Abstract
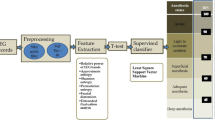
Distinguishing between awake and anesthetized states is one of the important problems in surgery. Vital signals contain valuable information that can be used in prediction of different levels of anesthesia. Some monitors based on electroencephalogram (EEG) such as the Bispectral (BIS) index have been proposed in recent years. This study proposes a new method for characterizing between awake and anesthetized states. We validated our method by obtaining data from 25 patients during the cardiac surgery that requires cardiopulmonary bypass. At first, some linear and non-linear features are extracted from EEG signals. Then a method called “LLE”(Locally Linear Embedding) is used to map high-dimensional features in a three-dimensional output space. Finally, low dimensional data are used as an input to a quadratic discriminant analyzer (QDA). The experimental results indicate that an overall accuracy of 88.4 % can be obtained using this method for classifying the EEG signal into conscious and unconscious states for all patients. Considering the reliability of this method, we can develop a new EEG monitoring system that could assist the anesthesiologists to estimate the depth of anesthesia accurately.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mortier, E.P., and Struys, M.M.R., Monitoring the depth of anaesthesia using bispectral analysis and closed-loop controlled administration of propofol. Best Pract. & Res. Clin. Anaesthesiology. 15(1):83–96, 2001.
Sinha, P.K., and Koshy, T., Monitoring devices for measuring the depth of anaesthesia-an overview. Indian J. Anaesthesia. 51(5):365–381, 2007.
Shalbaf, R., Behnam, H., Sleigh, J., Steyn-Ross, A., and Voss, L., Monitoring the depth of anesthesia using entropy features and an artificial neural network. J. Neurosci. Methods. 218(1):17–24, 2013.
Gugino, L.D., Chabot, R.J., Prichep, L.S., John, E.R., Formanek, V., and Aglio, L.S., Quantitative EEG changes associated with loss and return of consciousness in healthy adult volunteers anaesthetized with propofol or sevoflurane. Br. J. Anaesth. 87(3):421–428, 2001.
Rampil, I.J., A primer for EEG signal processing in anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 89:980–1002, 1998.
Schwender, D., Daunerer, M., Klasing, S., Finsterer, U., and Peter, K., Power spectral analysis of the electroencephalogram during increasing end-expiratory concentrations of isoflurane and sevoflurane. Anesthesiology. 53:335–342, 1998.
Hosseini, P.T., Shalbaf, R., and Nasrabadi, A.M., Extracting a seizure intensity index from one-channel EEG signal using bispectral and detrended fluctuation analysis. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 3:253–261, 2010.
Shalbaf, R., Behnam, H., Sleigh, J.W., Steyn-Ross, D.A., and Steyn-Ross, M.L., Frontal-temporal synchronization of EEG signals quantified by order patterns cross recurrence analysis during propofol anesthesia. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 23:468–474, 2015.
Viertiö-Oja, H., Maja, V., Särkelä, M., Talja, P., Tenkanen, N., et al., Description of the entropy algorithm as applied in the datex-ohmeda S/5 entropy module. Acta Anaesth. Scand. 48(2):154–161, 2004.
Paul, D.B., and Rao, G.S.U., Correlation of bispectral index with glasgow coma score in mild and moderate head injuries. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 20(6):399–404, 2006.
Kortelainen, J., Vayrynen, E., and Seppanen, T., Isomap approach to EEG-based assessment of neurophysiological changes during anesthesia. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 19:113–120, 2011.
Lopour, A.B., Tasoglu, S., Kirsch, H.E., Sleigh, J.W., and Szeri, A.J., A continuous mapping of sleep states through association of EEG with a mesoscale cortical model. J. Comput. Neurosci. 30:471–487, 2011.
Dodge Y (2003) The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms. ISBN 0–19-920613-9
MacKay, E.C., Sleigh, J.W., Voss, L.J., and Barnard, J.P., Episodic waveforms in the electroencephalogram during general anaesthesia: a study of patterns of response to noxious stimuli. Anaesth. Intensive Care. 38(1):102–112, 2010.
Olofsen, E., WSleigh, J., and Dahan, A., Permutation entropy of the electroencephalogram: a measure of anesthetic drug effect. Br. J. Anaesth. 101:810–821, 2008.
Shalbaf, R., Behnam, H., Sleigh, J., and Voss, L., Measuring the effects of sevoflurane on electroencephalogram using sample entropy. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 56:880–889, 2012.
Roweis, S.T., and Saul, L.K., Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science. 290:2323–2326, 2000.
Ataee P, Yazdani A, Setarehdan S, Noubari HA (2007) Manifold learning applied on EEG signal of the epileptic patients for detection of normal and pre-seizure states. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS 2007. 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE, 5489–5492, 2007.
Alizadeh-Sani, Z., Shalbaf, A., Behnam, H., and Shalbaf, R., Automatic computation of left ventricular volume change from echocardiography images using nonlinear dimensionality reduction. J. Digit. Imaging. 28:91–98, 2015.
Saul, L.K., Roweis, S.T., and Singer, Y., Think globally, fit locally: unsupervised learning of low dimensional manifolds. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 4:119–155, 2003.
Saul, L.K., and Roweis, S.T., Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science. 290:2323–2326, 2000.
Roweis ST, Saul LK (2009) Locally linear embedding. http://www.cstorontoedu/roweis/lle/
Cheng LL, Sako H, Fujisawa H (2002) Learning quadratic discriminant function for handwritten character classification. Pattern Recognition, 2002. Proceedings. 16th International Conference on (Volume:4 ), 44–47, 2002.
Shalbaf, R., Behnam, H., and Moghadam, H.J., Monitoring depth of anesthesia using combination of EEG measure and hemodynamic variables. Cogn. Neurodyn. 9:41–51, 2015.
Bostanov, V., BCI competition 2003—data sets ib and iib: feature extraction from event-related brain potentials with the continuous wavelet transform and the t-value scalogram. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51:57–61, 2004.
Hagihira, S., Takashina, M., Mori, T., Mashimo, T., and Yoshiya, I., Practical issues in bispectral analysis of electroencephalographic signals. Anesth. Analg. 93:966–970, 2001.
Shalbaf, R., Behnam, H., Sleigh, J.W., and Voss, L.J., Using the Hilbert-Huang transform to measure the electroencephalographic effect of propofol. Physiol. Meas. 33(2):271–285, 2012.
Muncaster, A., Sleigh, J., and Williams, M., Changes in consciousness, conceptual memory, and quantitative electroencephalographical measures during recovery from sevoflurane- and remifentanilbased anesthesia. Anesth. Analg. 96:720–725, 2003.
Johansen, J.W., and Sebel, P.S., Effects of the anesthetic agent propofol on neural populations. Cogn. Neurodyn. 4(37–59), 2000.
Sleigh, J.W., and Donovan, J., Comparison of the bispectral index, 95 % spectral edge frequency and approximate entropy of the EEG, with changes in heart rate variability during induction and recovery from general anaesthesia. Br J. Anesth. 82:666–671, 1999.
Pilge, S., Zanner, R., Schneider, G., Blum, J., Kreuzer, M., and Kochs, E.F., Time delay of index calculation: analysis of cerebral state, bispectral, and narcotrend indices. Anesthesiology. 104:488–494, 2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirsadeghi, M., Behnam, H., Shalbaf, R. et al. Characterizing Awake and Anesthetized States Using a Dimensionality Reduction Method. J Med Syst 40, 13 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0382-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0382-4