Abstract
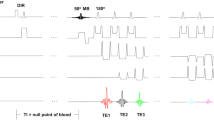
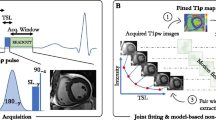
Harmonic Phase-Magnetic Resonance Imaging (HARP-MRI) is a tagged image analysis method that can measure myocardial motion and strain in near real-time and is considered a potential candidate to make magnetic resonance tagging clinically viable. However, analytical expressions of radially tagged transverse magnetization in polar coordinates (which is required to appropriately describe the shape of the heart) have not been explored because the physics required to directly connect myocardial deformation of tagged Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) transverse magnetization in polar geometry and the appropriate harmonic phase parameters are not yet available. The analytical solution of Bloch NMR diffusion equation in spherical geometry with appropriate spherical wave tagging function is important for proper analysis and monitoring of heart systolic and diastolic deformation with relevant boundary conditions. In this study, we applied Harmonic Phase MRI method to compute the difference between tagged and untagged NMR transverse magnetization based on the Bloch NMR diffusion equation and obtained radial wave tagging function for analysis of myocardial motion. The analytical solution of the Bloch NMR equations and the computational simulation of myocardial motion as developed in this study are intended to significantly improve healthcare for accurate diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cardiovascular related deceases at the lowest cost because MRI scan is still one of the most expensive anywhere. The analysis is fundamental and significant because all Magnetic Resonance Imaging techniques are based on the Bloch NMR flow equations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moore, C.C., McVeigh, E.R., and Zerhouni, E.A., Noninvasive measurement of three-dimensional myocardial deformation with tagged magnetic resonance imaging during graded local ischemia. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 1(3):207–222, 1999. https://doi.org/10.3109/10976649909088333.
Dawson, J., and Lauterbur, P.C., Magnetic resonance imaging. Scholarpedia. 3(7):3381, revision #123947, 2008. https://doi.org/10.4249/scholarpedia.3381.
Edvardsen, T., Rosen, B.D., Pan, L., Jerosch-Herold, M., Lai, S., Hundley, W.G., Sinha, S., Kronmal, R.A., Bluemke, D.A., and Lima, J.A., Regional diastolic dysfunction in individuals with left ventricular hypertrophy measured by tagged magnetic resonance imaging-the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). Am. Heart J. 151(1):109–114, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2005.02.018.
Baer, T., Gore, J.C., Boyce, S., and Nye, P.W., Application of MRI to the analysis of speech production. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 5(1):1–7, 1987. https://doi.org/10.1016/0730-725X(87)90477-2.
Juliane, A., Mobile NMR for rock porosity and permeability. Dissertation. RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany, 2007.
Rieu, R., In vivo study of physiological type flow in a bifurcation vascular prosthesis. J. Biomech. 24(10):923–933, 1991. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9290(91)90170-R.
Vogt, S. J., Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of biological and biogeochemical processes. Dissertation, Montana State University-Bozeman, 2013.
Awojoyogbe, O.B., A mathematical model of Bloch NMR equations for quantitative analysis of blood flow in blood vessels of changing cross-section I. Physica A. 303:163–175, 2002. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4371(01)00379-X.
Awojoyogbe, O.B., A mathematical model of Bloch NMR equations for quantitative analysis of blood flow in blood vessels with changing cross-section II. Physica A. 323:534–550, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4371(02)02025-3.
Awojoyogbe, O.B., Analytical solution of the time-dependent Bloch NMR flow equations: A translational mechanical analysis. Physica A. 339(3):437–460, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2004.03.061.
Awojoyogbe, O.B., Dada, O.M., Faromika, O.P., and Dada, O.E., Mathematical concept of the Bloch flow equations for general magnetic resonance imaging: A review. Concepts Magn Reson A. 38(3):85–101, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmr.a.20210.
Gupta, A., Stait-Gardner, T., Ghadirian, B., Price, W.S., Dada, O.M., and Awojoyogbe, O.B., Theory, dynamics and applications of MR imaging-I. Science PG, New York, 2014.
Awojoyogbe, O.B., Dada, O.M., Onwu, O.S., Ige, A.T., and Akinwande, I.N., Computational diffusion magnetic resonance imaging based on time-dependent Bloch NMR flow equation and Bessel functions. J. Med. Syst. 40:106, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0450-4.
Dada, O.M., Awojoyogbe, O.B., and Ukoha, A.C., A computational analysis for quantitative evaluation of petrol-physical properties of rock fluids based on Bloch NMR diffusion model for porous media. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 127:137–147, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2015.01.003.
