Abstract
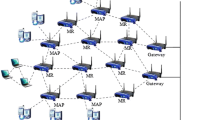
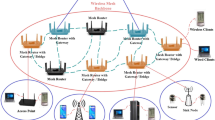
Wireless mesh networks recently emerge as a flexible, low-cost and multipurpose networking platform with wired infrastructure connected to the Internet. A critical issue in mesh networks is to maintain network activities for a long lifetime with high energy efficiency. As more and more outdoor applications require long-lasting, high energy efficient and continuously-working mesh networks with battery-powered mesh routers, it is important to optimize the performance of mesh networks from a battery-aware point of view. Recent study in battery technology reveals that discharging of a battery is nonlinear. Batteries tend to discharge more energy than needed, and reimburse the over-discharged energy later if they have sufficiently long recovery time. Intuitively, to optimize network performance, a mesh router should recover its battery periodically to prolong the lifetime. In this paper, we introduce a mathematical model on battery discharging duration and lifetime for wireless mesh networks. We also present a battery lifetime optimization scheduling algorithm (BLOS) to maximize the lifetime of battery-powered mesh routers. Based on the BLOS algorithm, we further consider the problem of using battery powered routers to monitor or cover a few hot spots in the network. We refer to this problem as the Spot Covering under BLOS Policy problem (SCBP). We prove that the SCBP problem is NP-hard and give an approximation algorithm called the Spanning Tree Scheduling (STS) to dynamically schedule mesh routers. The key idea of the STS algorithm is to construct a spanning tree according to the BLOS Policy in the mesh network. The time complexity of the STS algorithm is O(r) for a network with r mesh routers. Our simulation results show that the STS algorithm can greatly improve the lifetime, data throughput and energy consumption efficiency of a wireless mesh network.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz I, Wang X, Wang W (2005) Wireless mesh networks: a survey. Comput Networks 47:445–487
Bruno R, Conti M, Gregori E (2005) Mesh networks: commodity multihop ad hoc networks. IEEE Commun 43:123–131
Ma C, Ma M, Yang Y (2007) A battery aware scheme for energy efficient coverage and routing in wireless MIMO mesh networks. In: Proc. IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), Hong Kong, 11–15 March 2007
Lee K-D, Leung VCM (2006) Low-latency broadcast in multirate wireless mesh networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 24(11):2051–2060
Google Inc (2008) Google Wifi. http://wifi.google.com/
Suffolk County Government (2007) Wireless broadband initiative. http://www.co.suffolk.ny.us/wireless/pdfs/LIWirelessBroadbandInitRFP.pdf
Draves R, Padhye J, Zill B (2004) Routing in multi-radio, multi-hop wireless mesh networks. In: Proc. ACM MobiCom ’04, pp 114–128, Philadelphia, 26 September–1 October 2004
Barry J, Lee E, Messerschmitt D (2003) Digital communication, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Aguayo D, Bicket J, Biswas S, De Couto DSJ, Morris R (2003) MIT roofnet implementation. http://pdos.lcs.mit.edu/roofnet/design/
Firetide Networks Inc (2008) Firetide. http://www.firetide.com/
Rakhmatov D, Vrudhula S (2003) Energy management for battery-powered embedded systems. ACM Trans Embed Comput Syst 2(3):277–324
Yang Y, Ma C (2005) Battery aware-routing in wireless ad hoc networks – part I: energy model. In: Proc. 19th international teletraffic congress (ITC-19), pp 293–302, Beijing, 29 August–2 September 2005
Ma C, Yang Y (2005) Battery aware routing in wireless ad hoc networks - part II: battery-aware routing. In: Proc. 19th international teletraffic congress (ITC-19), pp 303–312, Beijing, 29 August–2 September 2005
Rakhmatov DN, Vrudhula SBK (2001) An analytical high-level battery model for use in energy management of portable electronic systems. In: Proc. 2001 IEEE/ACM int’l conf. computer-aided design, pp 488–493, San Jose, 4–8 November 2001
Doyle M, Fuller TF, Newman J (1993) Modeling of galvanostatic charge and discharge of the lithium/polymer/insertion cell. J Electrochem Soc 140(6):1526–1533
Panigrahi D et al (2001) Battery life time estimation of mobile embedded systems. In: Proc. 14th int’l conf. VLSI design. IEEE Computer Society, Silver Spring, pp 57–63
Rao R, Vrudbula S, Rakbmatov DN (2003) Battery modeling for energy-aware system design. IEEE Comput 36:77–87
Garey MR, Johnson DS (1978) Computers and intractability: a guide to the theory of NP-completeness. Freeman, Nashville
Cormen T, Leiserson C, Rivest R, Stein C (2001) Introduction to algorithms, 2nd edn. MIT, Cambridge
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The research work was supported in part by the U.S. National Science Foundation under grant numbers CCR-0207999 and ECS-0427345 and U.S. Army Research Office under grant number W911NF-04-1-0439.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, C., Zhang, Z. & Yang, Y. Battery-Aware Scheduling in Wireless Mesh Networks. Mobile Netw Appl 13, 228–241 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-008-0032-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-008-0032-x