Abstract
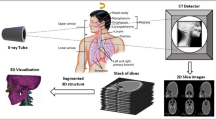
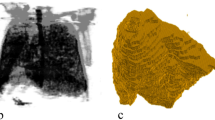
Computer Vision has provided immense support to medical diagnostics over the past two decades. Analogous to Non Destructive Testing of mechanical parts, advances in medical imaging has enabled surgeons to determine root cause of an illness by consulting medical images particularly 3-D imaging. 3-D modeling in medical imaging has been pursued using surface rendering, volume rendering and regularization based methods. Tomographic reconstruction in 3D is different from camera based scene reconstruction which has been achieved using various techniques including minimal surfaces, level sets, snakes, graph cuts, silhouettes, multi-scale approach, patchwork etc. In tomography limitations of image aquisition method i-e CT Scan, X Rays and MRI as well as non availability of camera parameters for calibration restrict the quality of final reconstruction. In this work, a comprehensive study of related approaches has been carried out with a view to provide a summary of state of the art 3D modeling algorithms developed over the past four decades and also to provide a foundation study for our future work which will include precise 3D reconstruction of human spine.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dhawan, A.: Radon transform wiley encyclopedia of biomedical engineering, 2006
Weisstein, E.W.: Radon Transform – from Wolfram MathWorld, Mathworld.wolfram.com. [Online]. Available: http://mathworld.wolfram.com/RadonTransform.html. [Accessed: 20- Oct- 2017], 2018
Physics.stackexchange.com, Why Fields? Why do nuclei precess in magnetic fields? [online] Available at: https://physics.stackexchange.com/questions/386863/why-donucleiprecess-in-magnetic-fields [Accessed 3- Jan- 2018], 2018
Mulay, C., AV, Patient Specific Bone Modeling for Minimum Invasive Spine Surgery. Journal of Spine 04:04, 2015.
Garutti, E.: Index of / garutti/LECTURES/BioMedical. [online] Desy.de. Available at: http://www.desy.de/garutti/LECTURES/BioMedical/ [Accessed 3 Feb. 2018], 2014
Sato, Y., Shiraga, N., Nakajima, S., Tamura, S., and Kikinis, R., Local maximum intensity projection (LMIP. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 22(6):912–917, 1998.
Creedy, M.: [Online]. Available: https://mipav.cit.nih.gov/pubwiki/index.php/Maximum-Intensity-Projection. [Accessed: 02- Jan- 2018], 2012
Kanitsar, A., Fleischmann, D., Wegenkittl, R., Felkel, P., and Groller, E.: CPR - Curved planar reformation, IEEE Visualization. VIS 2002, 2002
Kanitsar, A., Fleischmann, D., Wegenkittl, R., Felkel, P., and Groller, E.: CPR - curved planar reformation. IEEE Visualization. VIS 2002. [Accessed: 02- Jan- 2018], 2002
Whitted, T., An improved illumination model for shaded display. Commun. of the ACM 23(6):343–349, 1980.
Naiwen, l.: Shaded Surface Display Technique, Csee.umbc.edu. [Online]. Available: https://www.csee.umbc.edu/ebert/693/NLiao/node5.html. [Accessed: 23- Nov- 2017], 1996
Heffernan, P., and Robb, R., A new method for shaded surface display of biological and medical images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 4(1):26–38, 1985.
Radiology Imaging: Shaded surface displays of ct scan abdominal, Radiology Imaging. [Online]. Available: http://radiology-information.blogspot.com/2013/03/shaded-surface-displays-of-ct-scan.html. [Accessed: 11- Dec- 2017], 2015
Callahan, S., Callahan, J., Scheidegger, C., and Silva, C., Direct Volume Rendering: A 3D Plotting Technique for Scientific Data. Comput. Sci. Eng. 10(1):88–92, 2008.
Blinn, J.F.: Models of light reflection for computer synthesized pictures. In: Proceedings of the 4th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques - SIGGRAPH 77, 1977.
Kajiya, J.T.: New techniques for ray tracing procedurally defined objects. In: Proceedings of the 10th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques - SIGGRAPH 83, 1983.
