Abstract
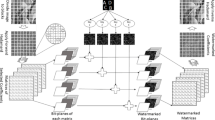
In this paper, we present a novel dynamic energy enabled differentiation (DEED) watermarking algorithm based on the wavelet tree classification and human visual system (HVS). The wavelet coefficients of the image are divided into disjoint trees and a wavelet tree consists of 21 coefficients which are divided into 6 blocks. One watermark bit is embedded into one wavelet tree using the energy differentiation of positive and negative modulation between coefficients of each block. In addition, the contrast sensitive function (CSF) of human visual system is also considered for better weighting in watermarking since the wavelet coefficients across the subbands perform different characteristics and importance. As DEED still requires extra storage of side information during the extraction and results non-blind watermarking approach, a random direction differentiation approach called DEEDR is then proposed which is a truly blind watermarking technique. This study has performed intensive comparison for the proposed scheme with other tree energy differentiation based techniques like WTQ, ABW-TMD and WTGM under various geometric and nongeometric attacks. From the experimental results, the advantage of DEED based algorithms is not only with low complexity, but also outperforms WTGM and WTQ in terms of robustness and imperceptibility of watermarking.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Otum HM, Samara NA (2006) Adaptive blind wavelet-based watermarking technique using tree mutual differences. J Electron Imaging 15(4):043011
Beegan AP, Iyer LR, Bell AE (2002) Design and evaluation of perceptual masks for wavelet image compression. Proc. 10th IEEE Digital Signal Processing Workshop, pp. 88-93
Cox IJ, Kilian J, Leighton FT, Shamoon T (1997) Secure spread spectrum watermarking for multimedia. IEEE Trans on Image Proc 6(12):1673–1687
Das TK, Maitra S (2004) Cryptanalysis of wavelet tree quantization watermarking scheme. IWDC 2004:219–230
Das TK, Maitra S, Mitra J (2005) Cryptanalysis of optimal differential energy watermarking (DEW) and a modified robust scheme. IEEE Trans on Signal Proc 53(2):768–775
Daubechies1 I, Sweldens W (1998) Factoring wavelet transforms into lifting steps. J Fourier Anal Appl 4(3):247–269
Huang BB, Tang SX (2006) A contrast-sensitive visible watermarking scheme. IEEE Multimedia 13(2):60–66
Kundur D, Hatzinakos D (1998) Digital watermarking using multiresolution wavelet decomposition. Proc IEEE ICASSP 5:2869–2972
Langelaar GC, Lagendijk RL (2001) Optimal differential energy watermarking of DCT encoded images and video. IEEE Trans on Image Proc 10(1):148–158
Lu CS, Huang SK, Sze CJ, Liao HY (2000) Cocktail watermarking for digital image protection. IEEE Trans on Multimedia 2(4):209–224
Mannos JL, Sakrison DJ (1974) The effects of a visual fidelity criterion on the encoding of images. IEEE Trans on Info Theory 20(4):525–536
Said A, Pearlman WA (1996) A new, fast, and efficient image codec based on set partitioning in hierarchical trees. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 6:243–250
StirMark, [Online]: http://www.petitcolas.net/fabien/software/StirMarkBenchmark_4_0_129.zip
Tsai M-J (2009) A visible watermarking algorithm based on the content and contrast aware (COCOA) technique. J Vis Commun Image Represent 20(5):323–338
Tsai MJ, Lin CW (2008) Wavelet based multipurpose color image watermarking by using dual watermarks with human vision system models. IEICE E91-A(6):1426–1437
Tsai MJ, Shen CH (2007) Wavelet Tree Group Modulation (WTGM) for digital image watermarking. IEEE ICASSP2007 2:173–176
Tsai MJ, Shen CH (2008) Differential energy based watermarking algorithm using Wavelet Tree Group Modulation (WTGM) and human visual system. IEICE E91-A(8):1961–1973
Wang SH, Lin YP (2002) Blind watermarking using wavelet tree quantization. IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo 1:589–592
Wang SH, Lin YP (2004) Wavelet tree quantization for copyright protection watermarking. IEEE Trans on Image Proc 13(2):154–165
Yong L, Cheng LZ, Xu ZH (2004) Translucent digital watermark based on wavelets and error-correct code. Chinese J of Computers 20(11):1533–1539
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the anonymous reviewers with their valuable comments to improve the quality of this manuscript and Bai-Jiun Chen at National Chiao Tung University who helps to write the programs for software experiments. This work is partially supported by the National Science Council in Taiwan, Republic of China, under Grant NSC96-2416-H009-015, NSC97-2410-H009-034 and 99-2918-1-009-008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, MJ. Dynamic energy enabled differentiation (DEED) image watermarking based on human visual system and wavelet tree classification. Multimed Tools Appl 52, 385–406 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-009-0422-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-009-0422-5