Abstract
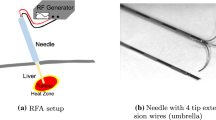
Radiofrequency ablation therapy of liver cancer is a local mini-invasive treatment technology with several advantages, such as low trauma, safety, effectiveness, and quick postoperative recovery. The application of the optical surgical navigation system in radiofrequency ablation therapy can realize the real-time positioning of surgical instruments and focus. The positioning results can be displayed on the computer, thereby guiding doctors to accurately insert the radiofrequency electrode into the focus and improving surgical efficiency. Meanwhile, the accurate evaluation of the form and size of the ablation focus by the navigation system is the key to realizing the complete ablation of liver cancer. Therefore, based on the heat conduction equation, this paper simplifies the simulation process of the ablation focus, calculates the volume of the ablation focus by distinguishing boundary points and internal points, achieves the effective simulation of the ablation results in the surgery, and reconstructs the ablation focus by using ray casting algorithm and mobile cube algorithm for 3D visualization processing, thereby providing doctors the convenience of being able to simulate the radiofrequency ablation surgery before the actual surgery.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kimman, M., Norman, R., Jan, S., Kingston, D., and Woodward, M., The burden of cancer in member countries of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 13(2):411–420, 2012.
Zhang, B., Moser, M., Zhang, E., and Zhang, W.J., Radiofrequency ablation technique in the treatment of liver tumours: review and future issues. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 37(2):150–159, 2013.
de Senneville, B.D., Roujol, S., Jaïs, P., Moonen, C.T., Herigault, G., and Quesson, B., Feasibility of fast MR-thermometry during cardiac radiofrequency ablation. NMR Biomed. 25(4):556–562, 2012.
Schoellnast, H., Deodhar, A., Hsu, M., Moskowitz, C., Nehmeh, S.A., Thornton, R.H., Sofocleous, C.T., Alago Jr., W., Downey, R.J., Azzoli, C.G., Rosenzweig, K.E., and Solomon, S.B., Recurrent non-small cell lung cancer: evaluation of CT-guided radiofrequency ablation as salvage therapy. Acta Radiol. 53(8):893–899, 2012.
Wang, Z., Aarya, I., Gueorguieva, M., Liu, D., Luo, H., Manfredi, L., Wang, L., McLean, D., Coleman, S., Brown, S., and Cuschieri, A., Image-based 3D modeling and validation of radiofrequency interstitial tumor ablation using a tissue-mimicking breast phantom. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 7(6):941–948, 2012.
Clasen, S., Schmidt, D., Boss, A., Dietz, K., Kröber, S.M., Claussen, C.D., and Pereira, P.L., Multipolar radiofrequency ablation with internally cooled electrodes: Experimental study in ex vivo bovine liver with mathematic modeling. Radiology. 238(3):881–890, 2006.
Rieder, C., Kröger, T., Schumann, C., and Hahn, H.K., GPU-based real-time approximation of the ablation zone for radiofrequency ablation. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 17(12):1812–1821, 2011.
Fiala, D., Lomas, K.J., and Stohrer, M., A computer model of human thermoregulation for a wide range of environmental conditions: the passive system. J. Appl. Physiol. 87(5):1957–1972, 1999.
Diller, K.R., Modeling of bioheat transfer processes at high and low temperatures. Adv. Heat Tran. 22:157–357, 1992.
Pennes, H.H., Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in the resting human forearm. 1948. J. Appl. Physiol. 85(1):5–34, 1998.
Brodlie, K., and Wood, J., Recent advances in volume visualization. Comput. Graph. Forum. 20(2):125–148, 2001.
Laha, B., Sensharma, K., Schiffbauer, J.D., and Bowman, D.A., Effects of immersion on visual analysis of volume data. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 18(4):597–606, 2012.
Westover, L., Footprint evaluation for volume rendering. Comput. Graph. 24(4):367–376, 1990.
Yu, H., Lee, T., Yeh, I., Yang, Y., Li, W., and Zhang, J.J., An RBF-based reparameterization method for constrained texture mapping. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 18(7):1115–1124, 2012.
Heinrich, J., Bachthaler, S., and Weiskopf, D., Progressive splatting of continuous scatterplots and parallel coordinates. Comput. Graph. Forum. 30(3):653–662, 2011.
Zhang, Q., Eagleson, R., and Peters, T.M., Volume visualization: a technical overview with a focus on medical applications. J. Digit. Imaging. 24(4):640–664, 2011.
Levoy, M., Display of surfaces from volume data. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 8(3):29–37, 1988.
van Almsick, M., Peeters, T.H., Prckovska, V., Vilanova, A., and Ter Haar Romeny, B., GPU-based ray-casting of spherical functions applied to high angular resolution diffusion imaging. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 17(5):612–625, 2011.
Schlegel, P., Makhinya, M., and Pajarola, R., Extinction-based shading and illumination in gpu volume ray-casting. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 17(12):1795–1802, 2011.
Rossler, F., Botchen, R.P., and Ertl, T., Dynamic shader generation for GPU-based multi-volume ray casting. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 28(5):66–77, 2008.
Schroeder, W.J., Avila, L.S., and Hoffman, W., Visualizing with VTK: a tutorial. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 20(5):20–27, 2000.
Rosset, A., Spadola, L., and Ratib, O., OsiriX: an open-source software for navigating in multidimensional DICOM images. J. Digit. Imaging. 17(3):205–216, 2004.
Lorensen, W.E., and Cline, H.E., Marching cubes: a high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. Comput. Graph. 21(4):163–169, 1987.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.61505037, the State Scholarship Fund under Grant CSC NO.201408440326, the Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou under Grant No.2014J2200049 and No.201506010035, the Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Program under Grant No.2013B090600057, No.2014A020215006 and 2014A020212657, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant No.2014ZG003D, the Natural Scientific Foundation of Guangxi under Grant No.2015GXNSFBA139259.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, K., Yang, R., Chen, H. et al. Simulation and Visualization of Liver Cancer Ablation Focus in Optical Surgical Navigation. J Med Syst 40, 19 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0397-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0397-x