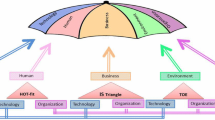
Abstract
The investments and costs of infrastructure, communication, medical-related equipments, and software within the global healthcare ecosystem portray a rather significant increase. The emergence of this proliferation is then expected to grow. As a result, information and cross-system communication became challenging due to the detached independent systems and subsystems which are not connected. The overall model fit expending over a sample size of 320 were tested with structural equation modelling (SEM) using AMOS 20.0 as the modelling tool. SPSS 20.0 is used to analyse the descriptive statistics and dimension reliability. Results of the study show that system utilisation and system impact dimension influences the overall level of services of the healthcare providers. In addition to that, the findings also suggest that systems integration and security plays a pivotal role for IT resources in healthcare organisations. Through this study, a basis for investigation on the need to improvise the Malaysian healthcare ecosystem and the introduction of a cloud computing platform to host the national healthcare information exchange has been successfully established.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakshi SMH, M. S., A study on hospital information system at a tertiary teaching. Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology 12(10), 2012.
Duan, W., Gu, B., and Whinston, A. B., Informational cascades and software adoption on the internet: an empirical investigation. MIS Quarterly 33(1), 2009.
Ismail NI, Abdullah NH An Overview of Hospital Information System (HIS) Implementation In Malaysia. In: 3rd International Conference On Business & Economic Research (3rd ICBER 2012), 2010. pp 1176–1182
Facts, H., Ministry of health Malaysia. Lumpur, Kuala, 2012.
Zhang, J., Patel, V. L., and Johnson, T. R., Medical error: is the solution medical or cognitive? J Am Med Inform Assoc 6(1):75–77, 2002.
Ratnam, K. A., Accelerating MSC telehealth flagship application through adoption of knowledge anagement: making medical knowledge available with windows communication foundation. KMICE, Penang, 2008.
Lee, H. W., Thurasamy, R., and Zakaria, N., External factors in hospital information system (HIS) adoption model: a case on Malaysia. Journal of Medical Systems 36(4):2129–2140, 2012.
Deborah, B., Healthy transformation. Intel Corporation, San Francisco, 2011.
Gartner Inc, Top 10 predictions. Gartner Inc, Orlando, 2009.
Cruickshank, B., The cloud changing the business ecosystem. KPMG International Inc, Amstelveen, 2011.
Ton, A. M. S., Cynthia, L., and Ken, T., Back to the future of IT adoption and evaluation in healthcare. International Journal of Healthcare Technology and Management 85(109):85–109, 2011.
Thiri N, Zainuddin Y, Zailani S Determinants of Information System Adoptions in Private Hospitals in Malaysia. In: Information and Communication Technologies: From Theory to Applications, 2008. ICTTA 2008. 3rd International Conference on, 7–11 April 2008. pp 1–2. doi:10.1109/ICTTA.2008.4529931
Horowitz BT (2011) Cloud Computing Brings Challenges for Health Care Data Storage, Privacy. E-Week.
Terry K (2012) Cloud Computing In Healthcare: The Question Is Not If, But When. FierceHealthIT
Chen, Y.-Y., Lu, J.-C., and Jan, J.-K., A secure EHR system based on hybrid clouds. Journal of Medical Systems 36(5):3375–3384, 2012. doi:10.1007/s10916-012-9830-6.
Muir E (2011) Challenges of cloud computing in healthcare integration. ZDNET.
Low, C., and Chen, Y., Criteria for the evaluation of a cloud-based hospital information system outsourcing provider. Journal of Medical Systems 36(6):3543–3553, 2012. doi:10.1007/s10916-012-9829-z.
J Craig M Cloud Computing: Opportunities and Challenges for Australia. In, 2010. The australian academy of Technological sciences and engineering (aTse),
Elsami, S. K., and Abu Hanna, A., The impact of ComputerisedPhysician order entry in hospitalized patients - a systematic review. International Journal of Medical Informatics 77(6):365–376, 2008.
Fernández-Cardeñosa, G., Torre-Díez, I., López-Coronado, M., and Rodrigues, J. P. C., Analysis of cloud-based solutions on EHRs systems in different scenarios. Journal of Medical Systems 36(6):3777–3782, 2012. doi:10.1007/s10916-012-9850-2.
