Abstract
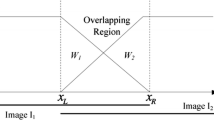
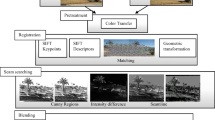
In this article, we propose a new method of image stitching that computes, in a robust manner, the transformation model applied to creating a panorama that is close to reality. The random selection of matching points used in existing methods, using Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) or the threshold of the execution process (iteration number) cannot generally provide sufficient precision. Our approach, in this regard, comes to solve this problem. The calculation of the transformation model is based on the VORONOI diagram that divides images into regions to be used in the matching instead of control points. In this case, the transformation estimation will be based on the regions seeds that provide the best correlation score. Among the advantages of our method is solving problems related to outliers that can, in existing methods, affect the reliability of the mosaic. The results obtained are satisfactory in terms of stability, quality, execution time and reduction of the computational complexity.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alahi A, Ortiz R, Vandergheynst P (2012) Freak: fast retina keypoint. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2012 I.E. Conference on, 510–517. Ieee. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247715
Allène C, Pons JP, Keriven R (2008) Seamless image-based texture atlases using multi-band blending. In Pattern Recognition, 2008. ICPR 2008. 19th International Conference on, 1–4. IEEE. doi:10.1109/ICPR.2008.4761913
Azzari P, Stefano LD, Bevilacqua A (2005) An effective real-time mosaicing algorithm apt to detect motion through background subtraction using a PTZ camera. Adv Video Signal Based Surveillance. AVSS 2005. IEEE Conf, 511–516. IEEE. doi:10.1109/AVSS.2005.1577321
Bay H, Ess A, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L (2008) Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Comput Vis Image Underst 110(3):346–359. doi:10.1016/j.cviu.2007.09.014
Bevilacqua A, Azzari P (2007) A fast and reliable image mosaicing technique with application to wide area motion detection. Image Analysis Recognition. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 501–512. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-74260-9_45
Brandt J (2010) Transform coding for fast approximate nearest neighbor search in high dimensions. IEEE Conf. Computer Vision Pattern Recognition. [Data file]. Retrieved from Adobe System: http://www.adobe.com/go/datasets
Brown M, Lowe DG (2007) Automatic panoramic image stitching using invariant features. Int J Comput Vis 74(1):59–73. doi:10.1007/s11263-006-0002-3
Burt PJ, Adelson EH (1983) A multiresolution spline with application to image mosaics. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2(4):217–236. doi:10.1145/245.247
Choi YH, Seong YK, Choi TS (2002) Image mosaicing with automatic scene segmentation for video indexing. Int Conf Consumer Electronics, 74–75. doi:10.1109/ICCE.2002.1013933
Fang X, Zhu J, Luo B (2012) Image mosaic with relaxed motion. SIViP 6(4):647–667. doi:10.1007/s11760-010-0194-4
Fischler MA, Bolles RC (1981) Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun ACM 24:381–395. doi:10.1145/358669.358692
Ghosh D, Kaabouch N (2016) A survey on image mosaicing techniques. J Vis Commun Image Represent 34:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.jvcir.2015.10.014
Hodge VJ, Austin JA (2004) Survey of outlier detection methodologies. Artif Intell Rev 22(2):85–126. doi:10.1007/s10462-004-4304-y
Hu J, Deng W, Guo J (2011) 2D projective transformation based active shape model for facial feature location. Eighth Int Conf Fuzzy Syst Knowl Discov 4:2442–2446. doi:10.1109/FSKD.2011.6019993
Huang W, Han X (2013) An improved RANSAC algorithm of color image stitching. Proc Chinese Intell Automation. 21–28. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-38466-0_3
