Abstract
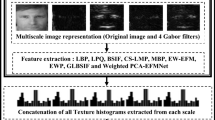
This paper proposes a novel method for recognizing facial images based on the relative distances between an input image and example images. Example facial images can be easily collected online, and a large example database can span new possible facial variations not sufficiently learned during the learning phase. We first extract facial features using a baseline classifier that has a certain degree of accuracy. To achieve a better performance of the proposed method, we divide the collected examples into groups using a clustering method (e.g., k-means), where each clustered group contains examples with similar characteristics. We then hierarchically partition a group formed in the previous level into other groups to analyze more specific facial characteristics, which represent an example pyramid. To describe the characteristics of a group using the clustered examples, we divide the example group into a number of sub-groups. We calculate the averages of the sub-groups and select an example most similar to the average in each sub-group because we assume that the averages of the sub-groups can directly represent their characteristics. Using the selected examples, we build example code words for a novel feature extraction. The example code words are used to measure the distances to an input image and serve as anchors to analyze a facial image in the example domain. The distance values are normalized for each group at all pyramid levels, and are concatenated to form novel features for face recognition. We verified the effectiveness of the proposed example pyramid framework using well-known proposed features, including LBP, HOG, Gabor, and the deep learning method, on the LFW database, and showed that it can yield significant improvements in recognition performance.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barkan O, Weill J, Wolf L, Aronowitz H (2013) Fast high dimensional vector multiplication face recognition. IEEE Inter Conf Comput Vis:1960–1967
Bengio Y, Boulanger-Lewandowski N, Pascanu R (2013) Advances in optimizing recurrent networks. IEEE Inter Conf Acoustics, Speech Signal Process:8624–8628
Chakraborty S, Singh SK, Chakraborty P (2016) Local directional gradient pattern: A local descriptor for face recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 76(1):1201–1216
Chellappa R, Wilson CL, Sirohey S (1995) Human and machine recognition of faces: A survey. Proc IEEE 83(5):705–741
Chen D, Cao X, Wang L, Wen F, Sun J (2012) Bayesian face revisited: A joint formulation. Eur Conf Comput Vis 7574:566–579
Cui J, Liu Y, Xu Y, Zhao H, Zha H (2013) Tracking generic human motion via fusion of low- and high-dimensional approaches. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 43(4):996–1002
Dalal N, Triggs B (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn 1:886–893
Deng X, Da F, Shao H (2017) Expression-robust 3d face recognition based on feature-level fusion and feature-region fusion. Multimed Tools Appl 76(1):13–31
Hua G, Yang M, Learned-Miller E, Ma Y, Turk M, Kriegman D, Huang TS (2011) Introduction to the special section on real-world face recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(10):1921–1924
Huang GB, Berg MRT, Learned-Miller E (2007) Labeled faces in the wild: A database for studying face recognition in unconstrained environments. University of Massachusetts, Amherst, Technical Report, pp 07–49
Huang D, Shan C, Ardabilian M, Wang Y, Chen L (2011) Local binary patterns and its application to facial image analysis: A survey. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C: Appl Rev 41(6):765–781
Hwang W, Kim J (2015) Markov network-based unified classifier for face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(11):4263–4275
Hwang W, Huang X, Li SZ, Kim J (2015) Face recognition using extended curvature gabor classifier bunch. Pattern Recogn 48(4):1243–1256
Jain AK, Klare B, Park U (2012) Face matching and retrieval in forensics applications. IEEE MultiMed 19(1):20
Lazebnik S, Shmid C, Ponce J (2006) Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn 2:2169–2178
Li H, Lin Z, Brandt J, Shen X, Hua G (2014) Efficient boosted exemplar-based face detection. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:1843–1850
Liu Y, Zhang X, Cui J (2010) Visual analysis of child-adult interactive behaviors in video sequences. International Conference on Virtual Systems and Multimedia
Liu L, Wang L, Liu X (2011) In defense of soft-assignment coding. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision
Liu Y, Nie L, Han L, Zhang L, Rosenblum DS (2015) Action2activity: Recognizing complex activities from sensor data. Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intell:1617–1623
Liu Y, Nie L, Liu L, Zhang L, Rosenblum DS (2016) From action to activity: Sensor-based activity recognition. Neurocomputing 181(12):108–115
Liu Y, Zhang L, Nie L, Yan Y, Rosenblum DS (2016) Fortune teller: Predicting your career path. AAAI Conf Artif Intell:201–207
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Liang Y, Liu S, Rosenblum DS (2016) Urban water quality prediction based on multi-task multi-view learning. Int Joint Conf Artif Intell:2576–2582
Lloyd SP (1982) Least squares quantization in pcm. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 28 (2):129–137
Lu J, Wang G, Moulin P (2016) Localized multifeature metric learning for image-set-based face recognition. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 2(3):529–540
Martinez A, Kak A (2001) PCA versus LDA. IEEE Trans Pattern Recogn Mach Intell 23(2):228–233
Ng AY, Jordan MI, Weiss Y (2001) On spectral clustering: Analysis and an algorithm. Proc Neural Inf Process Syst Conf:14
Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Harwood D (1996) A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on feature distributions. Pattern Recogn 29(1):51–59
Roweis ST, Saul LK (2000) Locality-constrained linear coding for image classification. Science 290:2323–2326
Schroff F, Treibitz T, Kriegman D, Belongie S (2013) Pose, illumination and expression invariant pairwise face-similarity measure via doppelganger list comparison. IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis:2494–2501
Schroff F, Kalenichenko D, Philbin J (2015) Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:815–823
Shen X, Lin Z, Brandt J, Wu Y (2013) Detecting and aligning faces by image retrieval. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:4321–4328
Su Y, Shan S, Chen X, Gao W (2009) Hierarchical ensemble of global and local classifiers for face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 18(8):1885–1896
Sun Y, Chen Y, Wang X, Tang X (2014) Deep learning face representation by joint identification-verification. Proceedings of Neural Information Processing Systems Conference
Sun Y, Wang X, Tang X (2014) Deep learning face representation from predicting 10,000 classes. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:1891–1898
Szeliski R (2011) Computer vision: algorithms and applications, Springer, Berlin
Taigman Y, Yang M, Ranzato M, Wolf L (2014) Deeface: Closing the gap to human-level performance in face verification. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:1701–1708
Wang J, Yang J, Yu K (2010) Locality-constrained linear coding for image classification. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:3360–3367
Wiskott L, Fellous JM, Kruger N, von der Malsburg C (1997) Face recognition by elastic bunch graph matching. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19 (7):775–779
Xiong X, la Torre FD (2013) Supervised descent method and its applications to face alignment. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:532–539
Yi D, Liao ZLS, Li SZ (2014) Learning face representation from scratch. arXiv:1411.7923
Yin Q, Tang X, Sun J (2011) An associate-predict model for face recognition. IEEE Inter Conf Comput Vis:497–504
Zhang T (2011) Adaptive forward-backward greedy algorithm for learning sparse representations. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 57(7):4689–4708
Zhang Z, Liang Y, Bai L, Hancock ER (2016) Discriminative sparse representation for face recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 75(7):3973–3991
Zhao W, Chellappa R, Phillips PJ, Rosenfeld A (2003) Face recognition: A literature survey. ACM Comput Surv 35(4):399–458
Zhou F, Brandt J, Lin Z (2013) Exemplar-based graph matching for robust facial landmark localization. IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis:1025–1032
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea NRF-2014R1A2A2A01003140 and partially supported by the Ajou University research fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, W., Kim, J. Example image-based feature extraction for face recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 23429–23447 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5571-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5571-3