Weston R, Gore Jr. PA (September 2006) A Brief Guide to Structural Equation Modelling. The Counseling Psychologist
Steiger, J. H., Structural model evaluation & modification: an interval estimation approach. Multivariate Behavioural Research 25:173–180, 1990.
Bollen, K. A., and Long, J. S., Testing structural equation models. Sage Publications, New York, 1993.
Byrne, B. M., Structural equation modeling with EQS and EQS/windows. Publications Sage, New York, 1994.
Schumacker, R. E., and Lomax, R. G., A Beginner’s guide to structural equation modeling, Second editionth edition. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey, 2004.
Schulz, W., Ainley, J., and Fraillon, J., ICCS 2009 technical report. International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA), Amsterdam, 2011.
Fornell C, Larcker DF (1981) Evaluating Structural Equation Models With Unobservable Variables & Measurement Error. Journal of Marketing Research:39–50
Carlson KD, Herdman AO (2010) Understanding the Impact of Convergent on Research Results. Organisational Research Methods:17–32
Chin WW, Gopal A, Salisbury WD (1997) Advancing the Theory of Adaptive Structuration: The Development of a Scale to Measure Faithfulness of Appropriation. Information Systems Research:342–367
Gefen, D., Straub, D. W., and Boudreau, M.-C., Structural equation modelling and regression: guidelines for research practice. Communications of the Association for Information Systems 4(7):1–70, 2000.
Bentler PM, Bonett DG (1980) Significant tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychological Bulletin
Hair, J. F., Black, B. C., and Babin, B. J., Multivariate data analysis, 6th edition. Pearson International, London, 2006.
Buhi, E. R., Goodson, P., and Neilands, T. B., Structural equation modeling: a primer for health behavior researchers. American Journal of Health Behavior 31(1):74–85, 2007.
Lovis C (2011) Clinical information systems: cornerstone for an efficient hospital management. Journal of Health Information Technology:69–75
Zarour, K., A coherent architectural framework for the development of hospital information systems. Journal of Applied Medical Informatics 31(4):33–41, 2012.
Crounse, B., Improving efficiency in healthcare. Incorporated Microsoft, Washington, 2010.
Nepal S, Zic J, Jaccard F (2007) A Trusted System for Sharing Patient Electronic Medical Records in Autonomous Distributed Health Care Systems. International Journal of Healthcare Information Systems and Informatics (IJHISI):18–33
Montazemi, A. R., Pittaway, J. J., and Keshavjee, K., State of integration in the context of patient-centered care: a network analysis and research directions. International Journal of Healthcare Information Systems and Informatics 6:11–19, 2011.
Wickramasinghe, N., The competitive forces facing E-health. Int J of Healthcare Information Systems and Informatics 1(4):68–81, 2006.
Sobol, M., Adoption, usage and efficiency: benchmarking healthcare IT in private practices. International Journal of Healthcare Information Systems and Informatics (IJHISI) 6:15–30, 2011.
Reddy, M. C., Bardram, J., and Bardram, P., CSCW research in healthcare: past, present, and future. Microsoft Research Inc, Washington, 2010.
Hecle, R. R., and Lutters, W. G., Tensions of network security and collaborative work practice: understanding a single sign-on deployment in a regional hospital. International Journal of Medical Informatics 80(8):49–61, 2011.
Sekhri, N. K., Managed care transactions. Streamling the Refferal Process, World Health Organisation, 2010.
Ransom G (2012) Insurance ‘prior authorisation’ wastes time, money. The Baltimore Sun
Tuppin P (2010) French national health insurance information system and the permanent beneficiaries sample. Journal of Epidemiology and Public Health:286–290
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support and generosity of The Ministry of Health Malaysia for providing input towards the survey, without which the present study could not be completed. Many thanks goes to the respondents who participated in this survey.
Statement on conflict of interest
The authors whose names are listed immediately below certify that they have NO affiliations with or involvement in any organisation or entity with any financial interest.
Authors contributions
Kalai Anand Ratnam (Main Author): Design, developing, analyzing, interpreting and drafting article.
Dr P. D. D. Dominic: Revising parts of the article including conclusion, final approval.
Prof. T. Ramayah: Refining the fitness of the Structural Equation Model, final approval.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ratnam, K.A., Dominic, P.D.D. & Ramayah, T. A Structural Equation Modeling Approach for the Adoption of Cloud Computing to Enhance the Malaysian Healthcare Sector. J Med Syst 38, 82 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-014-0082-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-014-0082-5