Abstract
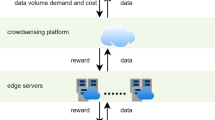
Owing to the acceleration of urbanization and the rapid development of mobile Internet, mobile crowd sensing (MCS) has been recognized as a promising method to acquire massive volume of data. However, due to the massive perception data in participatory MCS system, the data privacy of mobile users and the response speed of data processing in cloud platform are hard to guarantee. Stimulating the enthusiasm of participants could be challenging at the same time. In this paper, we first propose a three-layer MCS architecture which introduces edge servers to process raw data, protects users’ privacy and improve response time. In order to maximize social welfare, we consider two-stage game in three-layer MCS architecture. Then, we formulate a Markov decision process (MDP)-based social welfare maximization model and investigate a convex optimization pricing problem in the proposed three-layer architecture. Combined with the market economy model, the problem could be considered as a Walrasian equilibrium problem according to market exchange theory. We propose a pricing approach toward incentive mechanisms based on Lagrange multiplier method, dual decomposition and subgradient iterative method. Finally, we derive the experimental data from real-world dataset and extensive simulations demonstrate the performance of our proposed method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
IDC (2020) should bring the market back to growth as we expect many regions to rebound, according to IDC. https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=US44916519
Gao H, Huang W, Yang X (2019) Applying probabilistic model checking to path planning in an intelligent transportation system using mobility trajectories and their statistical data. Intell Autom Soft Comput 25(3):547–559
Li W, Liao K, He Q, Xia Y* (2019) Performance-aware Cost-effective Resource Provisioning for Future Grid IoT-Cloud System. J Energy Eng 145(5):1–13
Qi L, He Q, Chen F, et al (2019) Finding All You Need: Web API s Recommendation in Web of Things through Keywords Search. IEEE Trans Comput Social Syst 6(5):1063–1072
Akyildiz IF, Su W, Sankarasubramaniam Y, et al (2002) A survey on sensor networks. IEEE Commun Magazine 40(8):102–114
Guo B, Wang Z, Yu Z, et al (2015) Mobile crowd sensing and computing: The review of an emerging human-powered sensing paradigm. ACM Comput Surveys (CSUR) 48(1):7
Wu Y, Zeng J, Peng H, Chen H, Li C (2016) Survey on Incentive Mechanisms for Crowd Sensing. J Software 27(8):2025–2047
Nie J, Luo J, Xiong Z, et al (2019) A Stackelberg Game Approach Toward Socially-Aware Incentive Mechanisms for Mobile Crowdsensing. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun 18(1):724–738
Pouryazdan M, Kantarci B, Soyata T, et al (2017) Quantifying User Reputation Scores, Data Trustworthiness, and User Incentives in Mobile Crowd-Sensing. IEEE Access 5(99):1382–1397
Yin Y, Chen L, Xu Y, Wan J (2018) Location-Aware Service recommendation with enhanced probabilistic matrix factorization. IEEE Access 6:62815–62825
Chen Y, Zhang N, Zhang Y, et al (2019) TOFFEE: task offloading and frequency scaling for energy efficiency of mobile devices in mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput https://doi.org/10.1109/TCC.2019.2923692
Qi L, Chen Y, Yuan Y, et al (2019) A QoS-aware virtual machine scheduling method for energy conservation in cloud-based cyber-physical systems World Wide Web 1–23
Sun J (2013) Current states and challenges of work, arXiv:1310.8364
Yang D, Xue G, Fang X, et al (2016) Incentive mechanisms for crowdsensing: Crowdsourcing with smartphones. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw (TON) 24(3):1732–1744
Jin H, Su L, Chen D, et al (2018) Thanos: Incentive mechanism with quality awareness for mobile crowd sensing. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 1–14
Peng D, Wu F, Chen G (2017) Data quality guided incentive mechanism design for crowdsensing. IEEE trans Mob Comput 17(2):307–319
Gao G, Xiao M, Wu J, et al (2018) Truthful incentive mechanism for nondeterministic crowdsensing with vehicles. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 17(12):2982–2997
