Abstract
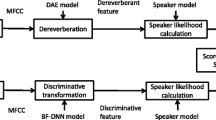
The performance of speech recognition in distant-talking environments is severely degraded by the reverberation that can occur in enclosed spaces (e.g., meeting rooms). To mitigate this degradation, dereverberation techniques such as network structure-based denoising autoencoders and multi-step linear prediction are used to improve the recognition accuracy of reverberant speech. Regardless of the reverberant conditions, a novel discriminative bottleneck feature extraction approach has been demonstrated to be effective for speech recognition under a range of conditions. As bottleneck feature extraction is not primarily designed for dereverberation, we are interested in whether it can compensate for other carefully designed dereverberation approaches. In this paper, we propose three schemes covering both front-end processing (cascaded combination and parallel combination) and back-end processing (system combination). Each of these schemes integrates bottleneck feature extraction with dereverberation. The effectiveness of these schemes is evaluated via a series of experiments using the REVERB challenge dataset.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
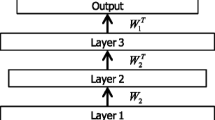
W i and \({W_{i}^{T}}\) correspond to f L in (1).
References
Abdel-Hamid O, Mohamed A-r, Jiang H, Deng L, Penn G, Yu D (2014) Convolutional neural networks for speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio, Speech, Lang Process 22(9):1533–1545
Evermann G, Woodland P C (2000) Posterior probability decoding, confidence estimation and system combination. In: Proc. Speech Transcr. Work., vol 27. Baltimore
Furui S (1981) Cepstral analysis technique for automatic speaker verification. Acoust Speech Signal Process IEEE Trans 29(2):254–272
Gesbert D, Duhamel P (1997) Robust blind channel identification and equalization based on multi-step predictors. In: ICASSP, IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. - Proc., vol 5, pp 3621–3624
Grézl F, Fousek P (2008) Optimizing bottle-neck features for LVCSR. In: ICASSP, IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. - Proc., pp 4729–4732
Grézl F, Karafiát M, Kontár S, Černocký J (2007) Probabilistic and bottle-neck features for LVCSR of meetings. In: ICASSP, IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. - Proc, vol 4. IEEE, pp 757–760
Hermansky H, Ellis D P W, Sharma S (2000) Tandem connectionist feature extraction for conventional HMM systems. In: ICASSP, IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. - Proc. IEEE, pp 1635–1638
Hinton G, Deng L, Yu D, Dahl G, Mohamed A R, Jaitly N, Senior A, Vanhoucke V, Nguyen P, Sainath T, Kingsbury B (2012) Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Process Mag 29(November):82–97
Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R R (2006) Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 313(July):504–507
Ishii T, Komiyama H, Shinozaki Y, Horiuchi T, Kuroiwa S (2013) Reverberant speech recognition based on denoising autoencoder. In: Proc. Annu. Conf. Int. Speech Commun. Assoc. INTERSPEECH, pp 3512–3516
Kinoshita K, Delcroix M, Nakatani T, Miyoshi M (2009) Suppression of late reverberation effect on speech signal using long-term multiple-step linear prediction. IEEE Trans Audio, Speech Lang Process 17:534–545
Kinoshita K, Delcroix M, Yoshioka T, Nakatani T, Sehr A, Kellermann W, Maas R (2013) The reverb challenge: A common evaluation framework for dereverberation and recognition of reverberant speech. In: Appl. Signal Process. to Audio Acoust. (WASPAA), 2013 IEEE Work. IEEE, pp 1–4
Lal P, King S (2013) Cross-lingual automatic speech recognition using tandem features. IEEE Trans Audio, Speech, Lang Process 21:2506–2515
Liang L, Renals S (2014) Probabilistic linear discriminant analysis with bottleneck features for speech recognition. In: Proc. Annu. Conf. Int. Speech Commun. Assoc. INTERSPEECH
