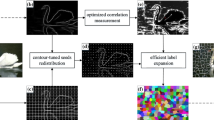
Abstract
The superpixel extraction algorithm is becoming increasingly significant for pattern recognition applications. Different superpixel generation methods have different properties and lead to various over-segmentation results. In this paper, we treat the over-segmentation as an image decomposition problem, and propose a novel discriminative sparse coding (DSC) algorithm to effectively extract the semantic superpixels. Specifically, the DSC algorithm incorporates a new discriminative regularization term in the traditional sparse representation model. Then the new regularization term is combined with the reconstruction error and sparse constraint to form a unified objective function. The extracted superpixels not only respect the local image boundaries, but also are dissimilar between each other. Meanwhile, the quantity of segments is sparse. These properties benefit for the semantic superpixel extraction. The final refined superpixels are generated based on an effective Bayesian-classification criterion in a post-processing step. Experimental results show that the over-segmentation quality of DSC algorithm outperforms the state of the art methods.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amri S, Barhoumi W, Zagrouba E (2010) A robust framework for joint background/foreground segmentation of complex video scenes filmed with freely moving camera. Multimed Tools Appl 46:175–205
Ayvaci A, Soatto S (2009) Motion segmentation with occlusions on the superpixel graph. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2009, pp 727–734
Chen Y, Chan A, Wang G (2012) Adaptive figure-ground classification. In: IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2012, pp 654–661
Dong W, Zhang D, Shi G (2011) Centralized sparse representation for image restoration. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2011, pp 1259–1266
Donoho DL (2004) For most large underdetermined systems of equations, the minimal l1-norm near-solution approximates the sparsest near-solution. In: Communications on pure and applied mathematics, pp 907–934
Elad M (2010) Sparse and redundant representations: from theory to appplications in signal and image processing. Springer
Elad M, Figueiredo MAT, Ma Y (2010) On the role of sparse and redundant representations in image processing. Proc IEEE 98:972–982
Felzenszwalb PF, Huttenlocher DP (2004) Efficient graph-based image segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 59:167–181
Fragkiadaki K, Zhang G, Shi J (2012) Video segmentation by tracing discontinuities in a trajectory embedding. In: IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2012, pp 1846–1853
Fulkerson B, Vedaldi A, Soatto S (2009) Class segmentation and object localization with superpixel neighborhoods. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2009, pp 670–677
Gkalelis N, Mezaris V, Kompatsiaris I, Stathaki T (2013) Mixture subclass discriminant analysis link to restricted gaussian model and other generalizations. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24:8–21
Golub GH, Hansen PC, O’Leary DP (1999) Tikhonov regularization and total least squares. SIAM J Matrix Anal Appl 21:185–194
Huang K, Aviyente S (2006) Sparse representation for signal classiffication. In: Adv. NIPS, pp 609–616
Huang S, Lee Y, Bell G, Ou Z (2010) An efficient segmentation algorithm for captchas with line cluttering and character warping. Multimed Tools Appl 48:267–289
Jing G, Shi Y, Kong D, Ding W, Yin B (2012) Image super-resolution based on multi-space sparse representation. Multimed Tools Appl. doi:10.1007/s11042-011-0953-4
Kalantidis Y, Tolias G, Avrithis Y, Phinikettos M, Spyrou E, Mylonas P, Kollias S (2011) Viral: visual image retrieval and localization. Multimed Tools Appl 51:555–592
Kawulok M (2010) Energy-based blob analysis for improving precision of skin segmentation. Multimed Tools Appl 49:463–481
Lee H, Battle A, Raina R, Ng AY (2006) Efficient sparse coding algorithms. In: NIPS, pp 801–808
Levinshtein A, Dickinson S, Sminchisescu C (2009) Multiscale symmetric part detection and grouping. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2009, pp 2162–2169
Levinshtein A, Stere A, Kutulakos K, Fleet D, Dickinson S, Siddiqi K (2009) Turbopixels: fast superpixels using geometric flows. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31:2290–2297
Li H, Ngan KN (2007) Unsupervised video segmentation with low depth of field. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 17:1742–1751
Li H, Ngan K (2008) Saliency model based face segmentation in head-and-shoulder video sequences. J Vis Commun Image Represent 19:320–333
Li H, Ngan K, Liu Q (2009) Faceseg: automatic face segmentation for real-time video. IEEE Trans Multimedia 11:77–88
Li H, Ngan KN (2011) A co-saliency model of image pairs. IEEE Trans Image Process 20:3365–3375
Li H, Ngan K (2011) Learning to extract focused objects from low dof images. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 21:1571–1580
Li Z, Wu X, Chang S (2012) Segmentation using superpixels: a bipartite graph partitioning approach. In: IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2012, pp 789–796
