Abstract
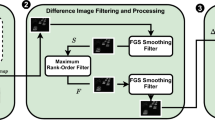
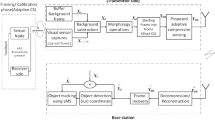
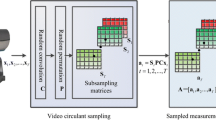
Limited memory, energy and bandwidth are the major constraints in wireless visual sensor network (WVSN). Video surveillance applications in WVSN attracts a lot of attention in recent years which requires high detection accuracy and increased network lifetime that can be achieved by reducing the energy consumption in the sensor nodes. Compressed sensing (CS) based background subtraction plays a significant role in video surveillance application for detecting the presence of anomaly with reduced complexity and energy. This paper presents a system based on CS for single and multi object detection that can detect the presence of an anomaly with higher detection accuracy and minimum energy. A novel and efficient mean measurement differencing approach with adaptive threshold strategy is proposed for detection of the objects with less number of measurements, thereby reducing transmission energy. The performance of the system is evaluated in terms of detection accuracy, transmission energy and network lifetime. Furthermore, the proposed approach is compared with the conventional background subtraction approach. The simulation results show that the proposed approach yields better detection accuracy with 90% reduction in samples compared to conventional approach.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasha Nandhini S, Radha S, Kishore R (2015) Video compressed sensing framework for wireless multimedia sensor networks using a combination of multiple matrices. Elsevier’s Comput Electric Eng 44:51–66. doi:10.1016/j.compeleceng.2015.02.008
Amiri M (2010) Measurements of energy consumption and execution time of different operations on Tmote Sky sensor nodes
Baraniuk R (2007) A lecture compressive sensing. IEEE Signal Proc Mag 24(4):118–121
Cao Y, Lei Z, Huang X, Zhang Z, Zhong T (2012) A vehicle detection algorithm based on compressive sensing and background subtraction. AASRI Procedia 1:480–485
Cevher V, Sankaranarayanan A, Duarte MF, Reddy D, Baraniuk RG, Chellappa R (2008) Compressive sensing for background subtraction. In Computer Vision–ECCV, 155–168. Springer. Berlin
Computer Vision Group, Available from: http://www.wisdom.weizmann.ac.il/~vision/SpaceTimeActions.html
Jiang H, Deng W, Shen Z (2013) Surveillance video processing using compressive sensing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1302.1942, 201–14
Kang B, Zhu W-P, Yan J (2015) Object detection oriented video reconstruction using compressed sensing. EURASIP J Adv Signal Proc 1:1–15
Manimozhi S (2015) Aasha Nandhini S, Radha S. Compressed Sensing Based Background Subtraction for Object Detection in WSN, IEEE Int Conf Commun Signal Proc (ICCSP)
Smitha H, Palanisamy V (2012) Detection of stationary foreground objects in region of interest from traffic video sequences. Int J Comput Sci Issues (IJCSI) 9(2)
Tropp J, Gilbert A (2007) Signal recovery from partial information via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 53(12):4655–4666
Video Trace Library, Available from: http://trace.eas.asu.edu/yuv/
Warnell G, Reddy D, Chellappa R (2012) Adaptive rate compressive sensing for background subtraction. IEEE Int Conf Acoustics, Speech Signal Proc (ICASSP). 1477–1480
Ye Y, Ci S, Katsaggelos AK, Liu Y, Qian Y (2013) Wireless video surveillance: a survey. Access IEEE 1:646–660
Yi Z, Liangzhong F (2010) Moving object detection based on running average background and temporal difference. IEEE Int Conf Int Syst Knowledge Eng (ISKE), 270–272
Zhang Y, Wang X, Qu B (2012) Three-frame difference algorithm research based on mathematical morphology. Procedia Eng 29:2705–2709
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandhini, S.A., Radha, S. & Kishore, R. Efficient compressed sensing based object detection system for video surveillance application in WMSN. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 1905–1925 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4345-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4345-2