Abstract
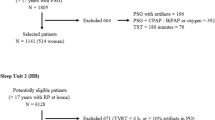
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a relatively common disease in the general population. Patients with OSA have a high risk of various comorbid medical diseases. Polysomnography (PSG) is the current gold standard for diagnosing OSA but is time consuming and expensive. This study aims to identify a sensitive screening parameter that can be used by clinicians to determine the time of referral for PSG examination in Taiwan. Eighty-seven patients, including 67 males and 20 females, were included in this study. We divided the patients into two groups: training data (n = 58) and testing group (n = 29). Pearson χ 2 test was used to perform bivariate analysis, and a decision tree was used to build a model. The decision model selected the frequency of desaturation > 4% per hour (DI4) as the indicator of OSA influence. The testing data accuracy of the C4.5 decision tree was 82.80%. External data were also used to validate the model reliability. The accuracy of the external data was 95.96%. Approximately one-third of patients with DI4 between 11 and 33 suffered from OSA. This population requires further diagnosis. Oximetry is an important and widely available screening method in Taiwan. This study proposes the need for PSG referral if DI4 is between 11 and 33.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrishami, A., Khajehdehi, A., and Chung, F., A systematic review of screening questionnaires for obstructive sleep apnea. Can. J. Anaesth. 57:423–38, 2010.
Bagai, K., Obstructive sleep apnea, stroke, and cardiovascular diseases. Neurologist 16:329–339, 2010.
Böhning, N., Schultheiss, B., Eilers, S., Penzel, T., Böhning, W., and Schmittendorf, E., Comparability of pulse oximeters used in sleep medicine for the screening of OSA. Physiol. Meas. 31:875–88, 2010.
Buchner, N. J., Quack, I., Stegbauer, J., Woznowski, M., Kaufmann, A., and Rump, L. C., Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea reduces arterial stiffness. Sleep. Breath. 16:123–133, 2011.
Chao C. M., Yu Y. W., Cheng B. W., Kuo Y. L., Construction the Model on the Breast Cancer Survival Analysis Use Support Vector Machine, Logistic Regression and Decision Tree. J Med Syst 38, 2014 10.1007/s10916-014-0106-1.
Chen L. F., Su C. T., Chen K. H., Wang P. C., Particle Swarm Optimization for Feature Selection with Application in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Diagnosis. Neural Comput Appl. 2011 10.1007/s00521-011-0632-4
Chen, N. H., Chen, M. C., Li, H. Y., Chen, C. W., and Wang, P. C., A two-tier screening model using quality-of-life measures and pulse oximetry to screen adults with sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep. Breath. 15:447–454, 2011.
Chuang, L. Y., Chang, H. W., and Yang, C. H., Improved binary PSO for feature selection using gene expression data. Comput. Biol. Chem. 32(1):29–38, 2008.
Collop, N. A., Tracy, S. L., Kapur, V., Mehra, R., Kuhlmann, D., Fleishman, S. A., and Ojile, J. M., Obstructive sleep apnea devices for out-of-center (OOC) testing: Technology evaluation. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 7:531–48, 2011.
Cruz, I. A. C., Drummond, M., and Winck, J. C., Obstructive sleep apnea symptoms beyond sleepiness and snoring: Effects of nasal APAP therapy. Sleep. Breath. 16:361–366, 2011.
De Silva, S., Abeyratne, U. R., and Hukins, C., Impact of gender on snore-based obstructive sleep apnea screening. Physiol. Meas. 33:587–601, 2012.
Dudenbostel, T., and Calhoun, D. A., Resistant hypertension, obstructive sleep apnoea and aldosterone. J. Hum. Hypertens. 26:281–287, 2011.
Gabbay, I. E., and Lavie, P., Age- and gender-related characteristics of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep. Breath. 16:453–460, 2012.
Gantner, D., Ge, J. Y., Li, L. H., Antic, N., Windler, S., Wong, K., Heeley, E., Huang, S. G., Cui, P., Anderson, C., Wang, J. G., and McEvoy, D., Diagnostic accuracy of a questionnaire and simple home monitoring device in detecting obstructive sleep apnoea in a Chinese population at high cardiovascular risk. Respirology 15:952–960, 2010.
