Abstract
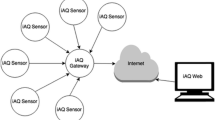
Indoor air quality monitoring in healthcare environment has become a critical part of hospital management and policy. Manual air sampling and analysis are cost-inhibitive and do not provide real-time air quality data and response measures. In this month-long study over 14 sampling locations in a public hospital in Taiwan, we observed a positive correlation between CO2 concentration and population, total bacteria, and particulate matter concentrations, thus monitoring CO2 concentration as a general indicator for air quality could be a viable option. Consequently, an intelligent environmental monitoring system consisting of a CO2/temperature/humidity sensor, a digital plug, and a ZigBee Router and Coordinator was developed and tested. The system also included a backend server that received and analyzed data, as well as activating ventilation and air purifiers when CO2 concentration exceeded a pre-set value. Alert messages can also be delivered to offsite users through mobile devices.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, X., Bi, X., Chen, D., Sheng, G., and Fu, J., Hospital indoor respirable particles and carbonaceous composition. Build. Environ. 41:992–1000, 2006.
Wang, X., Bi, X., Sheng, G., and Fu, J., Hospital indoor PM10/PM2.5 and associated trace elements in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 366:124–135, 2006.
Scaltriti, S., Cencetti, S., Rovesti, S., Marchesi, I., Bargellini, A., and Borella, P., Risk factors for particulate and microbial contamination of air in operating theatres. J. Hosp. Infect. 66:320–326, 2007.
Lu, H., Wen, S., Feng, Y., Wang, X., Bi, X., Sheng, G., and Fu, J., Indoor and outdoor carbonyl compounds and BTEX in the hospitals of Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 368:574–584, 2006.
Chen, H. W., Chung, C. Y., and Li, H. T., Indoor air distribution of nitrogen dioxide and ozone in urban hospitals. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 83:147–150, 2009.
Ortiz, G., Yague, G., Segovia, M., and Catalan, V., A study of air microbe levels in different areas of a hospital. Curr. Microbiol. 59:53–58, 2009.
Dharan, S., and Pittet, D., Environmental controls in operating theatres. J. Hosp. Infect. 51:79–84, 2002.
Leung, M., and Chan, A. H. S., Control and management of hospital indoor air quality. Med. Sci. Monit. 12:SR17–SR23, 2006.
Anttila, V. J., Nihtinen, A., Kuutamo, T., and Richardson, M., Air quality monitoring of HEPA-filtered hospital rooms by particulate counting. J. Hosp. Infect. 71:387–388, 2009.
Hathway, E. A., Noakes, C. J., Sleigh, P. A., and Fletcher, L. A., CFD simulation of airborne pathogen transport due to human activities. Build. Environ. 46:2500–2511, 2011.
Ho, S. H., Rosario, L., and Rahman, M. M., Three-dimensional analysis for hospital operating room thermal comfort and contaminant removal. Appl. Therm. Eng. 29:2080–2092, 2009.
Wan, G. W., Chung, F. F., and Tang, C. S., Long-term surveillance of air quality in medical center operating rooms. Am. J. Infect. Control 39:302–308, 2011.
Holcátová, I., Beneová, V., and Hartlová, D., Comparison of the environment in operating theatres in two hospitals. Indoor Built Environ. 12:121–124, 2003.
Kuehn, T. H., Airborne infection control in health care facilities. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 125:366–371, 2003.
Lin, J., Pai, J. Y., and Chen, C. C., Applied patent RFID systems for building reacting HEPA air ventilation system in hospital operation rooms. J. Med. Syst. 36:3399–3405, 2012.
Yu, C., Cui, Y.Z., Zhang, L., Yang, S.Q., Zigbee wireless sensor network in environmental monitoring applications. In Proc. of the 5th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, pp 1–5, 2009.
Zhang, Y., Xiong, P., Luo, Y., Li, L., Design of remote home environment monitoring and health care monitoring system based on data confusion. In Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, pp 35–39, 2011.
Bhunia, S.S., Roy. S., Mukherjee, N., IEMS: Indoor environment monitoring system using Zigbee wireless sensor network. In Proc. of the International Conference on Communication, Computing and Security, pp 142–145, 2011.
Ohura, T., Amagai, T., Shen, X., Li, S., Zhang, P., and Zhu, L., Comparative study on indoor air quality in Japan and China: Characteristics of residential indoor and outdoor VOCs. Atmos. Environ. 43:6352–6359, 2009.
Fleischer, M., Bober-Gheek, B., Bortkiewicz, O., and Rusiecka-Ziólkowska, J., Microbiological control of airborne contamination in hospitals. Indoor Build Environ. 15:53–56, 2006.
Obbard, J. P., and Fang, L. S., Airborne concentrations of bacteria in a hospital environment in Singapore. Water Air Soil Pollut. 144:333–341, 2003.
Tang, C. S., Chung, F. F., Lin, M. C., and Wan, G. W., Impact of patient visiting activities on indoor climate in a medical intensive care unit: a 1-year longitudinal study. Am. J. Infect. Control 37:183–188, 2009.
Napoli, C., Marcotrigiano, V., and Montagna, M. T., Air sampling procedures to evaluate microbial contamination: a comparison between active and passive methods in operating theatres. BMC Pub. Health 12:594, 2012.
Napoli, C., Tafuri, S., Montenegro, L., Cassano, M., Notarnicola, A., Lattarulo, S., Montagna, M. T., and Moretti, B., Air sampling methods to evaluate microbial contamination in operating theatres: results of a comparative study in an orthopaedics department. J. Hosp. Infect. 80:128–132, 2012.
Galvin, S., Dolan, A., Cahill, O., Daniel, S., and Humphrey, H., Microbial monitoring of the hospital environment: why and how? J. Hosp. Infect. 82:143–151, 2012.
Huang, P. Y., Shi, Z. Y., Chen, C. H., Den, W., Huang, H. M., and Tsai, J. J., Airborne and surface-bound microbial contamination in two intensive care units of a medical center in central Taiwan. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 13:1060–1069, 2013.
Li, C. S., and Hou, P. A., Bioaerosol characteristics in hospital clean rooms. Sci. Total Environ. 305:169–176, 2003.
Sudharsanam, S., Srikanth, P., Sheela, M., and Steinberg, R., Study of the indoor air quality in hospitals in Chennai, India - microbial profile. Indoor Built Environ. 17:435–441, 2008.
Acknowledgments
The research is funded in part by the following sources: i) the collaborating research program between Tunghai University and the Taichung Veteran General Hospital (TCVGH) through project grant TCVGH-T997806, ii) Tunghai University’s The U-Care ICT Integration Platform for the Elderly, No. 101GREEnS004-2, and iii) the National Science Council under grant numbers NSC 101-2218-E-029-004 and NSC 101- 2221-E-029-014. The authors are grateful to Dr. Sung-Yuan Hu and Dr. Yu-Tse Tsan of the TCVGH for their suggestion and facilitation of the air sampling work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, CT., Liao, CJ., Liu, JC. et al. Construction and Application of an Intelligent Air Quality Monitoring System for Healthcare Environment. J Med Syst 38, 15 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-014-0015-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-014-0015-3