Abstract
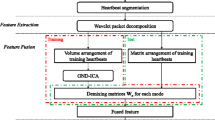
The classification of heartbeats is crucial to identify an arrhythmia. This paper proposes a new method that combines independent component analysis (ICA) with sparse representation-based classification (SRC) to distinguish eight types of heartbeats. We use ICA to extract useful features from heartbeats. A feature vector consists of 100 ICA features along with a RR interval. We use SRC to compute a sparse representation of a test feature vector with respect to all training feature vectors. The type of a test feature vector is determined using the concentration degree of sparse coefficients on each heartbeat type. For experimental purposes, 9800 heartbeats are extracted from the MIT-BIH electrocardiogram (ECG) database. The results show that our proposed method performs better than conventional methods, with 98.35% accuracy and 94.49%–100% sensitivities to several heartbeat types.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Chazal, P., O’Dwyer, M., and Reilly, R. B., Automatic classification of heartbeats using ECG morphology and heartbeat interval features. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51(7):1196–1206, 2004.
Osowski, S., and Linh, T. H., ECG beat recognition using fuzzy hybrid neural network. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 48(11):1265–1271, 2001.
Yeh, Y. C., Wang, W. J., and Chiou, C. W., Feature selection algorithm for ECG signals using range-overlaps method. Expert. Syst. Appl. 37:3499–3512, 2010.
Minhas, F. A., and Arif, M., Robust electrocardiogram (ECG) beat classification using discrete wavelet transform. Physiol. Meas. 29:555–570, 2008.
Yu, S. N., and Chen, Y. H., Electrocardiogram beat classification based on wavelet transformation and probabilistic beural network. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 28(10):1142–1150, 2007.
Yu, S. N., and Chou, K. T., Integration of independent component analysis and neural networks for ECG beat classification. Expert. Syst. Appl. 34:2841–2846, 2008.
Yu, S. N., and Chou, K. T., Selection of significant independent components for ECG beat classification. Expert. Syst. Appl. 36:2088–2096, 2009.
Jiang, X., Zhang, L. Q., Zhao, Q. B., and Albayrak, S., ECG arrhythmias recognition system based on independent component analysis feature extraction. TENCON 2006. 2006 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Hong Kong, China, 1–4, 2006.
Osowski, S., Linh, T. H., and Markiewcz, T., Support vector machine-based expert system for reliable heartbeat recognition. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51:582–589, 2004.
Yeh, Y. C., Wang, W. J., and Chiou, C. W., Cardiac arrhythmia diagnosis method using linear discriminant analysis on ECG signals. Measurement 42:778–789, 2009.
Christov, I., Jekova, I., and Bortolan, G., Premature ventricular contractionsclassification by the Kth nearest-neighbours rule. Physiol. Meas. 26:123–130, 2005.
Güler, İ., and Übeyli, E. D., A modified mixture of experts network structure for ECG beats classification with diverse features. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 18:845–856, 2005.
Güler, İ., and Übeyli, E. D., ECG beat classifier designed by combined neural network model. Pattern Recognit. 38:199–208, 2005.
Übeyli, E. D., Combining recurrent neural networks with eigenvector methods for classification of ECG beats. Digit. Signal Process. 19:320–329, 2009.
Acir, N., A support vector machine classifier algorithm based on a perturbation method and its application to ECG beat recognition systems. Expert. Syst. Appl. 31:150–158, 2006.
Übeyli, E. D., ECG beats classification using multiclass support vector machines with error correcting output codes. Digit. Signal Process. 17:675–684, 2007.
Übeyli, E. D., Usage of eigenvector methods in implementation of automated diagnostic systems for ECG beats. Digit. Signal Process. 18:33–48, 2008.
Donoho, D., For most large underdetermined systems of linear equations the minimal l 1-norm solution is also the sparsest solution. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 59(6):797–829, 2006.
Candès, E., Romberg, J., and Tao, T., Stable signal recovery form incomplete and inaccurate measurements. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 59(8):1207–1223, 2006.
Candès, E., and Tao, T., Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: universal encoding strategies? IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(12):5406–5425, 2006.
Wright, J., Yang, A. Y., Ganesh, A., Sastry, S. S., and Ma, Y., Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. PAMI. 31(2):210–227, 2009.
Comon, P., Independent component analysis, A new concept? Signal Process. 36:287–314, 1994.
Hyvärinen, A., and Oja, E., Independent component analysis: algorithms and application. Neural Netw. 13(4–5):411–430, 2000.
Mark, R., and Moody, G., MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database, available online: http://www.physionet.org/physiobank/database/mitdb/, 1997.
Hyvärinen, A., Fast and robust fixed-point algorithms for independent component analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural. Netw. 10(3):626–634, 1999.
Amaldi, E., and Kann, V., On the approximability of minimizing nonzero variables or unsatisfied relations in linear systems. Theor. Comput. Sci. 209:237–260, 1998.
Figueiredo, M. A. T., Nowak, R. D., and Wright, S. J., Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction: application to compressed sensing and other inverse problem. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signa. 1:586–597, 2007.
Candès, E. J., and Wakin, M. B., An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 25(2):21–30, 2008.
Baraniuk, R. G., Compressive sensing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 24(4):118–121, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H.F., Hu, G.S. & Zhu, L. Sparse Representation-Based Heartbeat Classification Using Independent Component Analysis. J Med Syst 36, 1235–1247 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9585-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9585-x