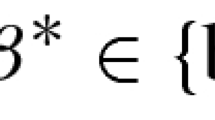Abstract
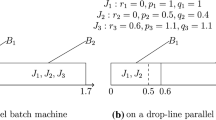
In this paper, we study unbounded parallel-batch scheduling with drop-line tasks to minimize a regular objective function, where by “drop-line tasks” we mean that the completion time of each task (job) is equal to the sum of the starting time of the batch containing the task and the processing time of the task. In the problems considered in this paper, we assume that the tasks have individual release dates and the general regular objective function to be minimized is either of the sum-form or of the max-form. We then study the computational complexity of these problems on an unbounded parallel-batch processor. We show that (i) the problems are binary NP-hard and are solvable in pseudo-polynomial times, and (ii) when the number of processing times or release dates is a constant, the problems are solvable in polynomial times. We also point out some consequences of approximation algorithms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brucker, P., Gladky, A., Hoogeveen, H., Kovalyov, M. Y., Potts, C. N., Tautenhahn, T., et al. (1998). Scheduling a batching machine. Journal of Scheduling, 1, 31–54.
Cheng, T. C. E., Liu, Z. H., & Yu, W. C. (2001). Scheduling jobs with release dates and deadlines on a batch processing machine. IIE Transaction, 33, 685–690.
Cheng, T. C. E., Ng, C. T., Yuan, J. J., & Liu, Z. H. (2004). Single machine parallel batch scheduling subject to precedence constraints. Naval Research Logistics, 51, 949–958.
Deng, X., Feng, H., Zhang, P., Zhang, Y., & Zhu, H. (2004). Minimizing mean completion time in a batch processing system. Algorithmica, 38, 513–528.
Dobson, G., & Nambimadom, R. S. (2001). The batch loading and scheduling problem. Operations Research, 49, 52–65.
Fan, B. Q., Yuan, J. J., & Li, S. S. (2012). Bi-criteria scheduling on a single parallel-batch machine. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 36, 1338–1346.
Feng, Q., Yuan, J. J., Liu, H. L., & He, C. (2013). A note on two-agent scheduling on an unbounded parallel-batching machine with makespan and maximum lateness objectives. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 37, 7071–7076.
Graham, R. L., Lawler, E. L., Lenstra, J. K., & Rinnooy Kan, A. H. G. (1979). Optimization and approximation in deterministic sequencing and scheduling: A survey. Annals of Discrete Mathematics, 5, 287–326.
Garey, M. R., & Johnson, D. S. (1979). Computers and intractability: A guide to the theory of NP-completeness. San Francisco, CA: Freeman.
Geng, Z. C., & Yuan, J. J. (2015). A note on unbounded parallel-batch scheduling. Information Processing Letters, 115, 969–974.
Hall, N. G., & Potts, C. N. (2003). Supply chain scheduling: Batch and delivery. Operations Research, 51, 566–583.
He, C., Lin, Y. X., & Yuan, J. J. (2007). Bicriteria scheduling on a batching machine to minimize maximum lateness and makespan. Theoretical Computer Science, 381, 234–240.
Lee, C. Y., & Chen, Z. L. (2001). Machine scheduling with transportation considerations. Journal of Scheduling, 4, 3–24.
Lee, C. Y., & Uzsoy, R. (1999). Minimizing makespan on a single batch processing machine with dynamic job arrivals. International Journal of Production Research, 37, 219–236.
Lee, C. Y., Uzsoy, R., & Martin-Vega, L. A. (1992). Efficient algorithms for scheduling semiconductor burn-in operations. Operations Research, 40, 764–775.
Li, S. S., & Yuan, J. J. (2012). Unbounded parallel-batching scheduling with two competitive agents. Journal of Scheduling, 15, 629–640.
Liu, Z. H., & Cheng, T. C. E. (2005). Approximation schemes for minimizing total (weighted) completion time with release dates on a batch machine. Theoretical Computer Science, 347, 288–298.
Liu, Z. H., Yuan, J. J., & Cheng, T. C. E. (2003). On scheduling an unbounded batch machine. Operations Research Letters, 31, 42–48.
Mathirajan, M., & Sivakumar, A. I. (2006). A literature review, classification and simple meta-analysis on scheduling of batch processors in semiconductor. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 29, 990–1001.
Potts, C. N., & Kovalyov, M. Y. (2000). Scheduling with batching: A review. European Journal of Operational Research, 120, 228–249.
Sabouni, M. T. Y., & Jolai, F. (2010). Optimal methods for batch processing problem with makespan and maximum lateness objectives. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 34, 314–324.
Tang, L. X., & Gong, H. (2009). The coordination of transportation and batching scheduling. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 33, 3854–3862.
Tian, J., Wang, Q., Fu, R. Y., & Yuan, J. J. (2016). Online scheduling on the unbounded drop-line batch machines to minimize the maximum delivery completion time. Theoretical Computer Science, 617, 65–68.
Webster, S. T., & Baker, K. R. (1995). Scheduling groups of jobs on a single machine. Operations Research, 43, 692–703.
Wei, Z. G. (2011). Scheduling on a batch machine with item-availability to minimize total weighted completion time. Master Degree Thesis, Zhengzhou University.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the associate editor and two anonymous referees for their constructive comments and helpful suggestions. This research was supported by NSFC (11671368), NSFC (11771406), and NSFC (11571323).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Yuan, J. & Wei, Z. Unbounded parallel-batch scheduling with drop-line tasks. J Sched 22, 449–463 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10951-018-0586-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10951-018-0586-9