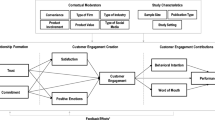
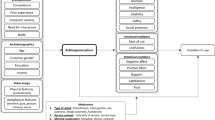
Abstract
One of the main problems of today’s ubiquitous computing systems is that they do not meet their quality requirements. Ubiquitous computing services such as mobile data services (MDS) are fundamentally different from traditional information systems (IS) in terms of important quality factors such as information or system quality because it has been used in various life contexts. We identify important quality factors on various contexts in Korea MDS market. Using the results of qualitative study, we propose research model. To identify the effect of motivational orientation type on users’ behavior, we classified users according to their propensities into intrinsic and extrinsic motivational orientation groups. The results show that the impact of quality factors on user satisfaction is differentiated depending on motivational orientation types. The paper concludes with a discussion of the study’s limitations and implications.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Service quality may entirely be appropriate measure of IS department effectiveness [34]. Information quality and system quality are attributes of applications not of IS department. This study focuses on application (mobile data service) not department. Therefore, we exclude service quality factor in our study.
\( {S_{\text{pooled}}} = \surd \left\{ {\left[ {\left( {{N_{{1}}}--{1}} \right)/\left( {{N_{{1}}} + {N_{{2}}} - {2}} \right)} \right] \times {\text{S}}{{\text{E}}_{{1}}}^{{2}} + \left[ {\left( {{N_{{2}}}--{1}} \right)/\left( {{N_{{1}}} + {N_{{2}}} - {2}} \right)} \right] \times {\text{S}}{{\text{E}}_{{2}}}^{{2}}} \right\},t = \left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{C}}_{{1}}}--{\text{P}}{{\text{C}}_{{2}}}} \right)/\left[ {{{\text{S}}_{\text{pooled}}} \times \surd \left( {{1}/{N_{{1}}} + {1}/{N_{{2}}}} \right)} \right] \)
where Spooled = pooled estimator for the variance, t = t-statistic with N1+N2-2 (degrees of freedom), Ni=sample size of dataset for groupi, SEi = standard error of path in structural model of group i, and PCi=path coefficient in structural model of group i
References
Federal Trade Commission (2002) The mobile wireless web, data services and beyond: Emerging technologies and consumer issues. Available at: http://www.ftc.gov/bcp/reports/wirelesssummary.pdf
Amabile TM (1988) A model of creativity and innovation in organizations. In: Staw BM, Cummings LL (eds) Research in organizaitonal behavior, vol 10. JAI Press, Greenwich, CT, pp 123–167
Amabile TM, Hill KG, Hennessey BA, Tighe EM (1994) The work preference inventory: assessing intrinsic and extrinsic motivational orientations. J Pers Soc Psychol 66(5):950–967
Ambrose PJ, Rai A, Ramaprasad A (2006) Internet usage for information provisioning: theoretical construct development and empirical validiation in the clinical decision-making context. IEEE Trans Eng Manag 53(1):112–129
Andrews FM, Withey SB (1976) Social indicators of well-being: America’s perception life. Plenum Press, New York
Bhattacherjee A, Premkumar G (2004) Understanding changes in belief and attitude toward information technology usage: a theoretical model and longitudinal test. MIS Q 28(2):229–254
Bollen KA, Lennox R (1991) Conventional wisdom on measurement: a structural equation perspective. Psychol Bull 110:305–314
Bruseberg A, McDonagh-Philp D (2001) New product development by eliciting user experience and aspirations. Int J Hum Comput Stud 55(4):435–452
Buchanan G, Farrant S, Marsden G, Pazzani M (2001) Improving mobile internet usability. In: Proceedings International WWW Conference, Hong-Kong
Campbell A, Converse PE, Rodgers WL (1976) The quality of American life. Russel Sage Foundation, New York
Chae MH, Kim JW, Kim HY, Ryu HS (2002) Information quality for mobile data services: a theoretical model with empirical validation. Electron Mark 12(1):38–46
Chin W (1998) The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. In: Marcoulides GA (ed) Modern methods for business research. Laurence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, New Jersey, pp 295–336
Choi M, Lee I, Choi H, Kim J (2003) A cross-cultural study on the post-adoption behavior of mobile internet users. In: Proceedings of DIGIT, Seattle
Davis FD, Bagozzi RP, Warshaw PR (1992) Extrinsic and intrinsic motivation to use computers in the workplace. J Appl Soc Psychol 22(14):1111–1132
Delone WH, McLean ER (1992) Information systems success: the quest for the dependent variable. Inf Syst Res 3(1):60–96
Diamantopoulos A, Winklhofer HM (2001) Index construction with formative indicators: an alternative to scale development. J Mark Res 37:269–277
Diener E (1984) Subjective well-being. Psychol Bull 95:542–575
Folmer E, Gurp J, Bosch J (2003) Scenario-based Assessment of Software Architecture Usability. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Bridging the Gaps Between Software Engineering and Human-Computer Interaction (SE-HCI). IFIP, 61–68
