Abstract
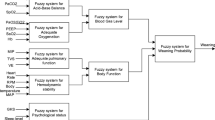
Weaning from mechanical ventilation represents one of the most challenging issues in management of critically ill patients. Currently used weaning predictors ignore many important dimensions of weaning outcome and have not been uniformly successful. A fuzzy logic inference system that uses nine variables, and five rule blocks within two layers, has been designed and implemented over mathematical simulations and random clinical scenarios, to compare its behavior and performance in predicting expert opinion with those for rapid shallow breathing index (RSBI), pressure time index and Jabour’ weaning index. RSBI has failed to predict expert opinion in 52% of scenarios. Fuzzy logic inference system has shown the best discriminative power (ROC: 0.9288), and RSBI the worst (ROC: 0.6556) in predicting expert opinion. Fuzzy logic provides an approach which can handle multi-attribute decision making, and is a very powerful tool to overcome the weaknesses of currently used weaning predictors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epstein, S. K., Weaning from ventilatory support. Curr Opin Crit Care. 15:36–43, 2009.
Epstein, S. K., Complications in ventilator supported patients. In: Tobin M. J., (Ed.), Principles and Practice of Mechanical Ventilation, Ch:41. New York: McGraw Hill, 877–902, 2006.
Budinger, G. R. S., and Tobin, M. J., Strategies for predicting successful weaning from mechanical ventilation. Lung Biol. Health Dis. 158:499–530, 2001.
Kollef, M. H., The prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 340:627–634, 1999.
Stauffer, J. E., Olson, D. E., and Petty, T. L., Complications and consequences of endotracheal intubation and tracheotomy. A prospective study of 150 critically ill patients. Am J Med. 70:65–76, 1981.
Weg, J. G., Anzueto, A., Balk, R. A., Wiedemann, H. P., Pattishall, E. N., and Schork, M. A., The relation of pneumothorax and other air leaks to mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 338:341–346, 1998.
Meade, M., Guyatt, G., and Cook, D., Predicting success in weaning from mechanical ventilation. Chest. 120 (6 Suppl)400S–424S, 2001.
Hess, D. R., Liberation from mechanical ventilation: weaning the patient or weaning old-fashioned ideas? Crit Care Med. 9:2154–2155, 2002.
Yang, K. L., and Tobin, M. J., A prospective study of indexes predicting the outcome of trials of weaning from mechanical ventilation. N Engl J Med. 324:1445–1450, 1991.
Vallverdu, I., Calaf, N., Subirana, M., Net, A., Benito, S., and Mancebo, J., Clinical characteristics, respiratory functional parameters, and outcome of a two-hour t-piece trial in patients weaning from mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 158:1855–1862, 1998.
Siner, J. M., and Manthous, C. A., Liberation from mechanical ventilation: what monitoring matters? Crit Care Clin. 23:613–638, 2007.
Hudson, D. L., and Cohen, M. E., Fuzzy systems. In: Hudson D. L., Cohen, M. E. (Ed.), Neural Networks and Artificial Intelligence for Biomedical Engineering Ch:16. New York: IEEE Press, 243–260, 2000.
Negnevitsky, M., Fuzzy expert systemsIn: Artificial Intelligence: A Guide to Intelligent Systems Ch:4Addison-Wesley, New York, pp. 87–129, 2005.
Epstein, S. K., and Ciubotaru, R. L., Independent effects of etiology of failure and time to reintubation on outcome for patients failing extubation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 158:489–493, 1998.
Brochard, L., Rauss, A., Benito, S., Conti, G., Mancebo, J., Rekik, N., Gasparetto, A., and Lemaire, F., Comparison of three methods of gradual withdrawal from ventilatory support during weaning from mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 150:896–903, 1994.
Esteban, A., Frutos, F., Tobin, M. J., Alia, I., Solsona, J. F., and Valverdu, I., A comparison of four methods of weaning patients from mechanical ventilation. N Engl J Med. 332:345–350, 1995.
Esteban, A., Alia, I., Tobin, M. J., Gil, A., Gordo, F., and Vallverdu, I., Effects of spontaneous breathing trial duration on outcome of attempts to discontinue mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 159:512–518, 1999.
Epstein, S. K., Ciubotaru, R. L., and Wong, J. B., Effect of failed extubation on the outcome of mechanical ventilation. Chest. 112:186–192, 1997.
Tahvanainen, J., Salmenpera, M., and Nikki, P., Extubation criteria after weaning from intermittent mandatory ventilation and continuous positive airway pressure. Crit Care Med. 11:702–707, 1983.
Slutsky, A. S., Mechanical ventilation. American College of Chest Physicians’ Consensus Conference. Chest. 104:1833–1859, 1993.