Spiegel, M.R., Schaum’s outline series of theory and problems of advanced mathematics for engineers and scientists. McGraw-Hill, Singapore, 1983.
Cowan, B.P., Nuclear magnetic resonance and relaxation, 1st edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1997.
Wylie, C.R., and Barrett, C.L., Advanced engineering mathematics, 5th edn. McGrawl – Hill, Tokyo, 1982.
Kreyszig, E., Advanced engineering mathematics, 7th edn. John Wiley and Sons, Singapore, 1996.
Parthasarathy, V., Characterization of harmonic phase MRI: theory, simulations, and applications. Dissertation, The John Hopkins University, 2006.
Price, W.S., Pulsed-field gradient NMR as a tool for studying translational diffusion. Part I. Basic theory. Concepts Magn Reson. 9:299–336, 1997. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0534(1997)9:5<299::AID-CMR2>3.0.CO;2-U.
Price, W.S., NMR studies of translational motion. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2009.
Hergan, K., Schuster, A., Mair, M., Burger, R., and Töpker, M., Normal cardiac diameters in cine-MRI of the heart. RoFo. 176(11):1599–1606, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-813627.
Osman, N.F., Kerwin, W.S., McVeigh, E.R., and Prince, J.L., Cardiac motion tracking using CINE harmonic phase (HARP) magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 42:1048–1060, 1999. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199912)42:6<1048::AID-MRM9>3.0.CO;2-M.
Stoeck, C.T., Kalinowska, A., von Deuster, C., Harmer, J., Chan, R.W., Niemann, M., Manka, R., Atkinson, D., Sosnovik, D.E., Mekkaoui, C., and Kozerke, S., Dual-phase cardiac diffusion tensor imaging with strain correction. PLoS One. 9(9):e107159, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107159.
Sung, Y.M., and Yong, H., Myocardial T1 and T2 mappings with automatic motion correction at 3 tesla MR: Comparison of T1 and T2 measurements by breathhold, free-breathing and cardiac cycle. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 15(1):P104, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1186/1532-429X-15-S1-P104.
Camargo, G.C., Rothstein, T., Junqueira, F.P., Fernandes, E., Greiser, A., Strecker, R., Pessoa, V., Lima, R.S., and Gottlieb, I., Comparison of myocardial T1 and T2 values in 3 T with T2* in 1.5 T in patients with iron overload and controls. Int. J. Hematol. 103:530, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-016-1950-1.
Osman, N.F., McVeigh, E.R., and Prince, J.L., Imaging heart motion using harmonic phase MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 19(3):186–202, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.845177.
Atalar, E., and McVeigh, E.R., Optimization of tag thickness for measuring position with magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 13(1):152–160, 1994. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.276154.
Young, A.A., and Axel, L., Three-dimensional motion and deformation of the heart wall: Estimation with spatial modulation of magnetization – a model-based approach. Radiology. 185(1):241–247, 1992. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.185.1.1523316.
Guttman, M.A., Prince, J.L., and McVeigh, E.R., Tag and contour detection in tagged MR images of the left ventricle. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 13(1):74–88, 1994. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.276146.
Denney, T.S., Identification of myocardial tags in tagged MR images without prior knowledge of myocardial contours. Proc. Inform .Processing. Med. Imag. 327–340, 1997. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-63046-5_25.
Acosta-Martínez, J., López-Haldón, J.E., Gutiérrez-Carretero, E., Díaz-Carrasco, I., Hajam, T.S., and Fernández, A.O., Radial and circumferential strain as markers of fibrosis in an experimental model of myocardial infarction. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 66(6):508–509, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rec.2013.01.009.
Nishimura, K., Okayama, H., Inoue, K., Saito, M., Yoshii, T., Hiasa, G., Sumimoto, T., Inaba, S., Ogimoto, A., Funada, J.I., and Higaki, J., Direct measurement of radial strain in the inner-half layer of the left ventricular wall in hypertensive patients. J. Cardiol. 59(1):64–71, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjcc.2011.08.003.
Ma, C., Wang, X., and Varghese, T., Segmental analysis of cardiac short-axis views using lagrangian radial and circumferential strain. Ultrason. Imaging. 38(6):363–383, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1177/0161734615613322.
Hoit, B.D., Strain and strain rate echocardiography and coronary artery disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 4(2):179–190, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.110.959817.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Education & Training
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dada, M.O., Jayeoba, B., Awojoyogbe, B.O. et al. Mathematical Development and Computational Analysis of Harmonic Phase-Magnetic Resonance Imaging (HARP-MRI) Based on Bloch Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Diffusion Model for Myocardial Motion. J Med Syst 41, 168 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-017-0816-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-017-0816-2