Abstract
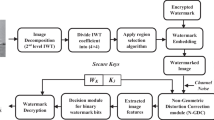
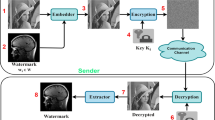
In this paper, we propose a partial reversible data hiding scheme using (7,4) Hamming code (PRDHHC) with secret position (κ). In this scheme, we partition the original cover image into (7 × 7) pixel block and adjust redundant LSB bits of each row using odd parity. Then we calculate secret position κ = (δ mod 7) + 1, where δ is a shared secret key. The bit at position κ and a suitable location for hidden message bit is modified through error creation caused by tamper in each row of the selected block. For the next row, the κ is updated by the data embedding position (ω) of the previous row. We repeat this process to embed secret message bits within the selected block. For each new block, the κ is updated by κ i+1 = (κ i × δ × ω) mod 7 + 1, where i = 0, 1, 2, 3, . . . , number of blocks. At the receiver end, we complement the bit at position κ then retrieve the secret message bit by applying Hamming error correcting code. The extraction process will be stopped when we find continuous no error within stego image. The propose PRDHHC scheme extract the hidden message successfully and recover hamming adjusted cover image by complement bits at both the κ and ω positions but can not recover original cover image, that is to say, our scheme is partial reversible. Finally, we compared our scheme with other state-of-the-art methods and obtained reasonably better performance in terms of visual quality (measured by PSNR). Also we analyze our generated stego image using some steganalysis techniques which give promising results.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan C.K., Cheng L.M. (2004) Hiding data in images by simple LSB substitution. Pattern Recogn 37(3):469–474
Chang C., Chou Y. (2008) Using nearest covering codes to embed secret information in gray scale images. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on ubiquitous information management and communication. ACM, pp 315–320
Chang C.C., Chan C.S., Fan Y.H. (2006) Image hiding scheme with modulus function and dynamic programming strategy on partitioned pixels. Pattern Recogn 39 (6):1155–1167
Chang C.C., Kieu T.D., Chou Y.C. (2008). A high payload steganographic scheme based on (7, 4) hamming code for digital images. In Electronic Commerce and Security, 2008 International Symposium on (pp. 16–21). IEEE
Cao Z., Yin Z., Hu H., Gao X., Wang L (2016) High capacity data hiding scheme based on (7, 4) Hamming code. SpringerPlus 5(1):1–13
Crandall R. (1998). Some notes on steganography. Posted on steganography mailing list
Fan L., Gao T., Cao Y. (2013) Improving the embedding efficiency of weight matrix-based steganography for grayscale images. Comput Electr Eng 39(3):873–881
Fridrich J., Goljan M., Du R. (2001). Invertible authentication. In photonics west 2001-electronic imaging (pp. 197-208). International society for optics and photonics
Guo J.M. (2008) Watermarking in dithered halftone images with embeddable cells selection and inverse halftoning. Signal Process 88(6):1496–1510
Kim C., Shin D., Shin D. (2011) Data hiding in a halftone image using hamming code (15, 11). Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 372–381
Kim C., Yang C.N. (2014) Improving data hiding capacity based on hamming code. Springer, Netherlands, pp 697–706
Lien B.K., Chen S.K., Wang W.S., King K.P. (2015) Dispersed Data Hiding Using Hamming Code with Recovery Capability. Springer International Publishing, pp 179–187
Lin C.C., Tai W.L., Chang C.C. (2008) Multilevel reversible data hiding based on histogram modification of difference images. Pattern Recogn 41(12):3582–3591
Ma Z.P., Li F.Y., Zhang X.P. (2013) Data hiding in halftone images based on hamming code and slave pixels. J Shanghai Univ (Nat Scie Edn) 2:003
Qin C., Chang C.C., Hsu T.J. (2014) Reversible data hiding scheme based on exploiting modification direction with two steganographic images. Multimed Tools Appl:1–12
Tian J. (2003) Reversible data embedding using a difference expansion. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Techn 13(8):890–896
Tsai P., Hu Y.C., Yeh H.L. (2009) Reversible image hiding scheme using predictive coding and histogram shifting. Signal Process 89(6):1129–1143
Westfeld A. (2001) F5-a Steganographic Algorithm. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 289–302
Wu D.C., Tsai W.H. (2003) A steganographic method for images by pixel-value differencing. Pattern Recogn Lett 24(9):1613–1626
Zhang W., Wang S., Zhang X. (2007) Improving embedding efficiency of covering codes for applications in steganography. Commun Lett IEEE 11(8):680–682
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jana, B., Giri, D. & Mondal, S.K. Partial reversible data hiding scheme using (7, 4) hamming code. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 21691–21706 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3990-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3990-1