Forenll C, Larcker D (1981) Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J Mark Res 18:39–50
Gefen D, Karahanna E, Straub D (2003) Trust and TAM in online shopping: an integrated model. MIS Q 27(1):51–90
Hulland J (1999) Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: a review of four recent studies. Strateg Manag J 20:195–204
Ives B, Olson MH, Baroudi JL (1983) The measurement of user information satisfaction. Commun ACM 26(10):785–793
Keil M, Tan BC, Wei K-K, Saarinen T (2000) A cross-cultural study on escalation of commitment behavior in software projects. MIS Q 24(2):299–325
Kim H, Kim J (2003) Post-adoption behavior of mobile internet users: a model-based comparison between continuers and discontinuers. In: Proceedings of the HCI/MIS'03 Workshop, Seattle
Konkka K, Oyj N, Koskinen S (2005) Mobile user experience: challenges in international end-user needs research and design. In: Proceedings of HCI international, Las Vegas
Lee MKO, Cheung CMK, Chen Z (2005) Acceptance of internet-based learning medium: the role of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation. Inf Manage 42:1095–1104
Lee DJ, Sirgy MJ (1995) Determinants of Involvement in the Consumer/Marketing Life Domain in Relation to Quality of Life: A Theoretical Model and Research Agenda. Developments in quality-of-life studies in marketing, vol. 5, edited by H. Lee Meadow, M. Joseph Sirgy, and Don Rahtz, DeKalb, IL: Academy Science, pp 13–18
Maguire M, Bevan N (2005) User requirements analysis: a review of supporting methods. In: Proceedings of IFIP 17th World Computer Congress, Montreal Canada, pp 25–30
Mankoff J, Carter S (2005) Crossing qualitative and quantitative evaluation in the domain of ubiquitous computing. In: CHI2005 Workshop Portland, Oregon, USA
McKinney V, Yoon K, Zahedi F (2002) The measurement of Web-customer satisfaction: an expectation and disconfirmation approach. Inf Syst Res 13:296–315
Pavot W, Diener E (1993) Review of the satisfaction with life scale. Psychol Assess 5:164–171
Ryan RM, Deci EL (2000) Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: classic definitions and new directions. Contemp Educ Psychol 25:54–67
Ryan C, Gonsalves A (2005) The effect of context and application type on mobile usability: an empirical study. In: Twenty-Eighth Australasian Computer Science Conference (ACSC2005), Newcastle, Australia, pp 115–124
Seddon PB (1997) A respecification and extention of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success. Inf Syst Res 8(3):240–253
Shang R-A, Chen Y-C, Shen L (2005) Extrinsic versus intrinsic motivations for consumers to shop on-line. Inf Manage 42:401–413
Sirgy MJ (2002) Psychology of quality of life. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands
Sirgy MJ, Cornwell T (2001) Further validation of the Sirgy et al’.s measure of community quality of life. Soc Indic Res 56:125–143
Sirgy MJ, Hansen DE, Littlefield JE (1994) Does hospital satisfaction affect life satisfaction? J Macromark 14:36–46
Spreng R, MacKenzie SB, Olshavsky RW (1996) A reexamination of the determinants of consumer satisfaction. J Mark 60(3):15–32
Straub DW, Watson RT (2001) Research commentary: transformational issues in researching IS and Net-enabled organizations. Inf Syst Res 12(4):337–345
Sun X, Collins R (2002) Attitudes and consumption values of consumers of imported fruit in Guangzhou, China. Int J Consum Stud 26(1):34–43
Venkatesh V, Brown SA (2001) A longitudinal investigation of personal computers in homes: adoption determinants and emerging challenges. MIS Q 25:71–102
Weiser M (1993) The computer for the twenty-first century. Sci Am 265(3):94–104
White JC, Varadarajan PR, Dacin PA (2003) Market situation interpretation and response: the role of cognitive style, organizational culture, and information use. J Mark 67(3):63–79
Wixom BH, Todd PA (2005) A theoretical integration of user satisfaction and technology. Acceptance. Inf Syst Res 16(1):85–102
Wixom BH, Watson HJ (2001) An empirical investigation of the factors affecting data warehousing success. MIS Q 25(1):17–41
Yi MY, Hwang Y (2003) Predicting the use of web-based information systems: self-efficacy, enjoyment, learning goal orientation, and the technology acceptance model. Int J Hum Comput Stud 59(4):431–449
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate comments from editors and reviewers of Multimedia Tools and Applications. This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (#2011-0012490).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, H., Im, K. & Kim, J. A comparative study of the motivational orientation type on users’ behavior: focusing on ubiquitous computing services. Multimed Tools Appl 68, 321–336 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-012-1118-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-012-1118-9