Abstract
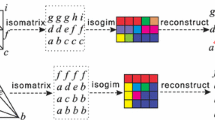
The benefit of using the geometry image to represent an arbitrary 3D mesh is that the 3D mesh can be re-sampled as a completely regular structure and coded efficiently by common image compression methods. For geometry image-based 3D mesh compression, we need to code the normal-map images while coding geometry images to improve the subjective quality and realistic effects of the reconstructed model. In traditional methods, a geometry image and a normal-map image are coded independently. However a strong correlation exists between these two kinds of images, because both of them are generated from the same 3D mesh and share the same parameterization. In this paper we propose a predictive coding framework, in which the normal-map image is predicted based on the geometric correlation between them. Additionally we utilize the strong geometric correlation among three components of normal-map image to improve the predicting accuracy. The experimental results show the proposed coding framework improves the coding efficiency of normal-map image, meanwhile the realistic effect of a 3D mesh is significantly enhanced.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alliez P, Gotsman C (2003) Recent advances in compression of 3D meshes, Proceedings the Symposium on Multiresolution in Geometric Modeling, pp 3–26
Aspert N, SantaCruz D, Ebrahimi T (2002) Mesh: measuring errors between surfaces using the Hausdorff distance. Proc IEEE Int Conf Multimed Expo 1:705–708
Floater MS (1997) Parametrization and smooth approximation of surface triangulations. Comput Aided Geome Des 14(3):231–250
Hoppe H (1996) Progressive meshes. Comput Graph 30:99–108
Hoppe H, Praun E (2005) Shape compression using spherical geometry images. Advances in Multiresolution for Geometric Modeling, pp 27–46
Lin NH, Huang TH, Chen BY (2007) 3D model streaming based on JPEG 2000. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 53(1):182–190
Peercy M, Airey J, Cabral B (1997) Efficient bump mapping hardware. Proceedings the ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Computer Graphics, pp 303–306
Peyre G, Mallat S (2005) Surface compression with geometric bandelets. ACM Trans Graph 24(3):601–608
Praun E, Hoppe H (2003) Spherical parametrization and remeshing. ACM Trans Graph 22(3):340–349
Sander P, Gortler S, Snyder J, Hoppe H (2002) Signal-Specialized Parametrization. Proceedings Eurographics Workshop on Rendering, pp 87–98
Shi Y, Wen W, Yin B, Shi J (2009) A novel geometry image coding. Proceedings 5th International Conference on Active Media Technology, pp:281–287
Wen W, Yin B, Shi Y, Shi J (2009) Photorealistic geometry image coding based on directional lifting wavelet transform. Proceedings 10th Pacific Rim Conference on Multimedia, Advances in Multimedia Information Processing, pp 1230–1236
Wenpeng D, Feng W (2007) Adaptive directional lifting based wavelet transform for image coding. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(2):416–427
Xianfeng G, Gortler SJ, Hoppe H (2002) Geometry images. ACM Trans Graph 21(3):355–361
Acknowledgement
This paper is supported by 973 Program (2011CB302703), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 60825203, 61033004, 60973056, 61170103, 61003182,U0935004), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (4102009, 4112007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Wen, B., Ding, W. et al. Prediction-based realistic 3D model compression. Multimed Tools Appl 70, 2125–2137 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-012-1231-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-012-1231-9