Abstract
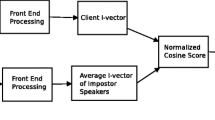
In speaker detection it is important to build an alternative model against which to compare scores from the ‘target’ speaker model. Two alternative strategies for building an alternative model are to build a single global model by sampling from a pool of training data, the Universal Background (UBM), or to build a cohort of models from selected individuals in the training data for the target speaker. The main contribution in this paper is to show that these approaches can be unified by using a Support Vector Machine (SVM) to learn a decision rule in the score space made up of the output scores of the client, cohort and UBM model.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Linguistic Data Consortium, http://www.ldc.upenn.edu/Catalog/CatalogEntry.jsp?catalogId=LDC95S22
References
Ariyaeeinia AM, Sivakumaran P (1997) Analysis and comparison of score normalisation methods for text-dependent speaker verification. In: Eurospeech
Auckenthaler R, Carey M, Lloyd-Thomas H (2000) Score normalization for text-independent speaker verification systems. Digit Signal Process 10(1–3):42–54
Bengio S, Mariethoz J (2001) Learning the decision function for speaker verification. In: ICASSP, IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, vol 1, pp 425–428
Bimbot F, Bonastre J, Fredouille C, Gravier G, Magrin-Chagnolleau I, Meignier S, Merlin T, Ortega-Garcia J, Petrovska-Delacretaz D, Reynolds D (2004) A tutorial on text-independent speaker verification. EURASIP J Appl Signal Process 4:430–451
Burges C (1998) A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 2(2):121–167
Campbell J, Reynolds D (1999) Corpora for the evaluation of speaker recognition systems. In: ICASSP, IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, vol 2, pp 829–832
Campbell W, Reynolds D, Campbell J (2004) Fusing discriminative and generative methods for speaker recognition: experiments on switchboard and nfi/tno field data. In: Odyssey: the speaker and language recognition workshop, ISCA
Charlet D, Zhao X, Dong Y (2008) Convergence between SVM-based and distance-based paradigms for speaker recognition. In: Interspeech
Higgins A, Bahler L, Porter J (1991) Speaker verification using randomized phrase prompting. Digit Signal Process 1(2):89–106
Ho P, Vasconcelos N (2004) A kullback-leibler divergence based kernel for SVM classification in multimedia applications. Proc Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 16:1385–1392
Kharroubi J, Petrovska-Delacretaz D, Chollet G (2001) Combining GMM’s with Support Vector Machines for text-independent speaker verification. In: Eurospeech
Le Q, Bengio S (2003) Client dependent GMM-SVM models for speaker verification. In: ICONP international conference on neural information processing. Springer, New York, pp 181–189
Louradour J, Daoudi K, Bach F (2006) SVM speaker verification using an incomplete cholesky decomposition sequence kernel. In: Odyssey: the speaker and language recognition workshop
Magrin-Chagnolleau I, Bimbot F (2000) Indexing telephone conversations by speakers using time-frequency principal component analysis. In: Multimedia and expo, ICME, vol 2, pp 881–884
Reynolds D (1997) Comparison of background normalization methods for text-independent speaker verification. In: Eurospeech
Reynolds D (2002) An overview of automatic speaker recognition technology. In: ICASSP, IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, vol 4, pp 4072–4075
Reynolds DA (1995) Speaker identification and verification using gaussian mixture speaker models. Speech Commun 17(1):91–108
Reynolds D, Quatieri T, Dunn R (2000) Speaker verification using adapted gaussian mixture models. Digit Signal Process 10(1-3):19–41
Rosenberg A, DeLong J, Lee C, Juang B, Soong F (1992) The use of cohort normalized scores for speaker verification. In: Second international conference on spoken language processing
Schmidt M, Gish H (1996) Speaker identification via support vector classifiers. In: ICASSP, IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, vol 1, pp 105–108
Stanford V, Garofolo J, Galibert O, Michel M, Laprun C (2003) The nist smart space and meeting room projects: signals, acquisition annotation, and metrics. In: ICASSP, IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, vol 4, pp 128–132
Sturim D, Reynolds D (2005) Speaker adaptive cohort selection for tnorm in text-independent speaker verification. In: ICASSP, IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, vol 1, pp 741–744
Sturim D, Reynolds D, Singer E, Campbell J (2001) Speaker indexing in large audio databases using anchor models. In: ICASSP, IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, vol 1, pp 429–432
Tax D, van Breukelen M, Duin R, Kittler J (2000) Combining multiple classifiers by averaging or by multiplying? Pattern Recogn 33(9):1475–1485
Vapnik V (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Wan V (2003) Speaker verification using support vector machines. PhD thesis, University of Sheffield
Wan V, Renals S (2005) Speaker verification using sequence discriminant support vector machines. Speech Audio Process 13(2):203–210
Zhu X, Barras C, Lamel L, Gauvain J (2006) Speaker diarization: from broadcast news to lectures. Lect Notes Comput Sci 4299:396
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brew, A., Cunningham, P. Combining cohort and UBM models in open set speaker detection. Multimed Tools Appl 48, 141–159 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-009-0381-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-009-0381-x