Abstract
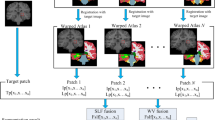
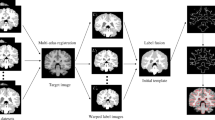
The multi-atlas based segmentation method can achieve the accurate segmentation of specific tissues of the human brain in the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The correct image registration and fusion scheme used in this method have an impact on the accuracy of segmentation. Similar to any traditional rigid registration method, we use the same method in our proposed target-oriented registration for the coarse registration between the target image and atlas image. However, to improve the registration accuracy in the area to be segmented, we propose a target-oriented image registration method for the refinement. We employ the distribution probability of the tissue (to be segmented) in the sparse patch-based label fusion process. Our aim is to determine if the proposed registration method can contribute the segmentation accuracy and which label fusion method is a good fit with this target-oriented registration. To evaluate the efficiency of our proposed method, we compare the performance of the majority voting method (MV), the nonlocal patch-based method (Nonlocal-PBM) and the sparse patch-based method (Sparse-PBM). Experimental results show that more accurate segmentation results can be obtained with the proposed registration method in this study. This result can provide more accurate clinical diagnosis information.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aljabar P, Heckemann RA, Hammers A, Hajnal JV, Ruechert D (2009) Multi-atlas based segmentation of brain images: Atlas selection and its effect on accuracy. NeuroImage 46(3):726–738
Artaechevarria X, Munoz-Barrutia A, Ortiz-de-Solorzano C (2015) Combination strategies in multi-atlas image segmentation: application to brain MR data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28(8):1266–1277
Bai W, Shi W, Ledig C, Rueckert D (2015) Multi-atlas segmentation with augmented features for cardiac MR images. Med Image Anal 19(1):98–109
Bryt O, Elad M (2008) Compression of facial images using the K-SVD algorithm. J Vis Commun Image Represent 19(4):270–282
Bryt O, Elad M (2008) Improving the k-svd facial image compression using a linear deblocking method. Electrical and electronics engineers in Israel, 2008 IEEEI 2008 I.E. 25th convention of: IEEE; 533–537
Buades A, Coll B and Morel J-M (2005) A non-local algorithm for image denoising. Computer vision and pattern recognition, 2005 CVPR 2005 I.E. computer society conference on. Volume 2: IEEE; 60–65
Chen M, Ma Y, Song J, Lai C, Hu B (2016) Smart clothing: connecting human with clouds and big data for sustainable health monitoring. ACM/Springer Mobile Networks and Applications 21(5):825–845
Chen M, Ma Y, Li Y, Wu D, Zhang Y, Youn C (Jan. 2017) Wearable 2.0: enable human-cloud integration in next generation healthcare system. IEEE Commun 55(1):54–61
Chupin M, Hammers A, Bardinet E, Colliot O, Liu R S N, Duncan J S, Garnero L Lemieux L (2015) Fully automatic segmentation of the hippocampus and the amygdala from MRI using hybrid prior knowledge. In Proceedings of the 10th international conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, October 29–November 02, 875–882, Brisbane, Australia
Coupé P, Manjón JV, Fonov V, Pruessner J, Robles M, Collins DL (2011) Patch-based segmentation using expert priors: application to hippocampus and ventricle segmentation. NeuroImage 54(2):940–954
Elad M, Aharon M (2006) Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(12):3736–3745
Hammers A, Allom R, Koepp MJ, Free SL, Myers R, Lemieux L, Mitchell TN, Brooks DJ, Duncan JS (2003) Three-dimensional maximum probability atlas of the human brain, with particular reference to the temporal lobe. Hum Brain Mapp 19(4):224–247
Heckemann R, Hajnal J, Aljabar P, Ruechert D, Hammers A (2016) Automatic anatomical brain MRI segmentation combining label propagation and decision fusion. NeuroImage 33(1):115–126
Hossain MS (2016) Patient state recognition system for healthcare using speech and facial expressions. J Med Syst 40:272
Hossain MS, Muhammad G (2016) Healthcare big data voice pathology assessment framework. IEEE Access 4:7806–7815
K. Hwang, M. Chen (2017) Big data analytics for cloud/IoT and cognitive computing, Wiley, U.K., ISBN: 9781119247029
Khan AR, Chung MK, Beg MF (2009) Robust atlas-based brain segmentation using multi-structure confidence-weighted registration[M]//medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2009. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 549–557