Zheng Z, Peng Y, Wu F, et al (2017) An online pricing mechanism for mobile crowdsensing data markets. Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing 26:1–10
Chen Y, Huang J, Lin C, et al (2015) A Partial Selection Methodology for Efficient QoS-Aware Service Composition. IEEE Trans Serv Comput 8(3):384–397
Gao H, Huang W, Duan Y, Yang X, Zou Q (2019) Research on Cost-Driven services composition in an uncertain environment. J Internet Technol (JIT) 20(3):755–769
Duan X, Zhao C, He S, et al (2016) Distributed algorithms to compute Walrasian equilibrium in mobile crowdsensing. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64(5):4048–4057
He S, Shin DH, Zhang J, et al (2017) An exchange market approach to mobile crowdsensing: pricing, task allocation, and walrasian equilibrium. IEEE J Selected Areas Commun 35(4):921– 934
Jin H, Su L, Chen D, et al (2018) Thanos: Incentive mechanism with quality awareness for mobile crowd sensing. IEEE Trans Mob Comput
Han K, Huang H, Luo J (2018) Quality-aware pricing for mobile crowdsensing. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 26(4):1728–1741
Xia Y, Zhou M, Luo X, et al (2015) Stochastic Modeling and Quality Evaluation of Infrastructure-as-a-Service Clouds. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 12(1):162–170
Chen Y, Zhang N, Zhang Y, et al (2019) Dynamic computation offloading in edge computing for internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J 6(3):4242–4251
Wang Y, Liu H, Zheng W, et al (2019) Multi-Objective Workflow scheduling with Deep-Q-Network-Based Multi-Agent reinforcement learning. IEEE Access 7:39974–39982
Chen X, Jiao L, Li W, et al (2015) Efficient multi-user computation offloading for mobile-edge cloud computing. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 24(5):2795–2808
Liu Y, Xu C, Zhan Y, et al (2017) Incentive mechanism for computation offloading using edge computing: A Stackelberg game approach. Comput Netw 129:399–409
Yu H, Cheung MH, Gao L, et al (2016) Economics of public Wi-Fi monetization and advertising, IEEE INFOCOM 2016-The 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, IEEE 1–9
Gong W, Qi L, Xu Y (2018) Privacy-aware multidimensional mobile service quality prediction and recommendation in distributed fog environment Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing
Zhou Z, Liao H, Gu B, et al (2018) Robust mobile crowd sensing: When deep learning meets edge computing. IEEE Netw 32(4):54–60
Duan X, Zhao C, He S, et al (2017) Distributed algorithms to compute walrasian equilibrium in mobile crowdsensing. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64(5):4048–4057
Esser E, Zhang X, Chan TF (2010) A general framework for a class of first order primal-dual algorithms for convex optimization in imaging science. SIAM J Imaging Sci 3(4):1015–1046
Chen Y, Zhang N, Zhang Y, et al (2019) Energy Efficient Dynamic Offloading in Mobile Edge Computing for Internet of Things. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput, https://doi.org/10.1109/TCC.2019.2898657
Leskovec J , Krevl A Snap Datasets: Stanford Large Network Dataset Collection. [Online]. Available: http://snap.stanford.edu/data
Li J, Cai Z, Wang J, et al (2018) Truthful Incentive Mechanisms for Geographical Position Conflicting Mobile Crowdsensing Systems, IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 1–11
Duan X, Zhao C, He S, et al (2016) Distributed algorithms to compute Walrasian equilibrium in mobile crowdsensing. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64(5):4048–4057
Yin Y, Chen L, Xu Y, et al (2019) Qos prediction for service recommendation with deep feature learning in edge computing environment. Mob Netw Appl 1–11
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61872044, 61872219, 61902029), Beijing Municipal Program for Top Talent Cultivation (CIT&TCD201804055), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2019MF001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Tang, C., Li, Z. et al. A Pricing Approach Toward Incentive Mechanisms for Participant Mobile Crowdsensing in Edge Computing. Mobile Netw Appl 25, 1220–1232 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-020-01538-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-020-01538-y