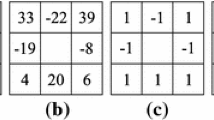
Abstract
Land-use classification using remote sensing images plays a key role in many applications such as urban mapping and geospatial object detection. With the rapid development of satellite sensors, high-resolution images which exhibit more detailed textures now can be acquired. How to effectively represent these images and recognize the categories of land-use/land-cover scenes has become a challenging task. In this paper, we propose a novel biologically inspired descriptor combined with the sparse coding spatial pyramid matching (ScSPM) for land-use classification. A color processing pipeline is first presented to simulate the opponent responses of human visual system. By extending the scale invariant feature transform (SIFT) on processed color channels, a descriptor that is able to jointly extract color and shape information for land-use images is proposed. Then the ScSPM model is employed to incorporate the local descriptors of an image, followed by a linear kernel support vector machine (SVM) for image classification. Performance evaluation on the publicly available LULC data set demonstrates that the proposed method achieves better classification accuracy than other reference methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alahi A, Ortiz R, Vandergheynst P (2012) FREAK: Fast retina keypoint. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, pp 510–517
Avramović A, Risojević V (2016) Block-based semantic classification of high-resolution multispectral aerial images. SIViP 10(1):75–84
Bay H, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L (2006) SURF: Speeded up robust features. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2006. Springer, pp 404–417
Bosch A, Zisserman A, Muoz X (2008) Scene classification using a hybrid generative/discriminative approach. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 30(4):712–727
Burghouts GJ, Geusebroek JM (2009) Performance evaluation of local colour invariants. Comput Vis Image Underst 113(1):48–62
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol (TIST) 2(3):27
Chen S, Tian Y (2015) Pyramid of spatial relatons for scene-level land use classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(4):1947–1957
Cheng G, Han J, Guo L, Liu Z, Bu S, Ren J (2015) Effective and efficient midlevel visual elements-oriented land-use classification using vhr remote sensing images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(8):4238–4249
Conway BR, Chatterjee S, Field GD, Horwitz GD, Johnson EN, Koida K, Mancuso K (2010) Advances in color science: from retina to behavior. J Neurosci 30(45):14,955–14,963
Csurka G, Dance C, Fan L, Willamowski J, Bray C (2004) Visual categorization with bags of keypoints. In: Workshop on statistical learning in computer vision, ECCV, Prague, vol 1, pp 1–2
Dalal N, Triggs B (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: IEEE Computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR 2005), vol 1, pp 886–893
Fei-Fei L, Perona P (2005) A bayesian hierarchical model for learning natural scene categories. In: IEEE Computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR 2005), vol 2, pp 524–531
Fei-Fei L, Fergus R, Perona P (2006) One-shot learning of object categories. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(4):594–611
Fei-Fei L, Fergus R, Perona P (2007) Learning generative visual models from few training examples: an incremental bayesian approach tested on 101 object categories. Comput Vis Image Underst 106(1):59–70
Gao S, Yang K, Li C, Li Y (2013) A color constancy model with double-opponency mechanisms. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 929–936
Gao S, Yang K, Li C, Li Y (2015) Color constancy using double-opponency. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(10):1973–1985
Griffin G, Holub A, Perona P (2007) Caltech-256 object category dataset
Hurlbert AC (1989) The computation of color. Tech. rep., DTIC Document
Ke Y, Sukthankar R (2004) PCA-SIFT: A more distinctive representation for local image descriptors. In: Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2004), vol 2, pp II–506
Lazebnik S, Schmid C, Ponce J (2006) Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In: 2006 IEEE Computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol 2, pp 2169–2178
Lennie P, Krauskopf J, Sclar G (1990) Chromatic mechanisms in striate cortex of macaque. J Neurosci 10(2):649–669
Leutenegger S, Chli M, Siegwart RY (2011) BRISK: Binary robust invariant scalable keypoints. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 2548–2555
Li Y, Tao C, Tan Y, Shang K, Tian J (2016) Unsupervised multilayer feature learning for satellite image scene classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 13(2):157–161
Liu L, Wang L, Liu X (2011) In defense of soft-assignment coding. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 2486–2493
