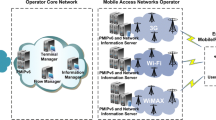
Abstract
IP multihoming is a networking concept with a deceptively simple definition in theory. In practice, however, multihoming has proved difficult to implement and optimize for. Moreover, it is a concept, which, once adopted in the core Internet architecture, has a significant impact on operation and maintenance. A trivial definition of multihoming would state that an end-node or an end-site has multiple first-hop connections to the network. In this paper, we survey and summarize in a comprehensive manner recent developments in IP multihoming. After introducing the fundamentals, we present the architectural goals and system design principles for multihoming, and review different approaches. We survey multihoming support at the application, session, transport, and network layers, covering all recent proposals based on a locator/identifier split approach. We critically evaluate multihoming support in these proposals and detail recent developments with respect to multihoming and mobility management.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arshad MJ, Mian MS (2008) Issues of multihoming implementation using FAST TCP: a simulation based analysis. Proc IJCSNS 8(9):104–114
Atkinson R, Bhatti S, Hailes S (2009) ILNP: mobility, multi-homing, localised addressing and security through naming. Telecommun Syst 42:273–291
Atkinson R, Bhatti S, Hailes S (2010) Evolving the internet architecture through naming. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 28(8):1319–1325
Bagnulo M, Garcia-Martinez A, Azcorra A (2007) IPv6 multihoming support in the mobile internet. IEEE Wirel Commun 14(5):92–98
Bagnulo M, Martinez AG, Azcorra A, de Launois C (2006) An incremental approach to IPv6 multihoming. Comput Commun 29(5):582–592
Budzisz L, Ferrús R, Brunstrom A, Grinnemo KJ, Fracchia R, Galante G, Casadevall F (2008) Towards transport-layer mobility: evolution of SCTP multihoming. Comput Commun 31(5):980–998
Dave M (2008) The locator identifier separation protocol (LISP). Internet Protocol J 11(1):23–36
De Launois C, Bagnulo M (2006) The paths toward IPv6 multihoming. Commun Surveys Tuts 8(2):38–51
Deleplace A, Ernst T, Noel T (2007) Multihoming in nested mobile networks with route optimization. In: Proc. SAINT, p 49
Dhraief A, Montavont N (2008) Toward mobility and multihoming unification—the Shim6 protocol: a case study. In: Proc. WCNC, pp 2840–2845
Espi J, Atkinson R, Andonovic I, Dunlop J (2009) Proactive route optimization for fast mobile IPv6. In: Proc. VTC-Fall, vol 6, pp 1–5
Fekete G (2010) Network interface management in mobile and multihomed nodes. PhD thesis, University of Jyväskyla, Faculty of Information Technology
Fekete G, Hämälänen T (2009) State of host-centric multihoming in IP networks. In: Proc. NTMS, pp 1–5
Fitzpatrick J, Murphy S, Atiquzzaman M, Murphy J (2009) Using cross-layer metrics to improve the performance of end-to-end handover mechanisms. Comput Commun 32(15):1600–1612
Ford A, Raiciu C, Barre S, Iyengar J (2011) Architectural guidelines for multipath TCP development. IETF request for comments: 6182
Garcia-Martinez A, Bagnulo M, Van Beijnum I (2010) The Shim6 architecture for IPv6 multihoming. IEEE Commun Mag 48(9):152–157
Gurtov A (2008) Host identity protocol (HIP): towards the secure mobile internet. Wiley Series
Gurtov A, Komu M, Moskowitz R (2009) Host identity protocol: identifier/locator split for host mobility and multihoming. Internet Protocol J 12(1):27–32
Habib A, Christin N, Chuang J (2007) Taking advantage of multihoming with session layer striping. In: Proc. INFOCOM, pp 1–6
Iyengar J, Amer P, Stewart R (2006) Concurrent multipath transfer using SCTP multihoming over independent end-to-end paths. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 14(5):951–964
Khare V, Jen D, Zhao X, Liu Y, Massey D, Wang L, Zhang B, Zhang L (2010) Evolution towards global routing scalability. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 28(8):1363–1375
Kim H, Choi S (2010) A method to support multiple interfaces a mobile node in next generation wireless network. In: Proc. NCM, pp 276–281
Komu M, Henderson T: Basic socket interface extensions for host identity protocol (HIP). IETF draft: draft-ietf-hip-native-api (work in progress) (2010)
Kong KS, Lee W, Han YH, Shin MK, You H (2008) Mobility management for al-IP mobile networks: mbile IPv6 vs. proxy mobile IPv6. Wirel Commun 15(2):36–45
