Abstract
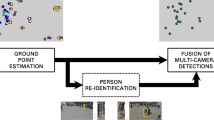
Real-time estimates of a crowd size is a central task in civilian surveillance. In this paper we present a novel system counting people in a crowd scene with overlapping cameras. This system fuses all single view foreground information to localize each person present on the scene. The purpose of our fusion strategy is to use the foreground pixels of each single views to improve real-time objects association between each camera of the network. The foreground pixels are obtained by using an algorithm based on codebook. In this work, we aggregate the resulting silhouettes over cameras network, and compute a planar homography projection of each camera’s visual hull into ground plane. The visual hull is obtained by finding the convex hull of the foreground pixels. After the projection into the ground plane, we fuse the obtained polygons by using the geometric properties of the scene and on the quality of each camera detection. We also suggest a region-based approach tracking strategy which keeps track of people movements and of their identities along time, also enabling tolerance to occasional misdetections. This tracking strategy is implemented on the result of the views fusion and allows to estimate the crowd size dependently on each frame. Assessment of experiments using public datasets proposed for the evaluation of counting people system demonstrates the performance of our fusion approach. These results prove that the fusion strategy can run in real-time and is efficient for making data association. We also prove that the combination of our fusion approach and the proposed tracking improve the people counting.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albiol A, Mora I, Naranjo V (2001) Real-time high density people counter using morphological tools. IEEE Trans Intell Trans Syst 2(4):204–218
Beymer D (2000) Person counting using stereo. In: Proceedings of workshop on human motion, pp 127–133
Cai Q, Aggarwal J (1998) Automatic tracking of human motion in indoor scenes across multiple synchronized video streams. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 356–362
Chan A, Vasconcelos N (2012) Counting people with low-level features and bayesian regression. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(4):2160–2177
Conte D, Foggia P, Percannella G, Tufano F, Vento M (2010) A method for counting moving people in video surveillance videos. EURASIP J Adv Signal Processing:1–10
Davies A, Yin JH, Velastin S (1995) Crowd monitoring using image processing. Electron Commun Eng J 7(1):37–47
Duin RPW, Tax DMJ (2000) Experiments with classifier combining rules. In: Proceedings of 1st international workshop on multiple classifier systems, pp 16–29
Englebienne G, Krose B (2010) Fast bayesian people detection. In: Proceedings of the 22nd benelux conference on artificial intelligence
Eshel R, Moses Y (2008) Homography based multiple camera detection and tracking of people in a dense crowd. In: Proceedings of 18th IEEE international conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–8
Ferryman J, Shahrokni A (2009) An overview of the pets 2009 challenge. In: Proceedings of the 11th IEEE international workshop on performance evaluation of tracking and surveillance, pp 25–30
Fleuret F, Berclaz J, Lengagne R (2008) Multi-camera people tracking with a probabilistic occupancy map. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 30(2):267–282
Fu H, Ma H, Xiao H (2014) Scene-adaptive accurate and fast vertical crowd counting via joint using depth and color. Multimed Tools Appl 73(1):273–289
Ge W, Collins R (2010) Crowd detection with a multiview sampler. In: Daniilidis K, Maragos P, Paragios N (eds) Computer vision ECCV 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp 324–337
Giacinto G, Roli F, Fumera G (2000) Selection of classifiers based on multiple classifier behaviour. In: Advances in pattern recognition, pp 87–93
Harville M (2004) Stereo person tracking with adaptive plan-view templates of height and occupancy statistics. Image Vis Comput 22(2):127–142
Hashemzadeh M, Pan G, Yao M (2014) Counting moving people in crowds using motion statistics of feature-points. Multimed Tools Appl 72(1):453–487
Hu W, Hu M, Zhou X, Tan T, Lou J, Maybank S (2006) Principal axis-based correspondence between multiple cameras for people tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(4):663–671
Khan S, Shah M (2003) Consistent labeling of tracked objects in multiple cameras with overlapping fields of view. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(10):1355–1360
Khan SM, Shah M (2006) A multi-view approach to tracking people in crowded scenes using a planar homography constraint. In: Proceedings of 9th European conference on computer vision, pp 133– 146