Liu F-H, Stern R M, Huang X, Acero A (1993) Efficient cepstral normalization for robust speech recognition, Proc. Work. Hum. Lang. Technol. - HLT ’93
Longbiao W, Kitaoka N, Nakagawa S, Wang L, Kitaoka N, Nakagawa S (2011) Distant-talking speech recognition based on spectral subtraction by multi-channel LMS algorithm. IEICE Trans Inf Syst 94(3):659–667
Nguyen Q B, Gehring J, Muller M, Stuker S, Waibel A (2014) Multilingual shifting deep bottleneck features for low-resource ASR. In: ICASSP, IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. - Proc., pp 5607–5611
Sainath T N (2012) Auto-encoder bottleneck features using deep belief networks. In: ICASSP, IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. - Proc., pp 4153– 4156
Sak H, Senior A, Beaufays F (2014) Long short-term memory based recurrent neural network architectures for large vocabulary speech recognition. arXiv: 1402.1128
Seide F, Li G, Yu D (2011) Conversational speech transcription using Context-Dependent Deep Neural Networks. In: Proc. Annu. Conf. Int. Speech Commun. Assoc. INTERSPEECH, pp 437–440
Sundermeyer M, Schl R, Ney H (2012) Context-Dependent MLPs for LVCSR : TANDEM, Hybrid or Both ?. In: Proc. Annu. Conf. Int. Speech Commun. Assoc. INTERSPEECH
Ueda Y, Wang L, Kai A, Xiao X, Chng E, Li H (2015) Single-channel Dereverberation for Distant-Talking Speech Recognition by Combining Denoising Autoencoder and Temporal Structure Normalization, J. Signal Process. Syst.
Vincent P, Larochelle H, Bengio Y, Manzagol P-A (2008) Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In: Proc. 25th Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. ACM Press, pp 1096–1103
Vincent P, Larochelle H, Lajoie I, Bengio Y, Manzagol P-A (2010) Stacked denoising autoencoders: learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. J Mach Learn Res 11:3371–3408
Wang L, Bo R, Ueda Y, Kai A, Teraoka S, Fukushima T (2014) Denoising autoencoder and environment adaptation for distant-talking speech recognition with asynchronous speech recording. In: APSIPA ASC
Wang L, Odani K, Kai A (2012) Dereverberation and denoising based on generalized spectral subtraction by multi-channel LMS algorithm using a small-scale microphone array. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2012:1–12
Xie X, Su R, Liu X, Wang L (2014) Deep neural network bottleneck features for generalized variable parameter HMMs. In: Proc. Annu. Conf. Int. Speech Commun. Assoc. INTERSPEECH. ISCA, pp 2739–2743
Yamada T, Wang L, Kai A (2013) Improvement of distant-talking speaker identification using bottleneck features of DNN. In: INTERSPEECH, pp 3661–3664
Yu D, Deng L, Dahl G E (2010) Roles of pretraining and fine-tuning in context-dependent DBN-HMMs for real-world speech recognition. In: NIPS Work. Deep Learn. Unsupervised Featur. Learn.
Yu D, Seltzer M L (2011) Improved Bottleneck Features Using Pretrained Deep Neural Networks. In: Proc. Annu. Conf. Int. Speech Commun. Assoc. INTERSPEECH, pp 237–240
Zhang Z, Wang L, Kai A (2014) Distant-talking speaker identification by generalized spectral subtraction-based dereverberation and its efficient computation. EURASIP J Audio, Speech, Music Process 2014(1):15
Zhang Z, Wang L, Kai A, Yamada T, Li W, Iwahashi M (2015) Deep neural network-based bottleneck feature and denoising autoencoder-based dereverberation for distant-talking speaker identification. EURASIP J Audio, Speech, Music Process 2015(1):12
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by JSPS KANKENHI Grant Number 15K16020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, B., Wang, L., Lu, L. et al. Combination of bottleneck feature extraction and dereverberation for distant-talking speech recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 75, 5093–5108 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2849-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2849-1