Abstract
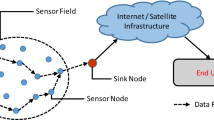
Sensor networks are deployed in numerous military and civil applications, such as remote target detection, weather monitoring, weather forecast, natural resource exploration and disaster management. Despite having many potential applications, wireless sensor networks still face a number of challenges due to their particular characteristics that other wireless networks, like cellular networks or mobile ad hoc networks do not have. The most difficult challenge of the design of wireless sensor networks is the limited energy resource of the battery of the sensors. This limited resource restricts the operational time that wireless sensor networks can function in their applications. Routing protocols play a major part in the energy efficiency of wireless sensor networks because data communication dissipates most of the energy resource of the networks. The above discussions imply a new family of protocols called chain-based protocols. In the protocols, all sensor nodes sense and gather data in an energy efficient manner by cooperating with their closest neighbors. The gathering process can be done until an elected node calculates the final data and sends the data to the base station. In our works, we have proposed two methods to optimize the lifetime of chain-based protocols using Integer Linear Programming (ILP) formulations. Also, a method to determine the bounds of the lifetime for any energy-efficient routing protocol is presented. Finally, simulation results verify the work in this chapter. Furthermore, previous researches assume that the base station position is randomly placed without optimization. In our works, a non convex optimization model has been developed for solving the base station location optimization problem.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heinzelman WB, Chandrakasan AP, Balakrishnan H (2000) Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks, 33rd Hawaii International Conference Systems Sciences, Jan 2000
Al-Karaki JN, Kamal AE (2004) Routing techniques in wireless sensor networks: a survey. IEEE Wirel Commun 11:6–28
Tung NT (2009) Energy-efficient routing algorithms in wireless sensor networks: PhD thesis, Monash University, Australia July 2009
Heinzelman WB, Chandrakasan AP (2002) An application specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 1(4):660–670
Lindsey S, Raghavendra C (2002) Power-efficient gathering in sensor information systems. IEEE Aerospace Conference, 2002
(2013) Traveling sale problem. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Travelling_salesman_problem
(2013) GLPK programming. http://www.gnu.org/software/glpk/
(2013) Linear Programming. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_programming, 2013
Tung NT, Vinh PC (2012) The energy-aware operational time of wireless Ad-hoc sensor networks, ACM/Springer Mobile Networks and Applications (MONET) Journal, Volumn 17, August, 2012, DOI: 10.1007/s11036-012-0403-1
Tung NT (2012) The power-save protocol of wireless ad-hoc sensor networks: Mediterranean Journal of Computers and Networks, Volumn 4, October, 2012 ISSN: 1744–2397
Tung NT (2012) Heuristic energy-efficient routing solutions to extend the lifetime of wireless Ad-Hoc Sensor Networks: Springer, LNCS 7197, p. 487–497, 2012, ISBN: 978-3-642-28489-2
Paschalidis ICh, Wu R (2012) Robust maximum lifetime routing and energy allocation in wireless sensor networks, Int J Distrib Sensor Networks Volume 2012, Article ID 523787, 14 pagesdoi:10.1155/2012/523787
Chang JH, Tassiulas L (2004) Maximum lifetime routingin wireless sensor networks. IEEE/ACM Trans Networking 12(4):609–619
Giridhar A, Kumar PR (2005) Maximizing the functional lifetime of sensor networks, in Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN’05), pp. 5–12, April 2005
Nama H, Mandayam N (2005) Sensor networks over information fields: optimal energy and node distributions, in Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC’05), vol. 3, 1842–1847, March 2005
Nguyen TT, Nguyen VD (2013) Optimizing the operating time of wireless sensor network, EURASIP J Wireless Commun Netwo. ISSN: 1687–1499, DOI: 10.1186/1687-1499-2012-348 (SCIE)
An LTH, Tao PD (2009) Minimum sum-of-squares clustering by DC programming and DCA, in advanced intelligent computing technology & applications, lecture notes in artificial intelligence (LNAI), Springer Verlag 2009, 14 pages
Tao PD, Nam NC, An LTH (2009) DC programming and DCA for globally solving the value-at-risk, computational management science (4)
An LTH, Moeini M, Tao PD (2009), Portfolio selection under downside risk measures and cardinality constraints based on DC programming and DCA, Computational Management Science, Issue 4
Le Thi HA, Pham Dinh T, Huynh VN (2011) Exact penalty techniques in DC programming. J Global Optim, 1–27, doi:10.1007/s10898-011-9765-3
(2011) Recent advances on modelling and optimization techniques for intelligent computing in industrial engineering and systems management organized by H.A Le Thi, T. Pham Dinh, D.T. Pham in 4th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Systems Management, IESM 2011, May 25–27, 2011, Metz, France
(2011) Nonconvex programming—local and global approaches” organized by H.A Le Thi, 12e congrès annuel de la Sociéte française de Recherche Opérationnelle et d’Aide à la Décision ROADEF 2011, St Etienne 2–4 mars 2011
Thi HA Le, Dinh TP, Van NH, Exact penalty and error bound in DC programming, to appear in J Global Optim
(2012) Stream DC Programming and DCA: Theory, algorithms and applications—local and global approaches” organized by H.A Le Thi, T. Pham Dinh in EURO Conference 2012 in Vilnius, OR creating competitive advantage, 25th European Conference on Operational Research, Vilinus (Lithuania), July 2012
Le Thi HA, Le Hoai M, Van Nguyen V, Pham Dinh T (2008) A DC Programming approach for feature selection in support vector machines learning. J Adv Data Anal Classif 2(3):259–278, CrossRef
Le Thi HA, Van Nguyen V, Ouchani S (2008) Gene selection for cancer classification using DCA. In: Tang C, Ling CX, Zhou X, Cercone NJ, Li X (eds.) ADMA 2008. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 5139, pp. 62–72. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)CrossRef
Weston J, Elisseeff A, Scholkopf B, Tipping M (2003) Use of the Zero-Norm with linear models and Kernel methods. J Mach Learn Res 3:1439–1461
Thi HAL, Nguyen QT, Phan KT, Dinh TP (2013) DC Programming and DCA based cross-layer, optimization in Multi-hop TDMA networks, The 5th Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems, LNCS 7803, p.398-408 March 2013, Malaysia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tung, N.T. Energy-Aware Optimization Model in Chain-Based Routing. Mobile Netw Appl 19, 249–257 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-014-0497-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-014-0497-8