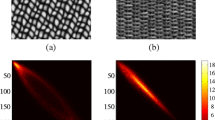
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a new two channels feature space active contours model for texture segmentation by using image decomposition and local self-similarity descriptor of textures. The piece-wise smooth component of image decomposition is regarded as one channel of feature space for segmentation. Defined as a symmetry matrix and a kind of features fusion tool, the local self-similarity descriptor SSM captures the internal geometric layout of local repetitive pattern regions and is computed on different features of textures including oscillatory component of image decomposition, phase congruency and log-Gabor filters responses. A distance map dSSM can measure the similarities between the descriptor of template and the local windows surrounding every pixel on the texture image. And then dSSM is set as another channel of feature space for segmentation. Based on the space, texture segmentation is performed by using active contours and level set technology. In addition, the accuracy of texture boundary localization and the template searching inside initial contour are also concerned in this paper. Compared with some recent approaches, our method is more convincing and works well for synthetic textured images and ones in the real world.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arsenault E, Baker C (2010) The role of higher-order statistics in naturalistic texture segmentation: modelling psychophysical data. J Vis 10:1354
Aujol JF, Aubert G, Blanc-Féraud L, Chambolle A (2003) Decomposing an image: application to textured images and SAR images. INRIA Res Rep 4704
Awate SP, Whitaker RT (2005) Higher-order image statistics for unsupervised, information-theoretic, adaptive, image filtering. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 2:44–51
Belongie S, Malik J, Puzicha J (2002) Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(4):509–522
Brox T, Weickert J (2004) A TV flow based local scale measure for texture discrimination. Proc 8th European Conf Comput Vis 2:578–590
BSDS500 image database, http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/Research/Projects/CS/vision/grouping/resources.html
Chambolle A (2004) An algorithm for total variation minimization and applications. JMIV 20:89–97
Clausi DA, Deng H (2005) Design-based texture feature fusion using gabor filters and co-occurrence probabilities. IEEE Trans Image Process 14(7):925–936
Clausi DA, Jernigan M (1998) A fast method to determine co-occurrence texture features. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 36(1):298–300
Cutler R, Davis L (2000) Robust real-time periodic motion detection, analysis, and applications. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22(8):781–796
Dalal N, Triggs B (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recog 2:886–893
De Grandi GD, Lee J-S, Schuler DL (2007) Target detection and texture segmentation in polarimetric SAR images using a wavelet frame: theoretical aspects. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 45(11):3437–3453
Deselaers T, Ferrari V (2010) Global and efficient self-similarity for object classification and detection. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recog 1:1633–1640
Dunn D, Higgins W (1995) Optimal Gabor filters for texture segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 4(7):964–974
Eckman JP et al (1987) Recurrence plots of dynamical systems. Europhys Lett 4:973–977
Foote JT, Cooper ML (2003) Media segmentation using self-similarity decomposition. SPIE Proceedings Vol 5021, Storage and Retrieval for Media Databases, 167–175
Gao Y, Bouix S, Shenton M, Tannenbaum A (2013) Sparse texture active contour. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(10):3866–3878
Kovesi P (1999, Summer) Image features from phase congruency. Videre: J Comput Vis Res. MIT Press. Volume 1, Number 3 http://mitpress.mit.edu/e-journals/Videre/001/v13.html
Lele S (1993) Euclidean distance matrix analysis (EDMA): estimation of mean form and mean form difference. Math Geol 25:573–602
Lifei Z (2002) Active contour technique based on minimum description length principle. Ph.D. dissertation, Insititute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Liu X, Wang D (2006) Image and texture segmentation using local spectral histograms. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(10):3066–3077
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Maizel JV Jr, Lenk RP (1981) Enhanced graphic matrix analysis of nucleic acid and protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 78(12):7665–7669
Malik J, Perona P (1990) Preattentive texture discrimination with early vision mechanisms. J Opt Soc Am A 7(5):923–932
Manjunath B, Derin H (1991) Unsupervised texture segmentation using Markov random fields models. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 13(5):478–482
Meyer Y (2001, Mar) Oscillating patterns in image processing and nonlinear evolution equations. Univ Lect Ser 22, Amer Math Soc
Mikolajczyk K, Schmid C (2005) A performance evaluation of local descriptors. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(10):1615–1630
Osher SJ, Solé A, Vese LA (2003) Image decomposition and restoration using total variation minimization and the H-1 norm. Multiscale Model Simul SIAM Interdiscip J 1(3):349–370
Paragios N, Deriche R (2002) Geodesic active regions and level set methods for supervised texture segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 46(3):223–247
Rousson M, Brox T, Deriche R (2003) Active unsupervised texture segmentation on diffusion based feature space. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 2:669–704
Sandberg B, Chan T, Vese L (2002) A level-set and gabor-based active contour algorithm for segmenting textured images. Proc UCLA Dept Math CAM Rep Conf 1–2
Shapiro B, Nussinov R, Lipkin L, Maizel J Jr (1987) An interactive dot matrix system for locating potentially significant features in nucleic acid molecules. J Bimol Struct Dyn 4(5):697–706
Shechtman E, Irani M (2007) Matching local self-similarities across images and videos. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recog 1–8
Unser M (1995) Texture classification and segmentation using wavelet frames. IEEE Trans Image Process 4(11):1549–1560
Vese LA, Osher SJ (2003) Modeling textures with total variation minimization and oscillating patterns in image processing. J Sci Comput 19:553–572
Wilscy M, Sasi RK (2010) Wavelet based texture segmentation. Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Intell Comput Res (ICCIC) 1–4
Zhang J, Tan T, Ma L (2002) Invariant texture segmentation via circular gabor filters. Proc Int Conf Pattern Recognit 3:901–904
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by The Importation and Development of High-Caliber Talents Project of Beijing Municipal Institutions (CIT&TCD201304115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Hou, X. Texture segmentation using image decomposition and local self-similarity of different features. Multimed Tools Appl 74, 6069–6089 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-014-1909-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-014-1909-2