Abstract
In order to develop an artificial intelligence and computer-aided diagnosis system that assists neuroradiologists to interpret magnetic resonance (MR) images. This paper employed Hu moment invariant (HMI) as the brain image features, and we proposed a novel predator-prey particle swarm optimization (PP-PSO) algorithm used to train the weights of single-hidden layer neural-network (SLN). We used five-fold stratified cross validation (FFSCV) for statistical analysis. Our proposed HMI + SLN + PP-PSO method achieved a sensitivity of 96.00 ± 5.16%, a specificity of 98.57 ± 0.75%, and an accuracy of 98.25 ± 0.65% for the DA-160 dataset, and yields a sensitivity of 97.14 ± 2.33%, a specificity of 97.00 ± 0.34%, and an accuracy of 97.02 ± 0.33% for the DA-255 dataset. Our method performs better than six state-of-the-art approaches.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal P (2016) Artificial intelligence and its applications 2014. Math Probl Eng: 3871575
Agarwal P, et al. (2013) Swarm intelligence and its applications. Sci World J: 528069
Agarwal P, et al. (2014) Swarm intelligence and Its Applications 2014. Sci World J: 204294
Alweshah M, Abdullah S (2015) Hybridizing firefly algorithms with a probabilistic neural network for solving classification problems. Appl Soft Comput 35:513–524
Awan AU et al (2016) Adaptive control of a shape memory alloy actuator using neural-network feedforward and RISE feedback. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 17(4):409–418
Balochian S (2014) Artificial intelligence and its applications. Math Probl Eng: 840491
Banerjee S et al (2016) Short term hydro-wind-thermal scheduling based on particle swarm optimization technique. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 81:275–288
Bansod PV, Mohanty AR (2016) Inverse acoustical characterization of natural jute sound absorbing material by the particle swarm optimization method. Appl Acoust 112:41–52
Buyukada M (2016) Co-combustion of peanut hull and coal blends: artificial neural networks modeling, particle swarm optimization and Monte Carlo simulation. Bioresour Technol 216:280–286
Chen M (2016) Morphological analysis of dendrites and spines by hybridization of ridge detection with twin support vector machine. Peer J 4:e2207
Chen Y et al (2008) Nonlocal prior Bayesian tomographic reconstruction. J Math Imaging Vision 30(2):133–146
Chen Y et al (2014) Artifact suppressed dictionary learning for low-dose CT image processing. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 33(12):2271–2292
Chen M, et al. (2015) Detection of dendritic spines using wavelet-based conditional symmetric analysis and regularized morphological shared-weight neural networks. Comput Math Methods Med: 454076
Chen Y et al (2016a) Curve-like structure extraction using minimal path propagation with backtracking. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(2):988–1003
Chen XY, Chau KW, Hybrid A (2016b) Double feedforward neural network for suspended sediment load estimation. Water Resour Manag 30(7):2179–2194
Das S et al (2013) Brain MR image classification using multiscale geometric analysis of Ripplet. Prog Electromagn Res-Pier 137:1–17
Dong Z (2014) Classification of Alzheimer disease based on structural magnetic resonance imaging by kernel support vector machine decision tree. Prog Electromagn Res 144:171–184
Duan HB et al (2013) Parameters identification of UCAV flight control system based on predator-prey particle swarm optimization. Sci China-Inf Sci 56(1):012202
El-Dahshan ESA et al (2010) Hybrid intelligent techniques for MRI brain images classification. Digital. Signal Process 20(2):433–441
Feng C (2015) Feed-forward neural network optimized by hybridization of PSO and ABC for abnormal brain detection. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 25(2):153–164
Feng C et al (2015) Automated classification of brain MR images using wavelet-energy and support vector machines. In: Liu C, Chang G, Luo Z (eds) International conference on mechatronics, electronic, industrial and control engineering. Atlantis Press, USA, pp. 683–686
Fu MY et al (2014) Background pixels mutation detection and Hu invariant moments based traffic signs detection on autonomous vehicles. In: 33rd Chinese control conference. IEEE, Nanjing, Peoples Republic China, pp. 670–674
Gorriz JM, Ramírez J (2016) Wavelet entropy and directed acyclic graph support vector machine for detection of patients with unilateral hearing loss in MRI scanning. Front Comput Neurosci 2016(10):160
Hu M-K (1962) Visual pattern recognition by moment invariants. Inf Theory, IRE Trans 8(2):179–187
Jang WS et al (2007) Optimized fuzzy clustering by predator prey particle swarm optimization. In: 3rd International Conference on Intelligent. Springer-Verlag Berlin, Computing, Qingdao, Peoples Republic China, pp. 370–379
Jia SM et al (2014) A Particle Filter Human Tracking Method based on HOG and Hu Moment. In: International conference on mechatronics and automation. IEEE, Tianjin, Peoples Republic China, pp. 1581–1586
Kumar M, et al. (2016) Cat swarm optimization based functional link artificial neural network filter for gaussian noise removal from computed tomography images. Appl Comput Intell Soft Comput: 6304915
Li J (2016) Detection of left-sided and right-sided hearing loss via fractional fourier transform. Entropy 18(5):194
Liu A (2015a) Magnetic resonance brain image classification via stationary wavelet transform and generalized eigenvalue proximal support vector machine. J Med Imaging Health Inf 5(7):1395–1403