Gliklich, R. E., and Wang, P. C., Validation of the snore outcomes survey for patients with sleep-disordered breathing. Arch Otolaryng - Head Neck 128:819–824, 2002.
Gouveris, H., Selivanova, O., Bausmer, U., Goepel, B., and Mann, W., First-night-effect on polysomnographic respiratory sleep parameters in patients with sleep-disordered breathing and upper airway pathology. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-L 267:1449–1453, 2010.
Gurubhagavatula I., Maislin G., An algorithm to stratify sleep apnea risk in a sleep disorders clinic population. Am J Resp Crit Care 1s70:371–376, 2001
Hwang, S. H., Gender-wise analysis of the cephalometric factors affecting obstructive sleep apnea. Korean. J. Orthod. 41:164–173, 2011.
Ip, M. S., Lam, B., Ng, M. M., Lam, W. K., Tsang, K. W., and Lam, K. S., Obstructive sleep apnea is independently associated with insulin resistance. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 165:670–676, 2002.
Jacob, S. V., Morielli, A., Mograss, M. A., Ducharme, F. M., Schloss, M. D., and Brouillette, R. T., Home testing for pediatric obstructive sleep apnea syndrome secondary to adenotonsillar hypertrophy. Pediatr. Pulm. 20:241–252, 1995.
Jayaraman, G., Majid, H., Surani, S., Kao, C., and Subramanian, S., Influence of gender on continuous positive airway pressure requirements in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep. Breath. 15:781–784, 2011.
John, B. D., Linda, M. S., and Brien, P. E., Predicting sleep apnea and excessive day sleepiness in the severely obese. Chest 123:1134–1141, 2003.
Kapsimalis, F., and Kryger, M. H., Gender and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep 25:497–504, 2002.
Lahsasna, A., Ainon, R. N., Zainuddin, R., and Bulgiba, A., Design of a fuzzy-based decision support system for coronary heart disease diagnosis. J. Med. Syst. 36:3293–3306, 2012.
Lee D. G., Ryu K. S., Bashir M., J. Bae W., Ryu K. H., Discovering Medical Knowledge using Association Rule Mining in Young Adults with Acute Myocardial Infarction. J Med Syst 37, 2013 10.1007/s10916-012-9896-1.
Lee, R. W. W., Sutherland, K., and Cistulli, P. A., Craniofacial morphology in obstructive sleep apnea. Clin. Pulm. Med. 17:189–195, 2010.
Malbois, M., Giusti, V., Suter, M., Pellaton, C., Vodoz, J. F., and Heinzer, R., Oximetry alone versus portable polygraphy for sleep apnea screening before bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 20:326–31, 2010.
Marin, J. M., Agusti, A., Villar, I., Forner, M., Nieto, D., Carrizo, S. J., Barbé, F., Vicente, E., Wei, Y., Nieto, J., and Jelic, S., Association between treated and untreated obstructive sleep apnea and risk of hypertension. JAMA-J. Am. Med. ASSOC. 307:2169–2176, 2012.
Patil, B. M., Joshi, R. C., Toshniwal, D., and Biradar, S., A New approach: Role of data mining in prediction of survival of burn patients. J. Med. Syst. 35:1531–1542, 2011.
Polat, K., Yosunkaya, Ş., and Güneş, S., Comparison of different classifier algorithms on the automated detection of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J. Med. Syst. 32:243–250, 2008.
Quinlan, J. R., Programs for machine learning. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, 1993.
Rofail, L. M., Wong, K. K., Unger, G., Marks, G. B., and Grunstein, R. R., Comparison between a single-channel nasal airflow device and oximetry for the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 33:1106–14, 2010.
Rosenthal, L. D., and Diana, D. C., The Epworth sleepiness scale in the identification of obstructive sleep apnea. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 196:429–431, 2008.
