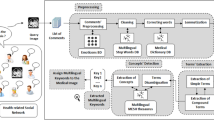
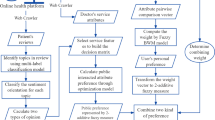
Abstract
Recently, the use of social media for health information exchange is expanding among patients, physicians, and other health care professionals. In medical areas, social media allows non-experts to access, interpret, and generate medical information for their own care and the care of others. Researchers paid much attention on social media in medical educations, patient–pharmacist communications, adverse drug reactions detection, impacts of social media on medicine and healthcare, and so on. However, relatively few papers discuss how to extract useful knowledge from a huge amount of textual comments in social media effectively. Therefore, this study aims to propose a Fuzzy adaptive resonance theory network based Information Retrieval (FIR) scheme by combining Fuzzy adaptive resonance theory (ART) network, Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI), and association rules (AR) discovery to extract knowledge from social media. In our FIR scheme, Fuzzy ART network firstly has been employed to segment comments. Next, for each customer segment, we use LSI technique to retrieve important keywords. Then, in order to make the extracted keywords understandable, association rules mining is presented to organize these extracted keywords to build metadata. These extracted useful voices of customers will be transformed into design needs by using Quality Function Deployment (QFD) for further decision making. Unlike conventional information retrieval techniques which acquire too many keywords to get key points, our FIR scheme can extract understandable metadata from social media.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, R. and Srikant, R. (1994). Fast algorithm for mining association rules. The 20th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, Santiago, Chile, 487–499.
Agrawal, R., Imielinski, T. and Swami, A. (1993). Mining association rules between sets of items in large databases. ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Washington, D.C., USA, 207–216.
Akritas, A. G., and Malaschonok, G. I., Applications of singular-value decomposition (SVD). Mathematics and Computers in Simulation 67:15–31, 2004.
Andersen, K. N., Medaglia, R., and Henriksen, H. Z., Social media in public health care: Impact domain propositions. Government Information Quarterly 29:462–469, 2012.
Antheunis, M. L., Tates, K., and Nieboer, T. E., Patients’ and health professionals’ use of social media in health care: Motives, barriers and expectations. Patient Education and Counseling 92:426–431, 2013.
Asano, E., A public outreach in epilepsy surgery using a serial novel on blog: A preliminary report. Brain & Development 29:102–104, 2007.
Batta, H. E., and Iwokwagh, N. S., Optimising the digital age health-wise: utilisation of new/social media by Nigerian teaching hospitals. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 176:175–185, 2015.
Benetoli, A., Chen, T. F., and Aslani, P., The use of social media in pharmacy practice and education. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy 11:1–46, 2015.
Berry, M. W., Dumais, S. T., and O'brien, G. W., Using linear algebra for intelligent information retrieval. SIAM Review 37:573–595, 1995.
Burke, L., and Kamal, S., Neural networks and the part family/machine group formation problem in cellular manufacturing: A framework using Fuzzy ART. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 14(3):148–159, 1995.
Cameron, D., Smith, G. A., Daniulaityte, R., Sheth, A. P., Dave, D., Chen, L., Anand, G., Carlson, R., Watkins, K. Z., and Falck, R., PREDOSE: A semantic web platform for drug abuse epidemiology using social media. Journal of Biomedical Informatics 46:985–997, 2013.
Carpenter, G. A., Grossberg, S., and Rosen, D. B., Fuzzy ART: Fast stable learning and categorization of analog patterns by an adaptive resonance system. Neural Networks 4:759–771, 1991.
Chau, M., and Xu, J., Mining communities and their relationships in blogs: A study of online hate groups. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies 65(1):57–70, 2007.
Chen, L.-S., and Su, C.-T., Using granular computing model to induce scheduling knowledge in dynamic manufacturing environments. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing 21(5):569–583, 2008.
Chen, L.-S., Hsu, C.-C., and Chen, M.-C., Customer segmentation and classification from blogs by using data mining: An example of VOIP phone. Cybernetics & Systems 40(7):608–632, 2009.
Chen, L.-S., Hsu, F.-H., Chen, M.-C., and Hsu, Y.-C., Developing recommender systems with the consideration of product profitability for sellers. Information Sciences 178(4):1032–1048, 2008.
Cohen, E., and Krishnamurthy, B., A short walk in the blogistan. Computer Networks 50(5):615–630, 2006.
Deerwester, S., Dumais, S. T., Landauer, T. K., Furnas, G. W., and Harshman, R. A., Indexing by latent semantic analysis. Journal of the Society for Information Science 41(6):391–407, 1990.
Denecke, K., and Nejdl, W., How valuable is medical social media data? Content analysis of the medical web. Information Sciences 179:1870–1880, 2009.
Du, H. S., and Wagner, C., Weblog success: Exploring the role of technology. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies 64:789–798, 2006.
Facca, F. M., and Lanzi, P. L., Mining interesting knowledge from weblogs: A survey. Data & Knowledge Engineering 53:225–241, 2005.
Foley, N. M., Maher, B. M., Mark, A., and Corrigan, M. A., Social media and tomorrow’s medical students—How do they fit? Journal of Surgical Education 71(3):385–390, 2014.
Gao, J., and Zhang, J., Clustered SVD strategies in latent semantic indexing. Information Processing and Management 41:1051–1063, 2005.
Grindrod, K., Pharm, P. D., Forgione, A., Tsuyuki, R. T., Gavura, S., and Giustini, M. L. S., Pharmacy 2.0: A scoping review of social media use in pharmacy. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy 10:256–270, 2014.
