Abstract
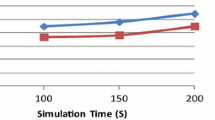
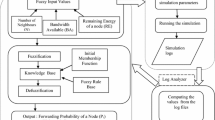
The control and routing performances of mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) depend upon the efficiency of the network-wide broadcasting schemes that are in place. Ad hoc networks are often characterized by poor infrastructure quality, limited resources, dynamic variation and a need for mobility; therefore, ease of deployment, adaptability and potential for energy-savings are the primary drivers considered in the design of typical broadcasting schemes. This paper proposes a distributed intelligent broadcasting protocol (DIBP) that is capable of dynamically determining the broadcasting nodes in a MANET, based upon the distribution of network nodes. This eliminates the need for active network monitoring and periodical maintenance is not required. In addition, the distributed intelligent broadcasting protocol employs an adjustable parameter for determining the broadcasting node, broadcasting timing and the number of broadcasting nodes. This parameter can be changed dynamically based on different operational requirements; such as energy savings, hop count, network delay and other similar targets. Simulations of networks employing the protocol yield results showing that the DIBP performs better in terms of delivery delay, number of rebroadcast nodes, and delivery ratio.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Committee IS (1997) Wireless LAN medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications. IEEE 802.11 Standard. IEEE, New York
Broch J, Maltz D, Johnson D, Hu Y, Jetvheva J (1998) Multi-hop wireless ad hoc network routing protocols. MOBICOM 1998:85–97
Camp T, Boleng J, Davies VA (2002) Survey of mobility models for ad hoc network research. wireless comm. & mobile computing (WCMC), special issue on mobile ad hoc networking: research, trends and applications 2(5):483–502
Chen B, Jamieson K, Balakrishnan H, Morris R (2001) Span: an energy-efficient coordination algorithm for topology maintenance in ad hoc wireless networks. MOBIHOC 2001:85–96
Dai F, Wu J (2004) Performance analysis of broadcast protocols in ad hoc networks based on self-pruning. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 15(11):1027–1040. doi:10.1109/TPDS.2004.69
Dai F, Wu J (2004) An extended localized algorithm for connected dominating set formation in ad hoc wireless networks. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 15(10):908–920. doi:10.1109/TPDS.2004.48
Feeney LM, Nilsson M (2001) Investigating the energy consumption of a wireless network interface in an ad hoc networking environment. INFOCOM 2001, Apr
Ho C, Obraczka K, Tsudik G, Viswanath K (1999) Flooding for reliable multicast in multi-hop ad hoc networks. International Workshop on Discrete Algorithms and Methods for Mobile Computing and Communication (DIALM)
Jetcheva J, Hu Y, Maltz D, Johnson D (2001) A simple protocol for multicast and broadcast in mobile ad hoc networks. Internet draft: draft-ietf-manet-simple-mbcast-01.txt. July
Johnson DB, Maltz DA (1996) Dynamic source routing in ad-hoc wireless networks. In: Imielinski T, Korth H (Eds) Mobile Computing, Chapter 5. Kluwer, pp 153–181
Ko YB, Vaidya NH (2000) Location-aided routing in mobile ad hoc networks. ACM Wireless Networks 6(4):307–321. doi:10.1023/A:1019106118419
Lim H, Kim C (2000) Multicast tree construction and flooding in wireless ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of the Third ACM International Workshop on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems (MSWiM). Aug
Lou W, Wu J (2002) On reducing broadcast redundancy in ad hoc wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 1(2):111–123. doi:10.1109/TMC.2002.1038347
Ni S, Tseng Y, Chen Y, Sheu J (1999) The broadcast storm problem in a mobile ad hoc network. ACM/IEEE International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking MOBICOM 151–162
Peng W, Lu X (2002) On the reduction of broadcast redundancy in mobile ad hoc networks. MOBIHOC 2000. Boston, MA, USA. doi:10.1109/MOBHOC.2002.869221
Peng W, Lu X (2002) AHBP: An efficient broadcast protocol for mobile ad hoc networks. Journal of Science and Technology—Beijing, China
Perkins CE, Royer EM (1999) Ad-hoc on-demand distance vector routing. Proc 2nd IEEE Wksp Mobile Comp Sys and App, 90–100, Feb
Qayyum A, Viennot L, Laouiti A (2000) Multipoint relaying: a efficient technique for flooding in mobile wireless networks. Technical Report 3898, INRIA—Rapport de recherché
Shen CC, Huang A, Jaikaeo C (2006) Directional broadcast for mobile ad hoc networks with percolation theory. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 5(4):317–332. doi:10.1109/TMC.2006.1599402
Sinha P, Sivakumar R, Bharghavan V (2001) Enhancing ad hoc routing with dynamic virtual infrastructures. INFOCOM 2001 3:1763–1772. Apr
Stojmenovic I, Seddigh M, Zunic J (2000) Dominating sets and neighbor elimination based broadcasting algorithms in wireless networks. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 13(1):14–25. doi:10.1109/71.980024
Tseng Y-C, Ni S-Y, Shih E-Y (2003) Adaptive approaches to relieving broadcast storms in a wireless multihop mobile ad hoc network. IEEE Trans Comput 52(5):545–557. doi:10.1109/TC.2003.1197122
Williams B, Camp T (2002) Comparison of broadcasting techniques for mobile ad hoc networks. MOBIHOC 2002. Lausanne, Switzerland. June
Wu J, Dai F (2003) Broadcasting in ad hoc networks based on self-pruning. IEEE INFOCOM 2240–2250
Wu J, Dai F (2005) Efficient broadcasting with guaranteed coverage in mobile ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 4(3):259–270. doi:10.1109/TMC.2005.40
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Science Council of the R.O.C. for financial support of this manuscript under Contract No. NSC-97-2221-E-030- 006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, HI. A Distributed Intelligent Broadcasting Protocol for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Mobile Netw Appl 14, 638–648 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-008-0147-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-008-0147-0