Abstract
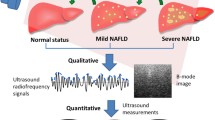
Fatty liver disease is a common disease caused by alcoholism, obesity, and diabetes, resulting in triglyceride accumulation in hepatocytes. Kurtosis coefficient, a measure of the peakedness of the probability distribution, has been applied to the analysis of backscattered statistics for characterizing fatty liver. This study proposed ultrasound kurtosis imaging as a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) method to visually and quantitatively stage the fatty liver. A total of 107 patients were recruited to participate in the experiments. The livers were scanned using a clinical ultrasound scanner with a 3.5-MHz curved transducer to acquire the raw ultrasound backscattered signals for kurtosis imaging. The kurtosis image was constructed using the sliding window technique. Experimental results showed that kurtosis imaging has the ability to visualize and quantify the variation of backscattered statistics caused by fatty infiltration. The kurtosis coefficient corresponding to liver parenchyma decreased from 5.41 ± 0.89 to 3.68 ± 0.12 with increasing the score of fatty liver from 0 (normal) to 3 (severe), indicating that fatty liver reduces the degree of peakedness of backscattered statistics. The best performance of kurtosis imaging was found when discriminating between normal and fatty livers with scores ≥1: the area under the curve (AUC) is 0.92 at a cutoff value of 4.36 (diagnostic accuracy =86.9 %, sensitivity =86.7 %, specificity =87.0 %). The current findings suggest that kurtosis imaging may be useful in designing CAD tools to assist in physicians in early detection of fatty liver.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Hamer, O.W., Aguirre, D.A., Casola, G., Lavine, J.E., Woenckhaus, M., and Sirlin, G.B., Fatty liver: imaging patterns and pitfalls. Radiographics. 26:1637–1653, 2006.
Sumida, Y., Nakajima, A., and Itoh, Y., Limitations of liver biopsy and non-invasive diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 20:475–485, 2014.
Nalbantoglu, I.L., and Brunt, E.M., Role of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 20:9026–9037, 2014.
Chan, D.F., Li, A.M., Chu, W.C., Chan, M.H., Wong, E.M., Liu, E.K., Chan, I.H., Yin, J., Lam, C.W., Fok, T.F., and Nelson, E.A., Hepatic steatosis in obese Chinese children. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 28:1257–1263, 2004.
Thijssen, J.M., Starke, A., Weijers, G., Haudum, A., Herzog, K., Wohlsein, P., Rehage, J., and De Korte, C.L., Computer-aided B-mode ultrasound diagnosis of hepatic steatosis: a feasibility study. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 55:1343–1354, 2008.
Ho, M.C., Lee, Y.H., Jeng, Y.M., Chen, C.N., Chang, K.J., and Tsui, P.H., Relationship between ultrasound backscattered statistics and the concentration of fatty droplets in livers: an animal study. PloS One. 8:e63543, 2013.
Subramanya, M.B., Kumar, V., Mukherjee, S., and Saini, M., A CAD system for B-mode fatty liver ultrasound images using texture features. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 39:123–130, 2015.
Ghoshal, G., Lavarello, R.J., Kemmerer, J.P., Miller, R.J., and Oelze, M.L., Ex vivo study of quantitative ultrasound parameters in fatty rabbit livers. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 38:2238–2248, 2012.
Shankar, P.M., A general statistical model for ultrasonic backscattering from tissues. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 47:727–736, 2000.
Zhou, Z., Huang, C.C., Shung, K.K., Tsui, P.H., Fang, J., Ma, H.Y., Wu, S., and Lin, C.C., Entropic imaging of cataract lens: an in vitro study. PLoS One. 9:e96195, 2014.
Kuc, R., Ultrasonic tissue characterization using kurtosis. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 33:273–279, 1986.
Xie, X., Luo, Y., Quan, J., Chen, K., and Lin, J., SD rats' fatty liver tissue classification based on ultrasound radiofrequency signal. In: Jin, D., and Lin, S. (Eds.), Advances in computer science and information engineering. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, pp. 643–647, 2012.
Suzuki, K., Hayashi, N., Sasaki, Y., Kono, M., Kasahara, A., Imai, Y., Fusamoto, H., and Kamada, T., Evaluation of structural change in diffuse liver disease with frequency domain analysis of ultrasound. Hepatology. 17:1041–1046, 1993.
Wan, Y.L., Tai, D.I., Chiang, B.H., Ma, H.Y., Chen, C.K., and Tsui, P.H., Effects of fatty infiltration in human livers on the backscattered statistics of ultrasound imaging. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H. - J. Eng. Med. 229:419–428, 2015.
Li, M.L., Li, D.W., Liu, H.L., Lin, M.S., Ultrasonic Nakagami visualization of HIFU-induced thermal lesions. In: IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), IEEE, pp. 2251–2253. San Diego, 2010.
