Abstract
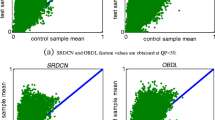
In this paper we present two compressed-domain features that are highly indicative of saliency in natural video. We demonstrate the potential of these two features to indicate saliency by comparing their statistics around human fixation points against their statistics at control points away from fixations. Then, using these features, we construct a simple and effective saliency estimation method for compressed video, which utilizes only motion vectors, block coding modes and coded residuals from the bitstream, with partial decoding. The proposed algorithm has been extensively tested on two ground truth datasets using several accuracy metrics. The results indicate its superior performance over several state-of-the-art compressed-domain and pixel-domain algorithms for saliency estimation.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Agarwal G, Anbu A, Sinha A (2003) A fast algorithm to find the region-of-interest in the compressed MPEG domain. In: Proc. IEEE ICME’03, vol 2, pp 133–136
Arvanitidou M G, Glantz A, Krutz A, Sikora T, Mrak M, Kondoz A (2009) Global motion estimation using variable block sizes and its application to object segmentation. In: Proc. IEEE WIAMIS’09, pp 173–176
Borji A, Itti L (2013) State-of-the-art in visual attention modeling. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):185–207
Borji A, Sihite D N, Itti L (2013) Quantitative analysis of human-model agreement in visual saliency modeling: a comparative study. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(1):55–69
Dagan I, Lee L, Pereira F (1997) Similarity-based methods for word sense disambiguation. In: Proc. European chapter of the association for computational linguistics, pp 56–63
Efron B, Tibshirani R (1993) An introduction to the bootstrap, vol 57. CRC press
Einhäuser W, Spain M, Perona P (2008) Objects predict fixations better than early saliency. J Vis 8(14)
Fang Y, Lin W, Chen Z, Tsai C M, Lin C W (2014) A video saliency detection model in compressed domain. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 24 (1):27–38
Garcia-Diaz A, Fdez-Vidal X R, Pardo X M, Dosil R (2012) Saliency from hierarchical adaptation through decorrelation and variance normalization. Image Vis Comput 30(1):51–64
Guo C, Zhang L (2010) A novel multiresolution spatiotemporal saliency detection model and its applications in image and video compression. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(1):185–198
Hadizadeh H, Bajić I V (2014) Saliency-aware video compression. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(1): 19–33
Hadizadeh H, Bajić I V, Cheung G (2013) Video error concealment using a computation-efficient low saliency prior. IEEE Trans Multimed 15(8):2099–2113
Hadizadeh H, Enriquez M J, Bajić I V (2012) Eye-tracking database for a set of standard video sequences. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(2):898–903
Han S, Vasconcelos N (2010) Biologically plausible saliency mechanisms improve feedforward object recognition. Vis Res 50(22):2295–2307
Harel J, Koch C, Perona P (2007) Graph-based visual saliency. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 19:545–552
Hochberg Y, Tamhane A C (1987) Multiple comparison procedures, Wiley
Itti L, Koch C (2001) Feature combination strategies for saliency-based visual attention systems. J Electron Imag 10(1):161–169
Itti L (2004) Automatic foveation for video compression using a neurobiological model of visual attention. IEEE Trans Image Process. 13(10):1304–1318
Itti L, Dhavale N, Pighin F (2004) Realistic avatar eye and head animation using a neurobiological model of visual attention. In: Optical science and technology, SPIE’s 48th annual meeting, pp 64–78
Itti L, Baldi P (2005) A principled approach to detecting surprising events in video. In: Proc. IEEE CVPR’05, vol 1, pp 631–637
Itti L, Baldi P F (2006) Bayesian surprise attracts human attention. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 19:547–554
Itti L, Baldi P (2009) Bayesian surprise attracts human attention. Vis Res 49(10):1295–1306
Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E (1998) A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20(11):1254–1259
Ji Q G, Fang Z D, Xie Z H, Lu Z M (2013) Video abstraction based on the visual attention model and online clustering. Signal Process Image Commun 28 (3):241–253
Khalilian H, Bajić I V (2013) Video watermarking with empirical PCA-based decoding. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(12):4825–4840
Khatoonabadi S H, Bajić I V, Shan Y (2014) Comparison of visual saliency models for compressed video. In: Proc. IEEE ICIP’14, pp 1081–1085
Khatoonabadi S H, Bajić I V, Shan Y (2014) Compressed-domain correlates of fixations in video. In: Proc. 1st Intl. workshop on perception inspired video processing (PIVP’14), pp 3–8
Kim W, Jung C, Kim C (2011) Spatiotemporal saliency detection and its applications in static and dynamic scenes. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 21 (4):446–456
Kreyszig E (1970) Introductory mathematical statistics: principles and methods. Wiley, p New York
Le Meur O, Baccino T (2013) Methods for comparing scanpaths and saliency maps: strengths and weaknesses. Behav Res Methods 45(1):251–266
Lin J (1991) Divergence measures based on the Shannon entropy. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 37(1):145–151
Liu Z, Yan H, Shen L, Wang Y, Zhang Z (2009) A motion attention model based rate control algorithm for H. 264/AVC. In: The 8th IEEE/ACIS international conference on computer and information science (ICIS’09), pp 568–573
Ma YF, Zhang HJ A new perceived motion based shot content representation. In: Proc. IEEE ICIP’01, vol 3, pp 426-429
Ma Y F, Zhang H J (2002) A model of motion attention for video skimming. In: Proc. IEEE ICIP’02, vol 1, pp 129–132
Mahadevan V, Vasconcelos N (2013) Biologically inspired object tracking using center-surround saliency mechanisms. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35 (3):541–554
Mateescu VA, Bajić IV (2014) Attention retargeting by color manipulation in images. In: Proc. 1st Intl. workshop on perception inspired video processing (PIVP’14), pp 15-20
Moorthy A K, Bovik A C (2009) Visual importance pooling for image quality assessment. IEEE J Sel Topics Signal Process 3(2):193–201
Muthuswamy K, Rajan D (2013) Salient motion detection in compressed domain. IEEE Signal Process Lett 20(10):996–999
Niebur E, Koch C (1998) Computational architectures for attention. The Attentive Brain, chapter, chapter 9. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 163–186
Peters R J, Iyer A, Itti L, Koch C (2005) Components of bottom-up gaze allocation in natural images. Vis Res 45(18):2397–2416
Reinagel P, Zador A M (1999) Natural scene statistics at the center of gaze. Netw Comput Neural Syst 10:1–10
Seo H J, Milanfar P (2009) Static and space-time visual saliency detection by self-resemblance. J Vis 9(12):1–27
Sinha A, Agarwal G, Anbu A (2004) Region-of-interest based compressed domain video transcoding scheme. In: Proc. IEEE ICASSP’04, vol 3, pp 161–164
Sullivan G J, Ohm J, Woo-Jin H, Wiegand T (2012) Overview of the high efficiency video coding (HEVC) standard. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 22 (12):1649–1668
Swets A (1996) Signal detection theory and ROC analysis in psychology and diagnostics: collected papers. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc
The Dynamic Images and Eye Movements (DIEM) project. http://thediemproject.wordpress.com
Treisman A M, Gelade G (1980) A feature-integration theory of attention. Cognitive Psychol 12(1):97–136
Wiegand T, Sullivan G J, Bjontegaard G, Luthra A (2003) Overview of the H. 264/AVC video coding standard. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 13 (7):560–576
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Cisco Research Award CG# 573690 and NSERC Grant RGPIN 327249.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khatoonabadi, S.H., Bajić, I.V. & Shan, Y. Compressed-domain correlates of human fixations in dynamic scenes. Multimed Tools Appl 74, 10057–10075 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2802-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2802-3