Abstract
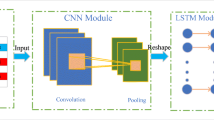
Depression affects large number of people across the world today and it is considered as the global problem. It is a mood disorder which can be detected using electroencephalogram (EEG) signals. The manual detection of depression by analyzing the EEG signals requires lot of experience, tedious and time consuming. Hence, a fully automated depression diagnosis system developed using EEG signals will help the clinicians. Therefore, we propose a deep hybrid model developed using convolutional neural network (CNN) and long-short term memory (LSTM) architectures to detect depression using EEG signals. In the deep model, temporal properties of the signals are learned with CNN layers and the sequence learning process is provided through the LSTM layers. In this work, we have used EEG signals obtained from left and right hemispheres of the brain. Our work has provided 99.12% and 97.66% classification accuracies for the right and left hemisphere EEG signals respectively. Hence, we can conclude that the developed CNN-LSTM model is accurate and fast in detecting the depression using EEG signals. It can be employed in psychiatry wards of the hospitals to detect the depression using EEG signals accurately and thus aid the psychiatrists.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E., ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Proces. Syst., 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2014.09.007.
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., Rabinovich, A., Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2015.
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A., Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556, 2014.
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., and Haffner, P., Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86:2278–2323, 1998. https://doi.org/10.1109/5.726791.
Bashivan, P., Rish, I., Yeasin, M., and Codella, N., Learning representations from EEG with deep recurrent-convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06448, 2015.
Talo, M., Baloglu, U. B., Yildirim, O., and Acharya, U. R., Application of deep transfer learning for automated brain abnormality classification using MR images. Cogn. Syst. Res., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.12.007.
Bhat, S., Acharya, U. R., Hagiwara, Y., Dadmehr, N., and Adeli, H., Parkinson’s disease: Cause factors, measurable indicators, and early diagnosis. Comput. Biol. Med., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.09.008.
Acharya, U. R., Vinitha Sree, S., Swapna, G., Martis, R. J., and Suri, J. S., Automated EEG analysis of epilepsy: A review. Knowledge-Based Syst 45:147–165, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2013.02.014.
Janga Vijaykumar, P., and Sreenivasareddy, E., A review on Machine Learning Techniques for Neurological disorders estimation by Analyzing EEG Waves. Int J Trend Sci Res Dev., 2018.
Acharya, U. R., Hagiwara, Y., Deshpande, S. N., Suren, S., Koh, J. E. W., Oh, S. L., Arunkumar, N., Ciaccio, E. J., and Lim, C. M., Characterization of focal EEG signals: A review. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst., 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.08.044.
Petrosian, A., Prokhorov, D., Homan, R., Dasheiff, R., and Wunsch, D., Recurrent neural network based prediction of epileptic seizures in intra- and extracranial EEG. Neurocomputing., 2000. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-2312(99)00126-5.
Mirowski, P., Madhavan, D., LeCun, Y., and Kuzniecky, R., Classification of patterns of EEG synchronization for seizure prediction. Clin. Neurophysiol., 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2009.09.002.
Acharya, U. R., Oh, S. L., Hagiwara, Y., Tan, J. H., and Adeli, H., Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 100:270–278, 2018.
Wulsin, D. F., Gupta, J. R., Mani, R., Blanco, J. A., and Litt, B., Modeling electroencephalography waveforms with semi-supervised deep belief nets: Fast classification and anomaly measurement. J. Neural Eng., 2011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/8/3/036015.
Stober, S., Sternin, A., Owen, A. M., and Grahn, J. A., Deep feature learning for EEG recordings. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.04306, 2015.
Yıldırım, Ö., Baloglu, U. B., and Acharya, U. R., A deep convolutional neural network model for automated identification of abnormal EEG signals. Neural Comput. & Applic.:1–12, 2018.
Ding, S., Zhang, N., Xu, X., Guo, L., and Zhang, J., Deep Extreme Learning Machine and Its Application in EEG Classification. Math. Probl. Eng., 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/129021.
Jirayucharoensak, S., Pan-Ngum, S., and Israsena, P., EEG-Based Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning Network with Principal Component Based Covariate Shift Adaptation. Sci. World J., 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/627892.
Supratak, A., Dong, H., Wu, C., and Guo, Y., DeepSleepNet: A model for automatic sleep stage scoring based on raw single-channel EEG. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng., 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2017.2721116.
Oh, S. L., Ng, E. Y. K., Tan, R. S., and Acharya, U. R., Automated diagnosis of arrhythmia using combination of CNN and LSTM techniques with variable length heart beats. Comput. Biol. Med., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.06.002.
Yildirim, Ö., A novel wavelet sequence based on deep bidirectional LSTM network model for ECG signal classification. Comput. Biol. Med., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.03.016.
Yıldırım, Ö., Pławiak, P., Tan, R. S., and Acharya, U. R., Arrhythmia detection using deep convolutional neural network with long duration ECG signals. Comput. Biol. Med., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.09.009.
Sharma, M., Achuth, P. V., Deb, D., Puthankattil, S. D., and Acharya, U. R., An automated diagnosis of depression using three-channel bandwidth-duration localized wavelet filter bank with EEG signals. Cogn. Syst. Res., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.07.010.
Bairy, G. M., Lih, O. S., Hagiwara, Y., Puthankattil, S. D., Faust, O., Niranjan, U. C., and Acharya, U. R., Automated diagnosis of depression electroencephalograph signals using linear prediction coding and higher order spectra features. J Med Imaging Health Inform 7(8):1857–1862, 2017.
