics (23JSQ031), the National Social Science Fund of China (22BGL118), and the MOE Project of Key Research Institute of Humanities and Social Sciences (22JJD110001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any Conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, J., Chen, Y., Yu, X. et al. Generalized Asymmetric Forward–Backward–Adjoint Algorithms for Convex–Concave Saddle-Point Problem. J Sci Comput 102, 80 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-025-02802-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-025-02802-7
Keywords
- Saddle-point problem
- Asymmetric forward–backward–adjoint algorithm
- Convergence and complexity
- Image processing