Mutlu, G. M., and Factor, P., Complications of mechanical ventilation. Respir Care Clin N Am. 6:213–252, 2000.
Epstein, S. K., Endotracheal extubation. Respir Care Clin N Am. 6:321–360, 2000.
Jubran, A., and Tobin, M. J., Pathophysiologic basis of acute respiratory distress in patients who fail a trial of weaning from mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 155:906–915, 1997.
Jubran, A., Mathru, M., Dries, D., and Tobin, M. J., Continuous recordings of mixed venous oxygen saturation during weaning from mechanical ventilation and the ramifications thereof. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 158:1763–1769, 1998.
Kilic, Y. A., Yorganci, K., and Sayek, I., Visualizing multiple organ failure: a method for analysing temporal and dynamic relations between failing systems and interventions. Crit Care. 11:417–418, 2007.
Saliba, S., Kilic, Y. A., and Uranues, S., Chaotic nature of sepsis and multiple organ failure cannot be explained by linear statistical methods. Crit Care. 12:417, 2008.
Kahraman, C., Multi-criteria decision making methods and fuzzy setsIn: Fuzzy Multi-criteria Decision Making: Theory and Applications with Recent DevelopmentsSpringer, Berlin, pp. 1–18, 2008.
Kerstholt, J. H., and Raaijmakers, J. G. W., Decision making in dynamic task environmentsIn: Decision Making: Cognitive Models and ExplanationsRoutledge, Evanston, pp. 205–217, 1997.
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank Prof. Dr. Inan Guler, for his invaluable inputs in the preliminary discussion of the subject.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix 1. Calculation of conventional weaning predictors
Appendix 1. Calculation of conventional weaning predictors
-
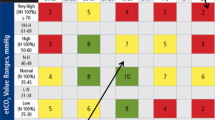
Rapid Shallow Breathing Index has been calculated as
$${\text{RSBI}} = {f_{{\text{S}}} } \mathord{\left/{\vphantom {{f_{{\text{S}}} } {{\text{TV}}_{{\text{S}}} }}} \right.\kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {{\text{TV}}_{{\text{S}}} }$$ -
Pressure Time Index has been calculated as
$${\text{PTI}} = {\left( {{P_{{{\text{breath}}}} } \mathord{\left/{\vphantom {{P_{{{\text{breath}}}} } {{\text{NIP}}}}} \right.\kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {{\text{NIP}}}} \right)} \times {\left( {{T_{{\text{I}}} } \mathord{\left/{\vphantom {{T_{{\text{I}}} } {T_{{{\text{TOT}}}} }}} \right.\kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {T_{{{\text{TOT}}}} }} \right)}$$where
$$P_{{{\text{breath}}}} = {\left( {P_{{{\text{peak}}}} - {\text{PEEP}}} \right)} \times {\left( {{{\text{TV}}_{{\text{S}}} } \mathord{\left/{\vphantom {{{\text{TV}}_{{\text{S}}} } {{\text{TV}}_{{\text{M}}} }}} \right.\kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {{\text{TV}}_{{\text{M}}} }} \right)}$$ -
Jabour’ Weaning Index has been calculated as
$${\text{JWI}} = {\text{PTI}} \times {\left( {{{\text{VE}}_{{40}} } \mathord{\left/{\vphantom {{{\text{VE}}_{{40}} } {{\text{TV}}_{{\text{M}}} }}} \right.\kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {{\text{TV}}_{{\text{M}}} }} \right)}$$where
$${\text{VE}}_{{40}} = {\left( {f_{{\text{M}}} \times {\text{TV}}_{{\text{M}}} } \right)} \times {\left( {{{\text{PaCO}}_{{\text{2}}} } \mathord{\left/{\vphantom {{{\text{PaCO}}_{{\text{2}}} } {40}}} \right.\kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {40}} \right)}$$
- P breath :
-
Avarage inspiratory muscle pressure per breath
- NIP:
-
Negative inspiratory pressure
- T I :
-
Inspiratory time
- T TOT :
-
Total breath duration
- P peak :
-
Peak airway pressure
- PEEP:
-
Positive end expiratory pressure
- TVS :
-
Tidal volume on spontaneous breathing
- TVM :
-
Tidal volume on mechanical ventilation
- VE40 :
-
Estimate of minute volume required to achieve a PCO2 of 40 mmHg
- f M :
-
Frequency on mechanical ventilation
- f S :
-
Frequency on spontaneous ventilation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilic, Y.A., Kilic, I. A Novel Fuzzy Logic Inference System for Decision Support in Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation. J Med Syst 34, 1089–1095 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-009-9327-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-009-9327-0