Mumtaz, W. et al., Electroencephalogram (EEG)-based computer-aided technique to diagnose major depressive disorder (MDD). Biomed Signal Process Control 31:108–115, 2017.
Liao, S. C., Te, W. C., Huang, H. C., Cheng, W. T., and Liu, Y. H., Major depression detection from EEG signals using kernel eigen-filter-bank common spatial patterns. Sensors (Switzerland), 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17061385.
Bachmann, M. et al., Methods for classifying depression in single channel EEG using linear and nonlinear signal analysis. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 155:11–17, 2018.
Puthankattil, S. D., and Joseph, P. K., Classification of eeg signals in normal and depression conditions by ann using rwe and signal entropy. J Mech Med Biol., 2012. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra90093c.
Acharya, U. R., Oh, S. L., Hagiwara, Y., Tan, J. H., Adeli, H., and Subha, D. P., Automated EEG-based screening of depression using deep convolutional neural network. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.04.012.
Bengio, Y., Simard, P., and Frasconi, P., Learning Long-Term Dependencies with Gradient Descent is Difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw., 1994. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.279181.
Hochreiter, S., and Schmidhuber, J. J., Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9:1–32, 1997. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735.
Oh, S. L., Ng, E. Y., Tan, R. S., and Acharya, U. R., Automated beat-wise arrhythmia diagnosis using modified U-net on extended electrocardiographic recordings with heterogeneous arrhythmia types. Comput. Biol. Med., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.12.012.
Martinez-Murcia, F. J., Górriz, J. M., Ramírez, J., and Ortiz, A., Convolutional Neural Networks for Neuroimaging in Parkinson’s Disease: Is Preprocessing Needed? Int. J. Neural Syst., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129065718500351.
Pławiak, P., and Acharya, U. R., Novel Deep Genetic Ensemble of Classifiers for Arrhythmia Detection Using ECG Signals. Neural Comput. & Applic., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-03980-2.
Yildirim, O., Tan, R. S., and Acharya, U. R., An efficient compression of ECG signals using deep convolutional autoencoders. Cogn. Syst. Res., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.07.004.
Antoniades, A., Spyrou, L., Martin-Lopez, D., Valentin, A., Alarcon, G., Sanei, S., and Took, C. C., Deep Neural Architectures for Mapping Scalp to Intracranial EEG. Int. J. Neural Syst., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129065718500090.
Książek, W., Abdar, M., Acharya, U. R., and Pławiak, P., A novel machine learning approach for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cogn. Syst. Res., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.12.001.
Yuan, Q., Zhou, W., Xu, F., Leng, Y., and Wei, D., Epileptic EEG Identification via LBP Operators on Wavelet Coefficients. Int. J. Neural Syst., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129065718500107.
Pławiak, P., Novel genetic ensembles of classifiers applied to myocardium dysfunction recognition based on ECG signals. Swarm Evol Comput., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2017.10.002.
Li, Y., Cui, W., Luo, M., Li, K., and Wang, L., Epileptic seizure detection based on time-frequency images of EEG signals using Gaussian mixture model and gray level co-occurrence matrix features. Int. J. Neural Syst.:1850003, 2018.
Yuan, S., Zhou, W., and Chen, L., Epileptic Seizure Prediction Using Diffusion Distance and Bayesian Linear Discriminate Analysis on Intracranial EEG. Int. J. Neural Syst. 28(01):1750043, 2018.
Abdar, M., Zomorodi-Moghadam, M., Zhou, X., Gururajan, R., Tao, X., Barua, P. D., and Gururajan, R., A new nested ensemble technique for automated diagnosis of breast cancer. Pattern Recogn. Lett., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2018.11.004.
Abdar, M., Using Decision Trees in Data Mining for Predicting Factors Influencing of Heart Disease. Carpathian Journal of Electronic & Computer Engineering 8(2), 2015.
Ahmadlou, M., Adeli, H., and Adeli, A., Fractality analysis of frontal brain in major depressive disorder. Int. J. Psychophysiol., 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2012.05.001.
Faust, O., Aang, P. C. A., Puthankattil, S. D., and Joseph, P. K., Depression diagnosis support system based on eeg signal entropies. J Mech Med Biol., 2014. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219519414500353.
Acharya, U. R., Sudarshan, V. K., Adeli, H., Santhosh, J., Koh, J. E. W., Puthankatti, S. D., and Adeli, A., A novel depression diagnosis index using nonlinear features in EEG signals. Eur. Neurol. 74:79–83, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1159/000438457.
Hecht, D., Depression and the hyperactive right-hemisphere. Neurosci. Res. 68(2):77–87, 2010.
Yildirim, O., Baloglu, U. B., and Acharya, U. R., A deep learning model for automated sleep stages classification using psg signals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16(4):599, 2019.
Faust, O., Hagiwara, Y., Hong, T. J., Lih, O. S., and Acharya, U. R., Deep learning for healthcare applications based on physiological signals: A review. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 161:1–13, 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this work.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. We have obtained the ethical approval for depression data from Medical College Calicut, Kerala, India.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Image & Signal Processing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ay, B., Yildirim, O., Talo, M. et al. Automated Depression Detection Using Deep Representation and Sequence Learning with EEG Signals. J Med Syst 43, 205 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1345-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1345-y