Jalink A, McAdoo J, Halama G, Liu H (1996) CCD mosaic technique for large-field digital mammography. Med Imaging, IEEE Trans 15(3):260–267. doi:10.1109/42.500135
Jing N, Fan Y, Lingyi S (2013) Improved method of automatic image stitching based on SURF. Future Info Commun Technol Ubiquitous HealthCare (Ubi-HealthTech), 2013 First Int Symp, 1–5. IEEE. doi:10.1109/Ubi-HealthTech.2013.6708059
Kim BS, Lee SH, Cho NI (2011) Real-time panorama canvas of natural images. Consumer Electronics, IEEE Trans 57(4):1961–1968. doi:10.1109/TCE.2011.6131177
Laraqui A, Saaidi A, Jarrar A, Satori K (2014) Image stitching based on the geometric solution. Info Sci Tech (CIST), Third IEEE Int Colloquium IEEE, 340–344. doi:10.1109/CIST.2014.7016643
Laraqui M, Saaidi A, Mouhib A, Abarkan M (2015) Images matching using voronoï regions propagation. 3D Res 6(3):1–16. doi:10.1007/s13319-015-0056-5
Lhuillier M, Quan L (2002) Quasi-dense reconstruction from image sequence. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2002, 125–139. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. doi:10.1007/3-540-47967-8_9
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vision 60:91–110. doi:10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94
Ma X, Liu D, Zhang J, Xin J (2015) A fast affine-invariant features for image stitching under large viewpoint changes. Neurocomputing 151:1430–1438. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2014.10.045
Mikolajczyk K, Schmid C (2002) An affine invariant interest point detector. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2002, 128–142. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. doi:10.1007/3-540-47969-4_9
Montijano E, Martinez S, Sagues C (2015) Distributed robust consensus using RANSAC and dynamic opinions. Control Syst Technol, IEEE Trans 23(1):150–163. doi:10.1109/TCST.2014.2317771
Raguram R, Frahm JM, Pollefeys M (2008) A comparative analysis of RANSAC techniques leading to adaptive real-time random sample consensus. vol. 5303 LNCS, no. PART 2, 500–513. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-88688-4_37
Rosten E, Porter R, Drummond T (2010) Faster and better: a machine learning approach to corner detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(1):105–119. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2008.275
Saaidi A, Tairi H, Satori K (2006) Fast stereo matching using rectification and correlation techniques. ISCCSP, Second Int Symp Commun, Control Signal Proc, 1–4
Sali E, Wolfson H (1992) Texture classification in aerial photographs and satellite data. Int J Remote Sensing, 3395–3408. doi:10.1080/01431169208904130
Sooknanan K, Kokaram A, Corrigan D, Baugh G, Harte N, Wilson J (2012) Indexing and selection of well-lit details in underwater video mosaics using vignetting estimation. In OCEANS, 2012-Yeosu, 1–7. IEEE. doi:10.1109/OCEANS-Yeosu.2012.6263541
Szeliski R (2002) Video mosaics for virtual environments, IEEE Comput Graphics Appl, 22–30. doi:10.1109/38.486677
Trajković M, Hedley M (1998) Fast corner detection. Image Vis Comput 16(2):75–87. doi:10.1016/S0262-8856(97)00056-5
Wang X, Ying X, Liu Y-J, Xin S-Q, Wang W, Gu X, Mueller-Wittig W, He Y (2015) Intrinsic computation of centroidal Voronoi tessellation (CVT) on meshes. Comput Des, 51–61. doi:10.1016/j.cad.2014.08.023
Wei GQ, Qian J, Schramm HF, Novak CL (2003) Method for intensity correction in CR mosaic by combined nonlinear and linear transformations. Med Imaging 2003. Int Soc Optics Photonics. 979–985. doi:10.1117/12.480830
Yu G, Morel JM (2011) Asift: an algorithm for fully affine invariant comparison. Image Proc On Line, 2011. doi:10.5201/ipol.2011.my-asift
Zitova B, Flusser J (2003) Image registration methods: a survey. Image Vis Comput 21(11):977–1000. doi:10.1016/S0262-8856(03)00137-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laraqui, A., Baataoui, A., Saaidi, A. et al. Image mosaicing using voronoi diagram. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 8803–8829 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3478-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3478-z