Liu G (2015b) Pathological brain detection in MRI scanning by wavelet packet Tsallis entropy and fuzzy support vector machine. Springer Plus 4(1):716
Lu Z, A Pathological Brain (2016) Detection system based on radial basis function neural network. J Med Imaging Health Inf 6(5):1218–1222
Mallick S et al (2016) Optimal sizing and design of CMOS analogue amplifier circuits using craziness-based particle swarm optimization. Int J Numer Modell Electr Netw Devices Fields 29(5):943–966
Oyedotun OK, Khashman A (2016) Document segmentation using textural features summarization and feedforward neural network. Appl Intell 45(1):198–212
Peng B et al (2016) Image processing methods to elucidate spatial characteristics of retinal microglia after optic nerve transection. Sci Rep 6:21816
Phillips P et al (2015a) Pathological brain detection in magnetic resonance imaging scanning by wavelet entropy and hybridization of biogeography-based optimization and particle swarm optimization. Prog Electromagn Res 152:41–58
Phillips P et al (2015b) Detection of Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment based on structural volumetric MR images using 3D-DWT and WTA-KSVM trained by PSOTVAC. Biomed Signal Process Control 21:58–73
Shan R et al (2016) Network modeling and assessment of ecosystem health by a multi-population swarm optimized neural network ensemble. Appl Sci-Basel 6(6):175
Sharma MK, Dhaka VP (2016) Segmentation of english offline handwritten cursive scripts using a feedforward neural network. Neural Comput Appl 27(5):1369–1379
Sun P (2015) Pathological brain detection based on wavelet entropy and Hu moment invariants. Bio-Med Mater Eng 26(s1):1283–1290
Sun P (2016) Preliminary research on abnormal brain detection by wavelet-energy and quantum-behaved PSO. Technol Health Care 24(s2):S641–S649
Sun Y, A Multilayer Perceptron (2016) Based smart pathological brain detection system by fractional Fourier entropy. J Med Syst 40(7):173
Wang S, Wu L (2010) A novel method for magnetic resonance brain image classification based on adaptive chaotic PSO. Prog Electromagn Res 109:325–343
Wu LN (2008) Improved image filter based on SPCNN. Science in China series F. Inf Sci 51(12):2115–2125
Wu LN (2009) Segment-based coding of color images. Science in China series F. Inf Sci 52(6):914–925
Wu L (2011a) A hybrid method for MRI brain image classification. Expert Syst Appl 38(8):10049–10053
Wu L (2011b) Crop classification by forward neural network with adaptive chaotic particle swarm optimization. Sensors 11(5):4721–4743
Wu L (2012a) An MR brain images classifier via principal component analysis and kernel support vector machine. Prog Electromagn Res 130:369–388
Wu L (2012b) Classification of fruits using computer vision and a multiclass support vector machine. Sensors 12(9):12489–12505
Yang J (2015a) Preclinical diagnosis of magnetic resonance (MR) brain images via discrete wavelet packet transform with Tsallis entropy and generalized eigenvalue proximal support vector machine (GEPSVM). Entropy 17(4):1795–1813
Yang J (2015b) Identification of green, oolong and black teas in China via wavelet packet entropy and fuzzy support vector machine. Entropy 17(10):6663–6682
Yang J (2016a) Pathological brain detection in MRI scanning via Hu moment invariants and machine learning. J Exp Theor Artif Intell:1–14. doi:10.1080/0952813X.2015.1132274 Online
Yang M (2016b) Dual-tree complex wavelet transform and twin support vector machine for pathological brain detection. Appl Sci 6(6):169
Yang X et al (2015a) Pathological brain detection by a novel image feature—fractional Fourier entropy. Entropy 17(12):8278–8296
Yang G et al (2015b) Automated classification of brain images using wavelet-energy and biogeography-based optimization. Multimed Tools Appl. doi:10.1007/s11042-015-2649-7 Online
Yuan TF (2015) Detection of subjects and brain regions related to Alzheimer's disease using 3D MRI scans based on eigenbrain and machine learning. Front Comput Neurosci 9:66
Zhang Y (2015) Detection of Alzheimer's disease by displacement field and machine learning. Peer J 3:e1251
Zhang Y, Binary PSO (2014) With mutation operator for feature selection using decision tree applied to spam detection. Knowl-Based Syst 64:22–31
Zheng R et al (2016) Color image classification via quaternion principal component analysis network. Neurocomputing. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2016.08.006 Online
Zhou X-X (2016) Comparison of machine learning methods for stationary wavelet entropy-based multiple sclerosis detection: decision tree, k-nearest neighbors, and support vector machine. SIMULATION 92(9):861–871
Zhou X, et al. (2015) Detection of pathological brain in MRI scanning based on wavelet-entropy and naive Bayes classifier. In: Bioinformatics and biomedical engineering. Granada, Spain: Springer International Publishing, pp 201–209
Zunic J et al (2016) On a 3D analogue of the first Hu moment invariant and a family of shape ellipsoidness measures. Mach Vis Appl 27(1):129–144
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
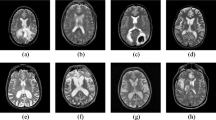
The original version of this article was revised: The white background of “44” in Fig. 3b should be removed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Lv, Y., Chen, H. et al. Smart pathological brain detection system by predator-prey particle swarm optimization and single-hidden layer neural-network. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 3871–3885 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4242-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4242-0