Liu P, Choo KKR, Wang L, Huang F (2016) SVM or deep learning? a comparative study on remote sensing image classification. Soft Computing. doi:10.1007/s00500-016-2247-2
Lowe DG (1999) Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In: The proceedings of the seventh IEEE international conference on computer vision, vol 2, pp 1150–1157
Ma J, Zhou H, Zhao J, Gao Y, Jiang J, Tian J (2015a) Robust feature matching for remote sensing image registration via locally linear transforming. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(12):6469–6481
Ma J, Zhao J, Yuille AL (2016) Non-rigid point set registration by preserving global and local structures. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(1):53–64
Ma Y, Wu H, Wang L, Huang B, Ranjan R, Zomaya A, Jie W (2015b) Remote sensing big data computing: challenges and opportunities. Futur Gener Comput Syst 51:47–60
Mekhalfi ML, Melgani F, Bazi Y, Alajlan N (2015) Land-use classification with compressive sensing multifeature fusion. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 12(10):2155–2159
Mikolajczyk K, Schmid C (2005) A performance evaluation of local descriptors. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(10):1615–1630
Oliva A, Torralba A (2001) Modeling the shape of the scene: a holistic representation of the spatial envelope. Int J Comput Vis 42(3):145–175
Savarese S, Winn J, Criminisi A (2006) Discriminative object class models of appearance and shape by correlatons. In: 2006 IEEE Computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol 2, pp 2033–2040
Shapley R, Hawken MJ (2011) Color in the cortex: single-and double-opponent cells. Vis Res 51(7):701–717
Sivic J, Zisserman A (2003) Video google: A text retrieval approach to object matching in videos. In: Proceedings of Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 1470–1477
Van De Sande KE, Gevers T, Snoek CG (2010) Evaluating color descriptors for object and scene recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(9):1582–1596
Van De Weijer J, Schmid C (2006) Coloring local feature extraction. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2006. Springer, pp 334–348
Wang L, Song W, Liu P (2016a) Link the remote sensing big data to the image features via wavelet transformation. Clust Comput 19(2):793–810
Wang L, Yan J, Ma Y, Zomaya A (2016b) Pipscloud: High performance cloud computing for remote sensing big data management and processing. Future Generation Computer Systems. doi:10.1016/j.future.2016.06.009
Wang L, Zhang J, Liu P, Choo KKR, Huang F (2016c) Spectral–spatial multi-feature-based deep learning for hyperspectral remote sensing image classification. Soft Computing pp 1–9
Yang J, Yu K, Gong Y, Huang T (2009) Linear spatial pyramid matching using sparse coding for image classification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2009), pp 1794–1801
Yang K, Gao S, Li C, Li Y (2013) Efficient color boundary detection with color-opponent mechanisms. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2810– 2817
Yang K, Gao S, Guo C, Li C, Li Y (2015) Boundary detection using double-opponency and spatial sparseness constraint. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(8):2565–2578
Yang Y, Newsam S (2010) Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification. In: Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, pp 270–279
Yang Y, Newsam S (2011) Spatial pyramid co-occurrence for image classification. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 1465–1472
Yu K, Zhang T, Gong Y (2009) Nonlinear learning using local coordinate coding. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 2223–2231
Zhang F, Du B, Zhang L (2015) Saliency-guided unsupervised feature learning for scene classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(4):2175–2184
Zhang J, Barhomi Y, Serre T (2012) A new biologically inspired color image descriptor. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2012. Springer, pp 312–324
Zhong Y, Zhu Q, Zhang L (2015) Scene classification based on the multifeature fusion probabilistic topic model for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(11):6207–6222
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Natural Foundation of Hubei Province under Grant 2016CFB278, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant 2016M602390, Open Research Project of the Hubei Key Laboratory of Intelligent Geo-Information Processing under Grant KLIGIP1608, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, T., Zhang, Y., Dou, H. et al. Land-use classification with biologically inspired color descriptor and sparse coding spatial pyramid matching. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 22943–22958 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4167-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4167-7