Khan AR, Cherbuin N, Wen W, Anstey KJ, Sachdev P, Beg MF (2014) Optimal weights for local multi-atlas fusion using supervised learning and dynamic information (SuperDyn): validation on hippocampus segmentation. NeuroImage 56(1):126–139
Kwak K, Yoon U, Lee D-K, Kim GH, Seo SW, Na DL, Shim HJ, Lee JM (2013) Fully-automated approach to hippocampus segmentation using a graph-cuts algorithm combined with atlas-based segmentation and morphological opening. Magn Reson Imaging 31(7):1190–1196
Mairal J, Elad M, Sapiro G (2008) Sparse representation for color image restoration. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(1):53–69
Michopoulou SK, Costaridou L, Panagiotopoulos E, Speller R, Panayiotakis G, Todd-Pokropek A (2009) Atlas-based segmentation of degenerated lumbar intervertebral discs from MR images of the spine. Biomedical Engineering, IEEE Transactions on 56(9):2225–2231
Rao A, Sanchez-Ortiz G, Chandrashekara R, et al. (2013) Construction of a cardiac motion atlas from MR using non-rigid registration. In: functional imaging and modeling of the heart. Berlin: Springer, 141–150
Romero JE, Manjón JV, Tohka J, Coupé P, Robles M (2015) NABS: non-local automatic brain hemisphere segmentation. Magn Reson Imaging 33(4):474–484
Rousseau F, Habas PA, Studholme C (2011) A supervised patch-based approach for human brain labeling. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 30(10):1852–1862
Sanroma G, Wu G, Thung K, Guo Y, Shen D (2014) Novel multi-atlas segmentation by matrix completion. Machine Learning in Medical Imaging: Springer:207–214
Shan L, Zach C, Charles C, Niethammer M (2014) Automatic atlas-based three-label cartilage segmentation from MR knee images. Med Image Anal 18(7):1233–1246
Sjöberg C, Ahnesjö A (2013) Multi-atlas based segmentation using probabilistic label fusion with adaptive weighting of image similarity measures. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 110(3):308–319
Suh J W, Schaap M, Lee A, et al. (2013) Automatic multi-atlas segmentation using dual registrations[C]//biomedical imaging (ISBI), 2013 I.E. 10th international symposium on. IEEE, 1284–1287
Tibshirani R (1996) Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol:267–288
Tong T, Wolz R, Hajnal JV and Rueckert D (2012) Segmentation of brain MR images via sparse patch representation. MICCAI Workshop on Sparsity Techniques in Medical Imaging (STMI)
Tong T, Wolz R, Coupé P, Hajnal JV, Rueckert D (2013) Segmentation of MR images via discriminative dictionary learning and sparse coding: application to hippocampus labeling. NeuroImage 76:11–23
Vemuri BC, Ye J, Chen Y, Leonard CM (2013) Image registration via level-set motion: applications to atlas-based segmentation. Med Image Anal 7(1):1–20
Wang H, Das SR, Suh JW, Altinay M, Pluta J, Craige C, Avants B, Yushkevich PAA (2011) Learning-based wrapper method to correct systematic errors in automatic image segmentation: consistently improved performance in hippocampus, cortex and brain segmentation. NeuroImage 55(3):968–985
Wang H, Suh JW, Das SR, Pluta JB, Craige C, Yushkevich P (2013) Multi-atlas segmentation with joint label fusion. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(3):611–623
Wolz R, Aljabar P, Hajnal JV, Hammers A, Rueckert DLEAP (2010) Learning embeddings for atlas propagation. NeuroImage 49(2):1316–1325
Wright J, Yang AY, Ganesh A, Sastry SS, Ma Y (2009) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(2):210–227
Wu G, Kim M, Sanroma G, Wang Q, Munsell BC, Shen D (2015) Hierarchical multi-atlas label fusion with multi-scale feature representation and label-specific patch partition. NeuroImage 106:34–46
Yan M, Liu H, Xu X et al (2017) An improved label fusion approach with sparse patch-based representation for MRI brain image segmentation. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 27(1):23–32
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the help comments and suggestions of the editor and reviews, which have improved the presentation. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61370179, Grant Nos. 61370181 and Grant Nos. 81671768).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, E., Qian, Y., Liu, H. et al. A target-oriented segmentation method for specific tissues in MRI images of the brain. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 9083–9099 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5484-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5484-1