Yang, X., Rossi, P., Bruner, D.W., Tridandapani, S., Shelton, J., and Liu, T., Noninvasive evaluation of vaginal fibrosis following radiotherapy for gynecologic malignancies: a feasibility study with ultrasound B-mode and nakagami parameter imaging. Med. Phys. 40:022901, 2013.
Tsui, P.H., and Chang, C.C., Imaging local scatterer concentrations by the nakagami statistical model. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 33:608–619, 2007.
Tsui, P.H., Ma, H.Y., Zhou, Z., Ho, M.C., and Lee, Y.H., Window-modulated compounding nakagami imaging for ultrasound tissue characterization. Ultrasonics. 54:1448–1459, 2014.
Liao, Y.Y., Li, C.H., Tsui, P.H., Chang, C.C., Kuo, W.H., Chang, K.J., and Yeh, C.K., Discrimination of breast microcalcifications using a strain-compounding technique with ultrasound speckle factor imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 61:955–965, 2014.
Osawa, H., and Mori, Y., Sonographic diagnosis of fatty liver using a histogram technique that compares liver and renal cortical echo amplitudes. J. Clin. Ultrasound. 24:25–29, 1996.
Cloutier, G., Daronatand, M., Savery, D., Garcia, D., Durand, L.G., and Foster, F.S., Non-gaussian statistics and temporal variations of the ultrasound signal backscattered by blood at frequencies between 10 and 58 MHz. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 116:566–577, 2004.
Ehman, R.L., Science to practice: can MR elastography be used to detect early steatohepatitis in fatty liver disease? Radiology. 253:1–3, 2009.
Charlton, M., Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a review of current understanding and future impact. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2:1048–1058, 2004.
Adams, L.A., Angulo, P., and Lindor, K.D., Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 172:899–905, 2005.
Chen, J., Talwalkar, J.A., Yin, M., Glaser, K.J., Sanderson, S.O., and Ehman, R.L., Early detection of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by using MR elastography. Radiology. 259:749–756, 2011.
Nadarajah, S., Statistical distributions of potential interest in ultrasound speckle analysis. Phys. Med. Biol. 52:N213–N227, 2007.
Nillesen, M.M., Lopata, R.G., Gerrits, I.H., Kapusta, L., Thijssen, J.M., and de Korte, C.L., Modeling envelope statistics of blood and myocardium for segmentation of echocardiographic images. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 34:674–680, 2008.
Destrempes, F., and Cloutier, G., A critical review and uniformized representation of statistical distributions modeling the ultrasound echo envelope. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 36:1037–1051, 2010.
Mamou, J., Coron, A., Oelze, M.L., Saegusa-Beecroft, E., Hata, M., Lee, P., Machi, J., Yanagihara, E., Laugier, P., and Feleppa, E.J., Three-dimensional high-frequency backscatter and envelope quantification of cancerous human lymph nodes. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 37:345–357, 2011.
Shankar, P.M., A statistical model for the ultrasonic backscattered echo from tissue containing microcalcifications. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 60:932–942, 2013.
Larrue, A., and Noble, J.A., Modeling of errors in nakagami imaging: illustration on breast mass characterization. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 40:917–930, 2014.
Tsui, P.H., Wan, Y.L., and Chen, C.K., Ultrasound imaging of the larynx and vocal folds: recent applications and developments. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 20:437–442, 2012.
Tsui, P.H., and Wang, S.H., The effect of transducer characteristics on the estimation of nakagami paramater as a function of scatterer concentration. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 30:1345–1353, 2004.
Toyoda, H., Kumada, T., Kamiyama, N., Shiraki, K., Takase, K., Yamaguchi, T., and Hachiya, H., B-mode ultrasound with algorithm based on statistical analysis of signals: evaluation of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Am. J. Roentgenol. 193:1037–1043, 2009.
Kramer, C., Jaspers, N., Nierhoff, D., Kuhr, K., Bowe, A., Goeser, T., and Michels, G., Acoustic structure quantification ultrasound software proves imprecise in assessing liver fibrosis or cirrhosis in parenchymal liver diseases. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 40:2811–2818, 2014.
Lin, S.C., Heba, E., Wolfson, T., Ang, B., Gamst, A., Han, A., Erdman Jr., J.W., O'Brien Jr., W.D., Andre, M.P., Sirlin, C.B., and Loomba, R., Noninvasive diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and quantification of liver fat using a new quantitative ultrasound technique. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 13:1337–1345, 2015.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (Taiwan) under Grant No. MOST 103-2221-E-182-001-MY3 and the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (Linkou, Taiwan) under Grant Nos. CIRPD1E0021, CMRPD1C0711, and CMRPD1C0661.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Hsiang-Yang Ma and Zhuhuang Zhou contributed equally to this work.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, HY., Zhou, Z., Wu, S. et al. A Computer-Aided Diagnosis Scheme For Detection Of Fatty Liver In Vivo Based On Ultrasound Kurtosis Imaging. J Med Syst 40, 33 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0395-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0395-z