Levoy, M., A hybrid ray tracer for rendering polygon and volume data. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 10(2): 33–40, 1990.
Li, G., Xie, H., Ning, H., Citrin, D., Capala, J., Maass-Moreno, R., Guion, P., Arora, B., Coleman, N., Camphausen, K., and Miller, R., Accuracy of 3D volumetric image registration based on CT, MR and PET/CT phantom experiments. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 9(4):17–36, 2008.
Westover, L.A., Splatting: a parallel, feed-forward volume rendering algorithm. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, 1992.
Celebi Tutorial, Volume Rendering, Byclb.com. [Online]. Available: https://www.byclb.com/TR/Tutorials/volume-rendering/ch1-1.htm. [Accessed: 11- Dec- 2017], 2014
Lacroute, P., and Levoy, M.: Fast volume rendering using a shear-warp factorization of the viewing transformation. In: Proceedings of the 21st annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques - SIGGRAPH 94, 1994.
Lorensen, W.E., and Cline, H.E., Marching cubes: a high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. ACM SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 21(4):163–169, 1987.
Naiwen, L.: Shaded surface display technique. [Online]. Available: https://www.csee.umbc.edu/ebert/693/NLiao/node5.html. [Accessed: 15-Nov-2017], 1996
Anderson, B.: Marching Cubes, Cs.carleton.edu. [Online]. Available: http://www.cs.carleton.edu/cs-comps/0405/shape/marching-cubes.html. [Accessed: 07- Nov- 2017]
Lun, Z., Gadelha, M., Kalogerakis, E., Maji, S., and Wang, R.: 3D Shape Reconstruction from Sketches via Multi-view Convolutional Networks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV) 2017, 2017.
Kuklisova-Murgasova, M., Quaghebeur, G., Rutherford, M.A., Hajnal, J.V., and Schnabel, J.A., Reconstruction of fetal brain MRI with intensity matching and complete outlier removal. Med. Image Anal. 16(8): 1550–1564, 2012.
Alansary, A., Rajchl, M., Mcdonagh, S.G., Murgasova, M., Damodaram, M., Lloyd, D.F.A., Davidson, A., Rutherford, M., Hajnal, J.V., Rueckert, D., and Kainz, B., PVR: Patch-to-volume reconstruction for large area motion correction of fetal MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 36(10):2031–2044, 2017.
Cai, Y., Osman, S., Sharma, M., Landis, M., and Li, S., Multi-Modality Vertebra recognition in arbitrary views using 3D deformable hierarchical model. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 34(8):1676–1693, 2015.
Hines, T.: Spine Anatomy, Anatomy of the Human Spine. [online] Available at: https://www.mayfieldclinic.com [Accessed 15 Jan. 2018], 2016
An, G., Hong, L., Zhou, X. -B., Yang, Q., Li, M. -Q., and Tang, X. -Y., Accuracy and efficiency of computer-aided anatomical analysis using 3D visualization software based on semi-automated and automated segmentations. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 210:76–83, 2017.
Mimics 5 Edit Mask in 3D pt2, YouTube. [Online]. Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xxw2klImERM. [Accessed: 10- Jan- 2018]
Syngo.via for Cardiovascular Care - Siemens Healthineers Global, Healthcare.siemens.com. [Online]. Available: https://www.healthcare.siemens.com/medical-imaging-it/syngoviaspecialtopics/syngo-via-for-sustainable-cardiovascular-care/coronary-artery-disease. [Accessed: 09- Jan- 2018]
Boileau, P., Cheval, D., Gauci, M., Holzer, N., Chaoui, J., and Walch, G., Automated Three-Dimensional measurement of glenoid version and inclination in arthritic shoulders. J. Bone Joint Surg. 100 (1):57–65, 2018.
Lee, S., Kim, H., Kim, H., Choi, J., and Cho, J., Comparison of image enlargement according to 3D reconstruction in a CT scan: Using an aneurysm phantom. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 72(7):805–810, 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Image & Signal Processing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, U., Yasin, A., Abid, M. et al. A Methodological Review of 3D Reconstruction Techniques in Tomographic Imaging. J Med Syst 42, 190 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-1042-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-1042-2