Khan SM, Shah M (2009) Tracking multiple occluding people by localizing on multiple scene planes. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(3):505–519
Kang J, Cohen I, Medioni G (2003) Continuous tracking within and across camera streams. In: Proceedings of international conference on computer vision pattern recognition, vol 1, pp 267– 272
Kim K, Davis LS (2006) Multi-camera tracking and segmentation of occluded people on ground plane using search-guided particle filtering. In: Proceedings of the 9th European conference on computer vision, pp 98–109
Kim J, Seo K, Chung K (1997) A systematic approach to classifier selection on combining multiple classifiers for handwritten digit recognition. In: Proceedings of international conference on document analysis and recognition, vol 2, pp 459–462
Kim JW, Choi KS, Park WS, Lee JY, Ko SJ (2002) Robust real-time people tracking system for security
Kim K, Chalidabhonse TH, Harwood D, Davis L (2005) Real-time foreground-background segmentation using codebook model. Elsevier Real-Time Imaging 11(3):167–256
Krahnstoever N, Yu T, Patwardhan K, Gao D (2009) Multi-camera person tracking in crowded environments. In: Proceedings of 12th IEEE international workshop on performance evaluation of tracking and surveillance, pp 1–7
Kuncheva LI, Whitaker CJ, Ship CA, Duin RPW (2000) Is independence good for combining classifiers?. In: Proceedings of international conference on pattern recognition, vol 2, pp 168–171
Kuncheva LI, Bezdek CJ, Duin RPW (2001) Decision templates for multiple classifier fusion : on experimental comparison. Pattern Recogn:299–314
Ma H, Zeng C, Ling CX (2012) A reliable people counting system via multiple cameras. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol 3(2)
Maddalena L, Petrosino A, Russi F (2014) People counting by learning their apperarance in a multi-view camera environment. Pattern Recogn Lett 36:125–134
Motamed C (2006) Motion detection and tracking using belief indicators for an automatic visual-surveillance system. Image Vis Comput:1192–1201
Mousse MA, Ezin EC, Motamed C (2014) Foreground-background segmentation based on codebook and edge detector. In: 10th international conference on signal-image technology and internet-based systems, pp 119–124
Qiuyu Z, Li T, Yiping J, Wei Jun D (2010) A novel approach of counting people based on stereovision and dsp. In: Proceedings of The 2nd international conference on computer and automation engineering, vol 1, pp 81–84
Subburaman V, Descamps A, Carincotte C (2012) Counting people in the crowd using a generic head detector. In: Proceedings of IEEE 9th international conference on advanced video and signal-based surveillance, pp 470–475
Sutherland IE, Sproull RF, Schumacker RA (1974) A characterization of ten hidden surface algorithms. In: ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), pp 1–55
van Oosterhout T, Bakkes S, Krse BJA (2011) Head detection in stereo data for people counting and segmentation. In: VISAPP, pp 620–625
Wren C, Azarbayejani A, Darrel T, Pentland A (1996) Pfinder: real-time tracking of the human body. In: Proceedings of 2nd international conference on automatic face and gesture recognition, pp 51– 56
Xu M, Orwell J, Lowey L, Thirde D (2005) Architecture and algorithms for tracking football players with multiple cameras. IEE Proc-Vis Image Signal Process 152(2):232–241
Xu M, Ren J, Chen D, Smith J, Wang G (2011) Real-time detection via homography mapping of foreground polygons from multiple. In: Proceedings of 18th IEEE international conference on image processing, pp 3593–3596
Yahiaoui T, Khoudour L, Meurie C (2010) Real-time passenger counting in buses using dense stereovision. J Electron Imaging 19(3)
Yang DB, Gonzalez-Banos HH, Guibas LJ (2003) Counting people in crowds with a real-time network of simple image sensors. In: Proceedings of 9th IEEE international conference on computer vision, vol 1, pp 122–129
Zhao T, Nevatia R (2003) Counting people in crowds with a real-time network of simple image sensors. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol 1, pp 122–129
Acknowledgments
This work is partially funded by the Association AS2V and Fondation Jacques De Rette, France. Authors are grateful to the Service de Coopération et d’Action Culturelle de l’Ambassade de France au Bénin. We also appreciate the valuable comments provided by the anonymous reviewers as these have improved the manuscript immensely.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mousse, M.A., Motamed, C. & Ezin, E.C. People counting via multiple views using a fast information fusion approach. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 6801–6819 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3352-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3352-z