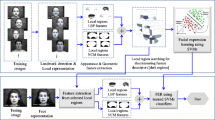
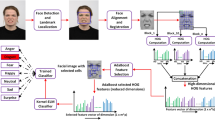
Abstract
Most facial expression recognition (FER) systems used facial expression data created during a short period of time and this data is used for learning/training of FER systems. There are many facial expression patterns (i.e. a particular expression can be represented in many different patterns) which cannot be generated and used as learning/training data in a short time. Therefore, in order to maintain its high accuracy and robustness for a long time of a facial expression recognition system, the classifier should be evolved adaptively over time and space. We proposed a facial expression recognition system that has the aptitude of incrementally learning and thus can learn all possible patterns of expressions that may be generated in feature. After extraction of region of interest (face), the system extracts Speeded-Up Robust Features (SURF). A novel SURF descriptor template based nearest neighbor classifier is proposed for classification. This classifier is used as base/weak classifier for incremental learning algorithm Learn++. A vast range of experimentation is performed on five different databases that demonstrate the incremental learning capability of the proposed system. The experiments using the incrementally learning classification demonstrate promising results.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aifanti N, Papachristou C, Delopoulos A (2010) The MUG facial expression database. Proc. 11th Int. Workshop on Image Analysis for Multimedia Interactive Services (WIAMIS), 12–14
Bay H, Ess A, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L (2008) Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Comput Vis Image Underst 110(3):346–359
Belhumeur PN, Hespanha JP, Kriegman DJ (1997) Eigenfaces vs. fisherfaces: recognition using class specific linear projection. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell 19(7):711–720
Bell C (1896) Essays on the anatomy of expression in painting 3rd edition. Longman, Reese, Hurst &Orme, London. First edition published 1806
Bettadapura V (2012) Face expression recognition and analysis: the state of the art. Tech Report April arXiv 1203:6722
Cheon Y, Kim D (2009) Natural facial expression recognition using differential-AAM and manifold learning. Patt Recog 42:1340–1350
Chin S, Lee C (2010) Exaggeration of facial expressions from facial motion capture data. Chin Opt Lett 8(1):29–32
Cohn JF, Tian, Kanade T (2001) Recognizing action units for facial expression analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(2):97–115
Darwin C (1872) The expression of the emotions in man and animal. J. Murray, London
Dreuw P, Steingrube P, Hanselmann H, Ney H (2009) SURF-face: face recognition under viewpoint consistency constraints. British Machine Vision Conference 2009
Ekman P, Friesen W (1978) Facial action coding system: A technique for the measurement of facial movement. Consulting Psychologists Press
Huang D, Shan C, Ardabilian M, Wang Y, Chen L (2011) Local binary patterns and its application to facial image analysis: a survey. IEEE Trans Sys Man Cyb 41(6):765–781
JinliSuo LL, Shan S (2011) High-resolution face fusion for gender conversion. IEEE Trans Sys Man Cyber Part A 41(2):226–237
Kanade T, Tian Y, Cohn JF (2000) Comprehensive database for facial expression analysis. Fourth IEEE ICAFGR
Kotsia I, Pitas I (2007) Facial expression recognition in image sequences using geometric deformation features and support vector machines. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(1):160–187
Lee CC, Huang SS, Shih CY (2010) Facial affect recognition using regularized discriminant analysis-based algorithms. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 10:596842
Lin L et al (2009) A stochasticgraphgrammarforcompositionalobjectrepresentationandrecognition. Patt Recog 42:1297–1307
Lin L et al (2012) Representing and recognizing objects with massive local image patches. Pattern Recognition 45:231–240
Lyons MJ, Akamatsu S, Kamachi M, Gyoba J (1998) Coding facial expressions with Gabor wavelets. Proceedings, Third IEEE ICAFGR, 200–205
MPEG Video and SNHC (1998) Text of ISO/IEC FDIS 14 496-3: Audio, in Atlantic City MPEG Mtg. Doc. ISO/MPEG N2503
Niu Z, Qiu X (2010) Facial expression recognition based on weighted principal component analysis and support vector machines. Adv Comput Theory Eng (ICACTE), 174–178
Ojala T, Pietikainen M (2002) Multi resolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell 24(7):971–987
Pantic M, Rothkrantz L (2000) Automatic analysis of facial expressions: the state of the art. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22(12):1424–1445
Polikar R (2007) Bootstrap-inspired techniques in computational intelligence. IEEE Sig Proc Mag 59–72
Polikar R, Udpa L, Udpa SS, Honavar V (2001) Learn++: an incremental learning algorithm for supervised neural networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern C 31(4):497–508
Shan C, Gong S, McOwan PW (2009) Facial expression recognition based on local binary patterns: a comprehensive study. Image Vis Comput 27:803–816
Shen L, Bai L (2006) Information theory for Gabor feature selection for face recognition. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process, 8–8
Valstar MF, Pantic M (2010) Induced disgust, happiness and surprise: an addition to the MMI facial expression database. Proceedings of Int’l Conf. Language Resources and Evaluation, Workshop on EMOTION, 65–70
Viola P, Jones MJ (2004) Robust real-time face detection. IEEE ICCV Workshop Stat Comput Theor Vis 137–154
Wallhoff F (2005) FEEDTUM: facial expressions and emotion database. Technical University of Munich. http://www.mmk.ei.tum.de/˜waf/fgnet/feedtum.html
Yan H, Ang MH Jr, Poo AN (2011) Cross-dataset facial expression recognition. IEEE Int Conf Robot Autom May 9–13, Shanghai, China
Zhao G, Pietikainen M (2009) Boosted multi-resolution spatiotemporal descriptors for facial expression recognition. Patt Recog Lett 30:1117–1127
Zhi R, Ruan Q (2008) Discriminant spectral analysis for facial expression recognition. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Image Processing, 1924–1927
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zia, M.S., Jaffar, M.A. An adaptive training based on classification system for patterns in facial expressions using SURF descriptor templates. Multimed Tools Appl 74, 3881–3899 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1803-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1803-3