Abstract
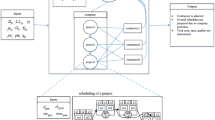
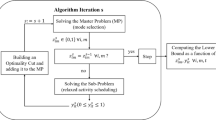
We study an assignment type resource-con- strained project scheduling problem with resources being multi-skilled personnel to minimize the total staffing costs. We develop a hybrid Benders decomposition (HBD) algorithm that combines the complimentary strengths of both mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) and constraint programming (CP) to solve this NP-hard optimization problem. An effective cut-generating scheme based on temporal analysis in project scheduling is devised for resolving resource conflicts. The computational study shows that our hybrid MILP/CP algorithm is both effective and efficient compared to the pure MILP or CP method alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Aksin, O. Z., Karaesmen, F., & Ormeci, E. L. (2006). A review of workforce cross-training in call centers from an operations management perspective. In D. Nembhard (Ed.), Workforce cross training handbook. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Baptiste, P., Le Pape, C., & Nuijten, W. (2001). Constraint-based scheduling: applying constraint programming to scheduling problems. New York: Springer.
Bartusch, M., Mohring, R. H., & Randermacher, F. J. (1988). Scheduling project networks with resource constraints and time windows. Annals of Operations Research, 16, 201–240.
Bellenguez, O., & Neron, E. (2004). Methods for solving the multi-skill project scheduling problem. In Proceedings of the ninth international workshop on project management and scheduling, Nancy, France.
Benders, J. F. (1962). Partition procedures for solving mixed variables programming problems. Numerische Mathematik, 4, 238–252.
Benoist, T., Laburthe, F., & Rotternbourg, B. (2001). Lagrange relaxation and constraint programming collaborative schemes for traveling tournament problems. In Integration of AI and OR techniques in constraint.
Benoist, T., Gaudin, E., & Rotternbourg, B. (2002). Constraint programming contribution to Benders decomposition: A case study. In The eighth international conference on principles and practice of constraint programming, Ithaca, New York.
Bockmayr, A., & Kasper, T. (1998). A unifying framework for integer and finite domain constraint programming. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 10(3), 287–300.
Brucker, P. (2001). Scheduling algorithms. Berlin: Springer.
Brucker, P. (2002). Scheduling and constraint propagation. Discrete Applied Mathematicsu, 123(1–3), 227–256.
Brucker, P., & Knust, S. (1998). Solving large-sized resource-constrained project scheduling problems. In J. Weglarz (Ed.), Project scheduling: recent models, algorithms and applications. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Brucker, P., & Knust, S. (2000). A linear programming and constraint propagation-based lower bound for the RCPSP. European Journal of Operational Research, 127(2), 335–362.
Brucker, P., & Knust, S. (2003). Lower bounds for resource-constrained project scheduling problems. European Journal of Operational Research, 149, 302–313.
Brucker, P., Drexl, A., Mohring, R. H., Neumann, K., & Pesch, E. (1999). Resource-constrained project scheduling: Notation, classification, models and methods. European Journal of Operational Research, 112(1), 3–41.
Dechter, R., Meiri, I., & Pearl, J. (1991). Temporal constraint networks. Artificial Intelligence, 49(1–3), 61–95.
Dincbas, M., Van Hentenryck, P., Simonis, H., & Aggoun, A. (1988). The constraint logic programming language CHIP. In Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on fifth generation computer systems.
Drexl, A., & Kimms, A. (2001). Optimization guided lower and upper bounds for the resource investment problem. Journal of Operational Research Society, 52, 340–351.
Drexl, A., Juretzka, J., Salewski, F., & Schirmer, A. (1998). New modeling concepts and their impact on resource-constrained project scheduling. In J. Weglarz (Ed.), Project scheduling: recent models, algorithms and applications. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Easton, K., Nemhauser, G., & Trick, M. (2004). CP based branch–and–price. In M. Milano (Ed.), Constraint and integer programming. Berlin: Springer.
Eremin, A., & Wallace, M. (2001). Hybrid Benders decomposition algorithms in constraint logic programming. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2239, 1–15.
Focacci, F., Laborie, P., & Nuijten, W. (2000). Solving scheduling problems with setup times and alternative resources. In Proceedings of the fifth international conference on artificial intelligence planning and scheduling.
Fox, M. (2006). Planning for mixed discrete continuous domains. In J. C. Beck & B. M. Smith (Eds.), Lecture notes in computer science: Vol. 3990. CPAIOR 2006 (p. 2). Berlin: Springer.
