Abstract
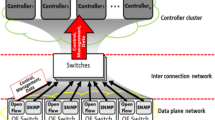
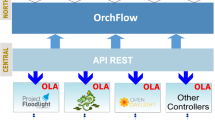
Software defined networking (SDN) provides great flexibility by decoupling the control and the data planes, allowing for the implementation of new and innovative network control plane experiments. Presently, the reference implementation for SDN architecture is reliant upon a single controller to push flow rules to all SDN-enabled switches in the network, creating a performance bottleneck and single-point of failure in large networks. To provide a scalable yet efficient solution to distributed SDN network management, we propose FlowBroker, a hierarchical brokering agent layer which manages and coordinates among distributed SDN controllers, where each controller is charged with the flow-rule maintenance of the switches in its managed domain. This paper proposes the FlowBroker architecture as a collaborative multi-domain approach to load balancing and network performance enhancement in software-defined networks. Moreover, we introduce distributed machine learning agents to allow controllers to evaluate which brokers are more advantageous than others, from a performance-based reputation perspective. Simulation results show that the FlowBroker architecture, with broker-based collaborative load-balancing and controller-based distributed reputation, can significantly increase the network performance of a multi-domain software-defined network. FlowBroker yields significant reductions in traffic loss, end-to-end delay and maximum link utilization when cooperative brokering and reputation are utilized.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Committee, O.M.E.: Software-Defined Networking: The New Norm for Networks. ONF White Paper. Palo Alto, US: Open Networking Foundation, (2012)
Reitblatt, M. et al: Consistent updates for software-defined networks: Change you can believe in! In Proceedings of the 10th ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks, ACM (2011)
OpenFlow Swtich Specification v1.3.2
McKeown, N., et al.: OpenFlow: enabling innovation in campus networks. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 38(2), 69–74 (2008)
Kim, H., Feamster, N.: Improving network management with software defined networking. Commun. Mag. IEEE 51(2), 114–119 (2013)
Yeganeh, S.H., Tootoonchian, A., Ganjali, Y.: On scalability of software-defined networking. Commun. Mag. IEEE 51(2), 136–141 (2013)
De Turck, F., Kiriha, Y., Hong, J.W.-K.: Management of the future internet: status and challenges. J. Netw. Syst. Manage. 20(4), 616–624 (2012)
Yoo, S.J.B. Multi-domain cognitive optical software defined networks with market-driven brokers. In 40th European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication. Cannes, France (2014)
Marconett, D., Liu, L., and Yoo, S.: Optical FlowBroker: load-balancing in software-defined multi-domain optical networks. In Optical Fiber Communication Conference. Optical Society of America (2014)
Tootoonchian, A. and Ganjali Y.: Hyperflow: a distributed control plane for openflow. In Proceedings of the 2010 internet network management conference on Research on enterprise networking. USENIX Association (2010)
Gude, N., et al.: NOX: towards an operating system for networks. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 38(3), 105–110 (2008)
Stribling, J., et al.: Flexible, wide-area storage for distributed systems with WheelFS. NSDI 9, 43 (2009)
Sherwood, R. et al.: Flowvisor: A network virtualization layer. OpenFlow Switch Consortium, Tech. Rep (2009)
Macapuna, C.A., Rothenberg, C.E., and Magalhaes, M.F. In-packet Bloom filter based data center networking with distributed OpenFlow controllers. In GLOBECOM Workshops (GC Wkshps), 2010 IEEE. (2010)
Phan, X.T., Thoai N., and Kuonen P. A.: Collaborative model for routing in multi-domains OpenFlow networks. In Computing, Management and Telecommunications (ComManTel), 2013 International Conference on IEEE. (2013)
Curtis, A.R., et al.: DevoFlow: scaling flow management for high-performance networks. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. ACM 41, 254 (2011)
Heller, B., Sherwood R., and McKeown N.: The controller placement problem. In Proceedings of the first workshop on Hot topics in software defined networks. ACM (2012)
Luo, T. et al.: Enhancing responsiveness and scalability for OpenFlow networks via control-message quenching. In ICT Convergence (ICTC), 2012 International Conference on. IEEE (2012)
Rubio-Loyola, J., et al.: Scalable service deployment on software-defined networks. Commun. Mag. IEEE 49(12), 84–93 (2011)
Levin, D. et al.: Logically centralized? State distribution trade-offs in software defined networks. In Proceedings of the first workshop on Hot topics in software defined networks. ACM (2012)
Cormen, T., Leiserson, C., Rivest, R., Stein, C.: Section 24.3: Dijkstra’s algorithm, in Introduction to Algorithms. pp. 595–60. MIT Press and McGraw–Hill. (2001)
Tootoonchian, A. et al.: On controller performance in software-defined networks. In USENIX Workshop on Hot Topics in Management of Internet, Cloud, and Enterprise Networks and Services (Hot-ICE) (2012)
Fukunaga, K.: Introduction to statistical pattern recognition. Academic press, Waltham (1990)
McLachlan, G.: Discriminant analysis and statistical pattern recognition (Vol. 544), Wiley, Hoboken (2004)
Nicholes, M.O., et al.: Analysis of inter-domain collaborative routing: provider competition for clients. J. Commun. Netw. 13(5), 499–510 (2011)
Mininet. http://mininet.org
Floodlight. http://floodlight.openflowhub.org
Anand, A., Sekar, V., Akella, A.: SmartRE: an architecture for coordinated network-wide redundancy elimination. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. ACM 39, 87 (2009)
Hua, Y., Liu, X., and Feng, D. Smart in-network deduplication for storage-aware SDN. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM 2013 Conference on SIGCOMM. ACM (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marconett, D., Yoo, S.J.B. FlowBroker: A Software-Defined Network Controller Architecture for Multi-Domain Brokering and Reputation. J Netw Syst Manage 23, 328–359 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-014-9325-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-014-9325-5