Kuntz R (2007) Deploying reliable IPv6 temporary networks thanks to NEMO basic support and multiple care-of addresses reistration. In: Proc. SAINT, p 46
Li T (2011) Recommendation for a routing architecture. IETF request for comments: 6115
Menth M, Hartmann M, Klein D (2010) Global locator, local locator, and identifier split (GLI-split). Tech. Rep. 470, University of Würzburg, Institute of Computer Science
Mitsuya K, Kuntz R, Sugimoto S, Wakikawa R, Murai J (2007) A policy management framework for flow distribution on multihomed end nodes. In: Proc. MobiArch, pp 1–7
Moore T, Pym D, Ioannidis C (2010) Internet multi-homing problems: explanations from economics, 1st edn, chap 5. Springer, pp 67–78
Nováczki S, Bokor L, Jeney G, Imre S (2008) Design and evaluation of a novel HIP- bsed network mobility protocol. J Netw 3(1):10–24
de la Oliva A, Soto I, García-Martínez A, Bagnulo M, Azcorra A (2010) Analytical characterization of failure recovery in REAP. Computer Commun 33(4):485–499
Pan J, Jain R, Paul S, Bowman M, Chen S (2009) Enhanced MILSA architecture for naming, addressing, routing and security issues in the next generation internet. In: Proc. ICC, pp 1–6
Pan J, Paul S, Jain R, Bowman M (2008) MILSA: a mobility and multihoming supporting identifier locator split architecture for naming in the next generation internet. In: Proc. GLOBECOM, pp 1–6
Pan JY, Lin JL, Pan KF: Multiple care-of addresses registration and capacity-aware preference on multi-rate wireless links. In: Proc. AINA, pp 768–773 (2008)
Pierrel S, Jokela P, Melen J, Slavov K (2007) A policy system for simultaneous multiaccess with host identity protocol. In: Proc. ACNM, pp 71–77
Rathnayake U, Petander H, Ott M, Seneviratne A (2010) Protocol support for bulk transfer architecture. In: Proc. WCNIS, pp 598–602
Scharf M, Ford A (2011) MPTCP application interface considerations. IETF draft: draft-ietf-mptcp-api (work in progress)
Shinta S, RyoJi K, ToshiKane O (2006) A comparative analysis of multihoming solutions. Information Processing Society of Japan (IPSJ), pp 209–216
Sousa B, Pentikousis K, Curado M (2011) A multiple care of addresses model. In: to appear in Proc. ISCC
Templin F (2011) The internet routing overlay network (IRON). IETF request for comments: 6179
Thompson N, He G, Luo H (2006) Flow scheduling for end-host multihoming. In: Proc. INFOCOM, pp 1–12
Toseef U, Udugama A, Goerg C, Fan C, Pittmann F (2008) Realization of multiple access interface management and flow mobility in IPv6. In: Proc. MOBILWARE, pp 1–8
Tse R: TCP fairness in multipath transport protocols. Bachelor thesis, Brown University, Department of Computer Science (2006)
Tsirtsis G, Soliman H, Montavont N, Giaretta G, Kuladinithi K (2011) Flow bindings in mobile IPv6 and nemo basic support. IETF request for comments: 6089
Ubillos J, Xu M, Ming Z, Vogt C (2010) Name-Based Sockets Architecture. IETF Draft: draft-ubillos-name-based-sockets-03 (work in progress)
Viagenie MB, Seite P (2011) Multiple interfaces and provisioning domains problem statement. IETF draft: draft-ietf-mif-problem-statement (work in progress)
Wang Q, Atkinson R, Dunlop J (2008) Design and evaluation of flow handoff signalling for multihomed mobile nodes in wireless overlay networks. Comput Netw 52(8):1647–1674
Wei DX, Jin C, Low SH, Hegde S (2006) FAST TCP: motivation, architecture, algorithms, performance. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 14(6):1246–1259
Ylitalo J, Melén J, Salmela P, Petander H (2008) An experimental evaluation of a HIP based network mobility scheme. In: Proc. WWIC, pp 139–151
Zhang W, Yin X, Wu J, Zhang W, Huang S (2010) Real aggregation for reducing routing information base size. JCIT 5(6):1–7
Acknowledgements
Bruno Sousa would like to acknowledge the support of the PhD grant SFRH/BD/61256/2009 from Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Ensino Superior, FCT, Portugal. This work has also been supported by CoFIMOM project PTDC/EIA-EIA/116173/2009 and TRONE project CMU-PT /RNQ/0015/2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sousa, B.M., Pentikousis, K. & Curado, M. Multihoming Management for Future Networks. Mobile Netw Appl 16, 505–517 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-011-0323-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-011-0323-5