Liu Q, Han T, Sun Y, Chu Z, Shen B (2012) A two step salient objects extraction framework based on image segmentation and saliency detection. Multimed Tools Appl 67(1):231–247
Mairal J, Bach F, Ponce J, Sapiro G, Zisserman A (2009) Non-local sparse models for image restoration. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2009, pp 2272–2279
Martin D, Fowlkes C, Tal D, Malik J (2001) A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2001, pp 416–423
Meng F, Li H, Liu G, Ngan KN (2012) Object co-segmentation based on shortest path algorithm and saliency model. IEEE Trans Multimedia 14:1429–1441
Nowozin S, Gehler PV, Lampert CH (2010) On parameter learning in crf-based approaches to object class image segmentation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV 2010, pp 98–111
Olshausen BA, Fieldt DJ (1997) Sparse coding with an overcomplete basis set: a strategy employed by v1? Vis Res 37:3311–3325
Pati YC, Rezaiifar R, Rezaiifar YCPR, Krishnaprasad PS (2012) Orthogonal matching pursuit: recursive function approximation with applications to wavelet decomposition. In: Proceedings of the 27th annual asilomar conference on signals, systems, and computers, pp. 40–44
Radhakrishna A, Appu S, Kevin S, Aurelien L, Pascal F, Sabine S (2010) SLIC Superpixels, EPFL Technical Report no. 149300
Ren X, Malik J (2003) Learning a classification model for segmentation. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2003, pp 10–17
Shi J, Malik J (1997) Normalized cuts and image segmentation. In: IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 1997, pp 731–737
Shotton J, Winn J, Rother C, Criminisi A (2009) Textonboost for image understanding: multi-class object recognition and segmentation by jointly modeling texture, layout, and context. Int J Comput Vis 81:2–23
Tibshirani R (1996) Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J R Stat Soc Ser B 58:267–288
Tighe J, Lazebnik S (2010) Superparsing: scalable nonparametric image parsing with superpixels. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV 2010, pp 352–365
Tropp J, Wright S (2010) Computational methods for sparse solution of linear inverse problems. Proc IEEE 98:948–958
Vazquez-Reina A, Avidan S, Pfister H, Miller E (2010) Multiple hypothesis video segmentation from superpixel flows. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV 2010, pp 268–281
Vedaldi A, Fulkerson B (2008) VLFeat: an open and portable library of computer vision algorithms. http://www.vlfeat.org/
Vedaldi A, Soatto S (2008) Quick shift and kernel methods for mode seeking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV 2008, pp 705–718
Vieux R, BenoisPineau J, Domenger J, Braquelaire A (2012) Segmentation-based multi-class semantic object detection. Multimed Tools Appl 60:305–326
Wright J, Yang A, Ganesh A, Sastry S, Ma Y (2009) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31:210–227
Wright J, Ma Y, Mairal J, Sapiro G, Huang T, Yan S (2010) Sparse representation for computer vision and pattern recognition. Proc IEEE 98:1031–1044
Xu C, Corso J (2012) Evaluation of super-voxel methods for early video processing. In: IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2012, pp 1202–1209
Yang J, Wright J, Huang T, Ma Y (2008) Image super-resolution as sparse representation of raw image patches. In: IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2008, pp 1–8
Yang J, Yu K, Gong Y, Huang T (2009) Linear spatial pyramid matching using sparse coding for image classiffication. In: IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2009, pp 1794–1801
Yang M, Zhang D, Zhang D, Wang S (2012) Relaxed collaborative representation for pattern classiffication. In: IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2012, pp 2224–2231
Zhang H, Yang J, Zhang Y, Nasrabadi N, Huang T (2011) Close the loop: joint blind image restoration and recognition with sparse representation prior. In: IEEE international Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2011, pp 770–777
Zhang D, Zhu P, Hu Q, Zhang D (2011) A linear subspace learning approach via sparse coding. In: IEEE international Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2011, pp 755–761
Zhang D, Yang M, Feng X (2011) Sparse representation or collaborative representation: which helps face recognition? In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), ICCV 2011, pp 471–478
Zhao J, Ching S, Cheung S (2012) Human segmentation by geometrically fusing visible-light and thermal imageries Multimed Tools Appl. doi:10.1007/s11042-012-1299-2
Zhu Y, Papademetris X, Sinusas A, Duncan J (2010) Segmentation of the left ventricle from cardiac mr images using a subject-specific dynamical model. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29:669–687
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by NSFC (No. 61179060, and 61101091), National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, No. 2012AA011503), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (ZYGX2012J019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Y., Huang, C. & Xu, L. Semantic superpixel extraction via a discriminative sparse representation. Multimed Tools Appl 73, 1247–1268 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1626-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1626-2