Han, J. and Kamber, M. (2001). Data mining: Concepts and techniques, Mogan Kaufmann Publishers.
Ko, H.-C., and Kuo, F.-Y., Can blogging enhance subjective well-being through self-disclosure? Cyberpsychology & Behavior 12(1):75–79, 2009.
Kontostathis, A., and Pottenger, W. M., A framework for understanding latent semantic indexing (LSI) performance. Information Processing and Management 42:56–73, 2006.
Kumar, R., Raghavan, P., Rajagopalan, S., and Tomkins, A., Trawling the web for emerging cyber-communities. Computer Networks 31(11–16):1481–1493, 1999.
Larkin, M., Blogs: New way to communicate about infectious diseases. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 5(12):748, 2005.
Lin, Y.-S., and Huang, J.-Y., Internet blogs as a tourism marketing medium: A case study. Journal of Business Research 59:1201–1205, 2006.
Ma, W.-Y. and Chen, K.-J. (2003). Introduction to CKIP Chinese word segmentation system for the first international Chinese word segmentation bakeoff. The 2nd SIGHAN Workshop on Chinese Language Processing, 168–171.
Metwally, A., Agrawal, D. and Abbadi, A. E. (2005). Using association rules for fraud detection in web advertising networks, Proceedings of VLDB International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, pp. 169–180.
Nardi, B. A., Schiano, D. J., Gumbrecht, M., and Swartz, L., Why we blog? Communications of the ACM 47(12):41–46, 2004.
Ngai, E. W. T., Tao, S. S. C., and Moon, K. K. L., Social media research: Theories, constructs, and conceptual frameworks. International Journal of Information Management 35:33–44, 2015.
Oeldorf-Hirsch, A., and Sundar, S. S., Posting, commenting, and tagging: Effects of sharing news stories on Facebook. Computers in Human Behavior 44:240–249, 2015.
Oransky, I., Cancer blogs. Lancet Oncology 6(11):838–839, 2005.
Paniagua, J., and Sapena, J., Business performance and social media: Love or hate? Business Horizons 57(6):719–728, 2014.
Park, J. S., Chen, M. S., Yu, P. S. (1995). An effective hash-based algorithm for mining association rules, ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, 24(16), pp.175 - 186.
Patel, D., and Jermacane, D., Social media in travel medicine: A review. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease, 2015. doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2015.03.006.
Pavelko, R. L., and Myrick, J. G., That’s so OCD: The effects of disease trivialization via social media on user perceptions and impression formation. Computers in Human Behavior 49:251–258, 2015.
Popoiu, M. C., Grosseck, G., and Holotescu, C., What do we know about the use of social media in medical education? Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 46:2262–2266, 2012.
Sarker, A., Nikfarjam, A., O’Connor, K., Ginn, R., Gonzalez, G., Upadhaya, T., Jayaraman, S., and Smith, K., Utilizing social media data for pharmacovigilance: A review. Journal of Biomedical Information, 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2015.02.004.
Saton, A., and Costa-i-Font, J., Social networking for medical information: A digital divide or a trust inquiry? Health Policy and Technology 2:139–150, 2013.
Savasee, A., Omiecinski, E., and Navathe, S. (1995). An efficient algorithm for mining association rules in large databases, Proceedings of 21st Very Large Data Bases Conference, pp.432 - 444.
Shcherbakova, N., and Shepherd, M., Community pharmacists, Internet and social media: An empirical investigation. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy 10:e75–e85, 2014.
Stelzner, M.A. (2014). Social media marketing industry report: How marketers are using social media to grow their businesses, available at http://www.socialmediaexaminer.com/SocialMediaMarketingIndustryReport2014.pdf, accessed December 20, 2014.
Su, C.-T., Chen, L.-S., and Yih, Y., Knowledge acquisition through information granulation for imbalanced data. Expert Systems with Applications 31(3):531–541, 2006.
Tai, X., Ren, F., and Kita, K., An information retrieval model based on vector space method by supervised learning. Information Processing and Management 38:749–764, 2002.
Todoroki, S., Konishi, T., and Inoue, S., Blog-based research notebook: Personal informatics workbench for high-throughput experimentation. Applied Surface Science 252(7):2640–2645, 2006.
Trammell, K. D., Blog offensive: An exploratory analysis of attacks published on campaign blog posts from a political public relations perspective. Public Relations Review 32(4):402–406, 2006.
Wiley, M. T., Jin, C., Hristidis, V., and Esterling, K. M., Pharmaceutical drugs chatter on online social networks. Journal of Biomedical Informatics 49:245–254, 2014.
Wong, C. A., Merchant, R. M., and Moreno, M. A., Using social media to engage adolescents and young adults with their health. Healthcare 2:220–224, 2014.
Yang, H.-L., and Hsiao, S.-L., Mechanisms of developing innovative IT-enabled services: A case study of Taiwanese health care service. Technovation 29:327–337, 2009.
Yang, M., Kiang, M., and Shang, W., Filtering big data from social media – Building an early warning system for adverse drug reactions. Journal of Biomedical Information, 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2015.01.011.
Zeng, B., and Gerritsen, R., What do we know about social media in tourism? A review. Tourism Management Perspectives 10:27–36, 2014.
Zhu, L., Sun, A., and Choi, B., Detecting spam blogs from blog search results. Information Processing and Management, 2010. doi:10.1016/j.ipm.2010.03.006.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported in part by Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (Grant No. MOST 101-2628-E-324-004-MY3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Transactional Processing Systems
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, LS., Lin, ZC. & Chang, JR. FIR: An Effective Scheme for Extracting Useful Metadata from Social Media. J Med Syst 39, 139 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0333-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0333-0