Ryan, P. J., Hilton, M. F., Boldy, D. A., Evans, A., Bradbury, S., Sapiano, S., Prowse, K., and Cayton, R. M., Validation of British thoracic society guidelines for the diagnosis of the sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome: can polysomnography be avoided? Thorax 50:972–975, 1995.
Saldías, P. F., Jorquera, A. J., and Díaz, P. O., Predictive value of clinical features and nocturnal oximetry for the detection of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Rev. Med. Chil. 138:941–50, 2010.
Schafer, H., Ewig, S., Hasper, E., and Luderitz, B., Predictive diagnostic value of clinical assessment and nonlaboratory monitoring system recordings in patients with symptoms suggestive of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. NCBI 64:194–199, 1997.
Sharma, S. K., Malik, V., Vasudev, C., Banga, A., Mohan, A., Handa, K. K., and Mukhopadhyay, S., Prediction of obstructive sleep apnea in patients presenting to a tertiary care center. Sleep. Breath. 10:147–154, 2006.
Shepertycky, M. R., Banno, K., and Kryger, M. H., Differences between men and women in clinical presentation of patients diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep 28:309–314, 2005.
Su, C. T., Chen, K. H., Chen, L. F., Wang, P. C., and Hsiao, Y. H., Prediagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea via multiclass MTS. Comput. Math. Method. M. 2012. doi:10.1155/2012/212498.
Su, C. T., Wang, P. C., Chen, Y. C., and Chen, L. F., Data mining techniques for assisting the diagnosis of pressure ulcer development in surgical patients. J. Med. Syst. 36:2387–239, 2012.
Subramanian, S., Hesselbacher, S., Mattewal, A., and Surani, S., Gender and age influence the effects of slow-wave sleep on respiration in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep. Breath. 17:51–56, 2013.
Tasali, E., Mokhlesi, B., and Van Cauter, E., Obstructive sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes: interacting epidemics. Chest 133:496–506, 2008.
Testik, M. C., Ozkaya, B. Y., Aksu, S., and Ozcebe, O. I., Discovering blood donor arrival patterns using data mining: A method to investigate service quality at blood centers. J. Med. Syst. 36:579–594, 2012.
Tiihonen, P., Hukkanen, T., Tuomilehto, H., Mervaala, E., and Töyräs, J., Evaluation of a novel ambulatory device for screening of sleep apnea. Telemed. J. E. Health. 15:283–9, 2009.
Walczak, B., and Massart, D. L., Rough sets theory. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 47:1–16, 1999.
Wang, P. C., Su, C. T., Chen, K. H., and Chen, N. H., The application of rough Set and Mahalanobis distance to enhance the quality of OSA diagnosis. Expert Syst. Appl. 38:7828–7836, 2011.
Wright, J., Johns, R., Watt, I., Melville, A., and Sheldon, T., Health effects of obstructive sleep apnea and the effectiveness of continuous positive airway pressure: A systematic review of the research evidence. Br. Med. J. 314:851–860, 1997.
Xiao, Y., Zhong, X., Huang, R., and Sun, G. Q., The evaluation of the severity of nocturnal oxygen desaturation of patients with obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome. Zhonghua. Nei. Ke. Za. Zhi. 46:458–61, 2007.
Young, T., Palta, M., Dempsey, J., Skatrud, J., Weber, S., and Badr, S., The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 328:1230–1235, 1993.
Young, T., Peppard, P. E., and Gottlieb, D. J., Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: A population health perspective. Am. Jnl. Resp. Crit. Care. Med. 165:1217–1239, 2002.
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the comments and suggestions of the editor and the reviewers. This study is partially sponsored by the National Taiwan University of Science and Technology – Taipei Medical University Joint Research Program (TMU-NTUST-102-06 & TMU-NTUST-101-07). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
This study has no conflict of interest to any parties/agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shou-Hung Huang and Nai-Chia Teng contributed equally to this work.
Kung-Jeng Wang and Kun-Huang Chen contributed equally to this work.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, SH., Teng, NC., Wang, KJ. et al. Use of Oximetry as a Screening Tool for Obstructive Sleep Apnea: a Case Study in Taiwan. J Med Syst 39, 29 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0195-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0195-5