Fox, M., & Long, D. (2001). Hybrid STAN: Identifying and managing combinatorial optimization sub-problems in planning. In Proceedings of the international joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI).
Fox, M., & Long, D. (2003). PDDL2.1: An extension to PDDL for expression temporal planning domains. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 20, 61–124.
Frank, J., & Kurklu, E. (2005). Mixed discrete and continuous algorithms for scheduling airborne astronomy observations. In R. Batak & M. Milano (Eds.), Lecture notes in computer science: Vol. 3524. CPAIOR 2005 (pp. 183–200). Berlin: Springer.
Harvey, W., & Ginsberg, M. (1995). Limited discrepancy search. In The fourteenth international joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI-95).
Hooker, J. (2000). Logic-based methods for optimization: combining optimization and constraint satisfaction. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
Hooker, J. (2002). Logic, optimization and constraint programming. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 14(4), 285–321.
Hooker, J., & Osorio, M. (1999). Mixed logical-linear programming. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 96–97, 395–442.
ILOG (2002a). ILOG Solver 5.3 User’s Manual.
ILOG (2002b). ILOG CPLEX 8.1 User’s Manual.
ILOG (2002c). OPL Studio 3.6.1 User’s Manual: ILOG, Inc.
Jain, V., & Grossmann, I. (2001). Algorithms for hybrid MILP/CP models for a class of optimization problems. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 13(4), 258–276.
Jasen, K. (1999). An approximation scheme for bin packing with conflicts. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 3, 363–377.
Joslin, D. E., & Clements, D. P. (1999). “Squeaky Wheel” optimization. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 10, 353–373.
Lasdon, L. S. (1970). Optimization theory for large systems. New York: Macmillan Co.
Li, H., & Womer, K. (2006a). Determining crew composition for a new technology (Working Paper).
Li, H., & Womer, K. (2006b). Project scheduling with multi-purpose resources: a combined MILP/CP decomposition approach. International Journal of Operations and Quantitative Management, 12(4), 305–325.
Li, H., & Womer, K. (2008). Modeling the supply chain configuration problem under resource constraints. International Journal of Project Management, 26(6), 646–654.
Milano, M., & Trick, M. (2004). Constraint and integer programming. In M. Milano (Ed.), Constraint and integer programming: toward a unified methodology. Berlin: Springer.
Nemhauser, G., & Wolsey, L. (1988). Integer and combinatorial optimization. New York: Wiley.
Neron, E., Bellenguez, O., & Heurtebise, M. (2006). Decomposition method for solving multi-skill project scheduling problem. In Proceedings of the tenth international workshop on project management and scheduling, Poznan.
Neumann, K., Schwindt, C., & Zimmermann, J. (2002). Project scheduling with time windows and scarce resources: temporal and resource-constrained project scheduling with regular and nonregular objective functions. New York: Springer.
Schwindt, C. (1996). Generation of resource-constrained project scheduling problems with minimal and maximal time lags (Technical Report WIOR-489). Institute für Wirtschaftstheorie und Operations Research, University of Karlsruhe.
Sellmann, M., & Fahle, T. (2003). Constraint programming based Lagrangian relaxation for the automatic recording problem. Annals of Operations Research, 118, 17–33.
Thesen, A. (1977). Measures of the restrictiveness of project networks. Networks, 7, 193–208.
Thorsteinsson, E. S. (2001). Branch–and–check: A hybrid framework integrating mixed integer programming and constraint logic programming. In Proceedings of the seventh international conference on principles and practices of constraint programming (CP-01). Berlin: Springer.
Tsang, E. (1993). Foundations of constraint satisfaction. San Diego: Academic Press.
Van Hentenryck, P. (1999). The OPL optimization programming language. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Wah, B. W., & Chen, Y. (2006). Constraint partitioning in penalty formulations for solving temporal planning problems. Artificial Intelligence, 170, 187–231.
Wallace, M., Novello, S., & Schimpf, J. (1997). ECLiPSe: A platform for constraint logic programming. Available from: http://www.icparc.ic.ac.uk/eclipse/reports/eclipse/eclipse.html.
Xing, Z., Chen, Y., & Zhang, W. (2006). An efficient hybrid strategy for temporal planning. In J. C. Beck & B. M. Smith (Eds.), Lecture notes in computer science: Vol. 3990. CPAIOR 2006 (pp. 273–287). Berlin: Springer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Womer, K. Scheduling projects with multi-skilled personnel by a hybrid MILP/CP benders decomposition algorithm. J Sched 12, 281–298 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10951-008-0079-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10951-008-0079-3