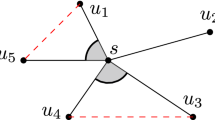
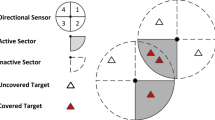
Abstract
This paper introduces a new wireless sensor network planning problem referred to as the Optimal Sensor Configuration (OSC) problem. In this problem, the goal is to find an optimal subset of locations where directional sensors and base stations are installed in order to minimize the total network cost while satisfying the requirements of coverage and connectivity. This goal is achieved by appropriately choosing the base station type and configuring each sensor to be installed in the sensor field. The optimal configuration of each sensor is determined by three parameters which are sensing range, field of view and orientation. The paper also gives an integer linear programming formulation of the OSC problem. The viability and effectiveness of the proposed formulation are illustrated through numerical results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soro S, Heinzelman WB (2005) On the coverage problem in video-based wireless sensor networks. In: Proc. international conference on broadband networks. IEEE, pp 932–939
Adriaens J, Megerian S, Potkonjak M (2006) Optimal worst-case coverage of directional field-of-view sensor networks. In: Proc. international conference on sensor and ad hoc communications and networks. IEEE, pp 336–345
Ai J, Abouzeid AA (2006) Coverage by directional sensors in randomly deployed wireless sensor networks. J Comb Optim 11(1):21–41
Chvatál V (1975) A combinatorial theorem in plane geometry. J Comb Theory Ser B 18:39–41
Fisk S (1975) A short proof of Chavtál’s watchman theorem. J Comb Theory Ser B 24:374
Marengonia M, Draperb BA, Hansona A, Sitaramana R (2000) A system to place observers on a polyhedral terrain in polynomial time. J Image Vis Comput 18:773–780
Horster E, Lienhart R (2006) Approximating optimal visual sensor placement. In: Proc. international conference on multimedia and expo. IEEE, pp 1257–1260
Horster E, Lienhart R (2006) On the optimal placement of multiple visual sensors. In: Proc. international workshop on video surveillance and sensor networks. ACM, New York, pp 111–120
Zhao J, Cheung S-CS (2007) Multi-camera surveillance with visual tagging and generic camera placement. In: Proc. international conference on distributed smart cameras. ACM/IEEE, New York, pp 259–266
Chakrabarty K, Sitharama S, Qi H, Cho E (2002) Grid coverage for surveillance and target location in distributed sensor networks. IEEE Trans Comput 51(12):1448–1453
Sahni S, Xu X (2005) Algorithms for wireless sensor networks. In: International journal of distributed sensor networks, vol 1, no 1. Taylor and Francis, London, pp 35–56
Wang J, Zhong N (2006) Efficient point coverage in wireless sensor networks. J Comb Optim 11(3):291–304
Berkelaar M, Notebaert P, Eikland K, Solve LP (2005) Linear programming code, ver 5.5. Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands
Xu X, Sahni S (2007,) Approximation algorithms for sensor deployment. IEEE Trans Comput 56(12):1681–1695
Han X, Cao X, Lloyd EL, Shen C-C (2008) Deploying directional sensor networks with guaranteed connectivity and coverage. In: Proc. sensor, mesh and ad hoc communications and networks. IEEE, pp 153–160
Cheng W, Li S, Liao X, Changxiang S, Chen H (2007) Maximal coverage scheduling in randomly deployed directional sensor networks. In: Proc. international conference on parallel processing workshops. IEEE, pp 68–73
Cai Y, Lou W, Li M, Li X-Y (2007) Target-oriented scheduling in directional sensor networks. In: Proc. international conference on computer communications. IEEE, Piscataway, pp 1550–1558
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osais, Y.E., St-Hilaire, M. & Yu, F.R. Directional Sensor Placement with Optimal Sensing Range, Field of View and Orientation. Mobile Netw Appl 15, 216–225 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-009-0179-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-009-0179-0